Spiders in Latin are Araneae, Aranei. They belong to the animal kingdom, the phylum of arthropods, the class of arachnids. There are 42 thousand modern species of spiders in the world, about 1.1 thousand fossils. They are widespread, inhabiting almost all continents of the globe. Obligate carnivores - feed on insects, small animals, and amphibians. An exception is the jumping spider Bagheera kiplingi, whose diet consists of the green part of the acacia tree. On the territory of Russia and the former CIS countries there are 2888 species. The science of spiders is called arachnology.
What kingdom do spiders belong to?
Small creatures, which are often found in the wild, in your own home, apartment, attics, outbuildings, resemble all kinds of insects and beetles. Spiders and insects are often combined into one family due to their small size and similar lifestyle. However, in tropical countries. where arthropods up to 35 cm in size live, such associations practically do not arise.
There are 5 kingdoms in total - animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and viruses. Historically, spiders and insects belong to the same kingdom, phylum - animals, arthropods. Only the class or squad is different. Therefore, the question of whether a spider is an animal or an insect is fundamentally wrong. The animal is a kingdom, insects are a class.
On a note!
Since everyone has long been accustomed to the fact that insects are insects, and animals are full-fledged mammals, confusion in concepts has arisen among ordinary people. Why the spider stands apart is explained by its unusual lifestyle and small size. In order not to seem uneducated, you need to clearly understand that a spider is not an insect.
Spiders
Other predatory insects
Rodolia
Adults and larvae burrow into the egg sacs of mature female coccids, pulling out white wax to reach the eggs below. The jaws are used to hold and chew prey.
Cryptolemus
Adults and larvae eat small insects, especially bedbugs. The jaws hold and chew prey. One larva eats 250 bedbugs before pupation. Three pairs of paws are used for walking.
Thaumatomy
The male flaps his wings to disperse pheromones from the abdominal pouches. The thorax, abdomen and edges of the eyes are bright yellow, the mesonotum has brown and yellow longitudinal stripes.
Swimming beetle
The beetles are aquatic, freely swim and dive using their hind legs, and move awkwardly on land. They breathe underwater with air that is collected and stored directly under the elytra.
What class do spiders belong to?
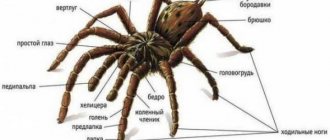
In this case, there is no confusion in concepts, since the class has a consonant name - arachnids. In total, 42 thousand modern species and 1.1 thousand fossils are known. In all animals, the body is divided into 2 parts - the abdomen and cephalothorax.
The main external difference from insects is the number of legs - 8 legs instead of 6. Arachnids also have chelicerae located in front of the cephalothorax and pelipalps, similar to tentacles. They are located on the sides, slightly different in length from the forelimbs, and perform similar functions - they help move, hold the prey.
On a note!
The question is often asked - which family do spiders belong to, which group of animals. These are arachnids and arthropods.
Giant stick insect
The giant stick insect is one of the longest insects in the world
This beetle is the rarest insect on Earth. It is also called tree lobster. Giant stick insects were discovered in 1788 on Lord Howe Island, which is located in the Tasman Sea. The sizes of these insects averaged 12 cm in length and 1.5 cm in width. However, later the island was inhabited by rats and the giant stick insect was no longer seen on it. It was officially declared extinct. It was only in 2001 that a colony of several dozen giant stick insects was discovered on the volcanic island of Balls Pyramids. By 2008, there were already 700 of them at the Melbourne Zoo. Australian scientists continue to fight to prevent this rare insect species from going extinct.
The volcanic island of Balls Pyramids, where the giant stick insect was discovered
Species and orders
It is very simple to answer the question of which order spiders belong to. To the order with the same name - spiders. They stand apart. They differ from other animals in their lifestyle, size, reproduction, and nutrition. There are differences among themselves in the same family, depending on what species the spiders belong to.
Spiders
General characteristics:
- The body consists of 2 parts - the cephalothorax, the abdomen is oval, round in shape.
- There are only 4 pairs of legs, a pair of chelicerae, and pelipalps.
- There are no antennae, but the forelimbs can be claw-shaped and end in claws.
- What distinguishes arachnids from insects is their ability to form webs. Not everyone weaves trapping nets, but they use threads of their own production to form a cocoon, move down, and migrate over long distances.
- Predators have poisonous glands that paralyze the prey. They turn the insides into a liquid mass.
- Unlike insects, they rarely live in pairs or in large families. All spiders lead a solitary lifestyle. In some species, young spiders live with their mother until they get stronger. Almost all females eat males after fertilization or in the near future.
Arachnids live everywhere, some of them get into a person’s house, apartment, or settle in utility rooms. Exotic, most beautiful specimens are kept as pets.
Rhinoceros cockroach
The giant burrowing rhinoceros cockroach is native to the Australian state of North Queensland. This is the largest and heaviest of all cockroach species on the planet: its weight can reach 30 g with a body length of up to 8 cm. The rhinoceros cockroach has no wings and is not able to move long distances. It lives in bushes. This cockroach is the only one in its squad that can make its home underground, digging long and deep tunnels. This insect feeds on fallen eucalyptus leaves. Its lifespan is approximately 10 years.
Is a spider an insect or an animal?
From a scientific point of view, it is believed that spiders are animals that belong to the phylum of arthropods and the class of arachnids. On the planet you can find about 42 thousand species of spiders, including 1.1 thousand fossils. Spiders inhabit almost every corner of the globe. They can be found in conditions where no living creature can live. This type of predator feeds on insects, small animal species, and amphibians. Among the many varieties there are spiders that feed on the green parts of plants. The science that studies the life of spiders is called arachnology.
A spider is an insect or animal
Spiders in Latin are Araneae, Aranei. They belong to the animal kingdom, the phylum of arthropods, the class of arachnids. There are 42 thousand modern species of spiders in the world, about 1.1 thousand fossils. They are widespread, inhabiting almost all continents of the globe. Obligate carnivores - feed on insects, small animals, and amphibians. An exception is the jumping spider Bagheera kiplingi, whose diet consists of the green part of the acacia tree. On the territory of Russia and the former CIS countries there are 2888 species. The science of spiders is called arachnology.
Book louse
The book louse is a tiny parasite that causes irreparable damage to book depositories, herbariums, grain stocks and other dry products. To feed, the parasite requires organic remains of plant and animal origin. In the home, the insect lives among dusty things and book bindings. It often damages the spines of books containing glue. A cluster of book lice is indicated by a faint ticking sound. It cannot be confused with anything. These insects do not affect human health, but their presence is detrimental to rare books and archival documents. Cleanliness and dry air are the main preventive measures.
Cannibal females
Redback spiders are one of the few animals that practice sexual cannibalism. Having found a female, the male spider courts her for more than four hours. He spins around, waving his paws. After fertilization, when the satisfied male is resting, the female injects digestive enzymes into his abdomen - and he begins to be digested alive. As a result, the spider kills two birds with one stone: it has offspring and gets lunch.
Share link
Main differences
With minimal knowledge of biology, one can easily discover that between these species of arthropods there is very little even external similarity, not to mention origin and numbers. Even the appearance of spiders and insects on Earth dates back a hundred million years. The last species appeared on Earth 100 million years later than spiders, which have lived on the planet for more than 400 million Earth periods.
Further differences are even more noticeable:
- there are about 43 thousand species of spiders (42 thousand modern and 1100 fossils), and more than a million insects have been described, and there are suggestions that this is not a complete list;
- spiders are obligate predators, there is only one known species that feeds on acacia, while the feeding of insects varies depending on the stage and species;
- web weavers have eight legs, while their opponents have six; the difference in structure is difficult to compare due to the huge number of varieties of the latter category;
- although spiders are also found with six or 2 eyes, in most cases they have 8 organs of vision, and insects have compound eyes consisting of ommatidia for comprehensive viewing;
- almost all tracheal breathers have digestive organs, even in their infancy, and a mouth for absorbing food, and in spiders, food digestion occurs outside the intestine, after injecting enzymes into the body of the victim;
- insects have an exoskeleton, head, thorax and abdomen, while spiders have only a cephalothorax and abdomen, although there are some species in which the head and thorax are separated by a groove, but still do not constitute separate body segments.
Spiders, being earlier inhabitants of the Earth, are equipped with hooks and channels for injecting poison into the food they catch. Enzymes that enter the body of the prey dissolve its contents, and the obligate predator can only suck out the contents.
The insect immediately absorbs the food received and digests it inside the body. This gives him the opportunity to get enough faster and not waste precious time, which means a greater chance of survival in interspecies struggle. Therefore, insects became a more branched branch of evolution.
Sydney funnel web spider
Lives on the east coast of Australia. This spider grows to an average of 7-8 cm. Its long fangs are so strong and long that it can easily bite not only human skin, but also a nail. At the same time, the Sydney funnel-web spider delivers its bites with lightning speed, and sometimes does this several times in a row. After this, the person begins to experience involuntary muscle twitching, followed by numbness of the limbs, tongue and lips. The antidote to the deadly bites of these spiders was created only in 1980.
Redback spider
Belongs to the genus of black widows and is considered the most dangerous spider in Australia. The redback spider is also found in Southeast Asia and New Zealand. Like other spiders, the female is larger than the male, measuring 3 to 4 mm in length. It is the females that are most dangerous to humans. They possess neurotoxic venom glands - their bite can lead to muscle weakness and nausea, vomiting, and sometimes general paralysis and death. A related species of the redback spider is the katipo spider, which is found only in New Zealand. The word "katipo" translated from the local Maori language means "stinging at night."
New Zealand postage stamp featuring the katipo spider
Classification of spiders and habitat
Spiders belong to the biological kingdom Animalia. Animals mean multicellular eukaryotic organisms that consume organic food, breathe oxygen and are capable of movement (not counting individual representatives).
Arachnids are one of the most famous species of the arachnid class. As of November 2015, at least 45,000 species and 113 families have been recorded by toxonamists. The order Spiders includes 2 suborders Mesothelae and Opisthothelae. The latter includes 2 infraorders: araneomorphic and mygalomorphic.
- Mesothelae (arthothiomorphs or lyphistiomorphs) is a suborder containing one living family Liphistiidae and a number of extinct ones. The group includes about 90 extant species. The arthroplasty is medium-sized, 8-23 mm in length. They are characterized by downward-pointing, dagger-like chelicerae, as well as segmented rows of plates on the upper surface of the abdomen. They are active and live for many years. Representatives of the family are common in Myanmar, Thailand, and the Malay Peninsula. Found in Vietnam, the eastern provinces of China and southern Japan.
- Opisthothelae. They differ from lyphistiomorphous spiders in their more primitive characteristics. Opisthotelians lack tergite plates and ganglia in the abdominal cavity. In Opisthothelae the spinning cells are located at the edge, while in mesothelae they are located in the middle.
- Arneomorphs or labidochnaths are an order of arachnids that differ in the position of their fangs. They lean toward each other and intersect in a pinching action. Arneomorphs are common in countries with temperate climates.
- Mygalomorphs are characterized by a parallel arrangement of the jaws, which, when compressed, bend under the basal segment. The infraorder includes the largest representatives of the class, found in the tropics, subtropics, and southern and western regions of the United States.