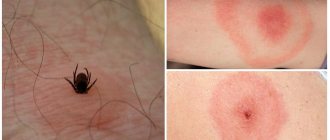
The first troubles and even ailments that we encounter in nature with the onset of warm weather are insect bites. We recently dealt with tick bites, and there are bites from wasps, bees, and mosquitoes ahead. How can they be dangerous and what should you do if you or a child are bitten and develop a severe reaction to the bite?
Who do mosquitoes love?
To be honest, I didn’t understand the hype around mosquito bites before and why everyone is so afraid of them. But one day we found ourselves in the wilds of a very dense forest. The mosquitoes there never saw people. At first I didn’t even understand why there was such background noise in the forest. And they were the ones squeaking. And no repellents bothered them at all - they were so hungry.
When we cooked buckwheat over the fire, the hungry insects went completely crazy. They rushed into the warmth of the boiled porridge and stuck their proboscis into it. It became clear that at night we would all simply be gnawed to the bones, and we hastily retreated to another place.
After that, I realized that a lot depends on the area of residence, the season, the level of hunger of mosquitoes, the person himself and his psychological fortitude. Some people get bitten more, some less. I’m not sure whether mosquitoes love any particular blood type more, but it’s a fact that they flock more actively to a person who sweats a lot. They hardly touch me, I hardly even use sprays, but my husband just goes crazy from the bites and rushes through the blueberry thickets like a bull maddened by horse flies.
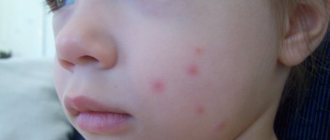
And of course, there are people with a pronounced reaction to mosquitoes; children with delicate and sensitive skin often suffer.
Causes
Bites/stings in the vast majority of cases are caused by provocative actions of the insect by humans. Essentially, biting is a way of defending/repelling an opponent. A number of insects attack humans for the purpose of reproduction (cutaneous gadfly, which lays larvae on the skin, which subsequently penetrate into tissues). Some types of insects bite humans for food.
Risk factors include frequent/long stay of people in suburban areas in the spring and autumn. Particularly at risk are persons who commit insect bites in high-risk areas without personal protective equipment (mosquito nets, thick fabric clothing, special shoes, pre-treatment with a dissectant).
Risk factors include staying in a suburban area in summer, spring and autumn. People who often go on trips to the forest, lakes, ponds, swamps, without using protective equipment (clothing made of thick fabric, special shoes, mosquito nets) are especially at risk.
Allergies to mosquito bites and other reactions
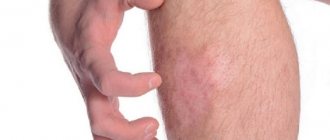
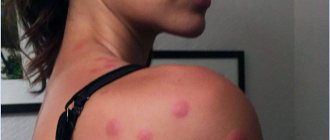
True allergy (with the participation of immunoglobulins E, as a reaction to a foreign protein) occurs quickly, starting from the second bite in life, and is characterized by severe itching and burning (at the site of one bite), swelling and redness form a spot of more than 10 cm, which can spread over the entire limb, be hot to the touch and not go away for several days.
Reactions to bites in the form of anaphylactic shock are extremely rare: during the first 20 minutes after the bite - tingling and itching throughout the body, fever, weakness, suffocation, shortness of breath, chest pain, swelling of the face and larynx, heart rhythm disturbances, drop in pressure, loss of consciousness.
At the first signs of anaphylactic shock, you must:
- call an ambulance;
- take an antihistamine;
- if available, take a hormonal drug or give it an intramuscular injection (prednisolone, dexamethasone);
- a tourniquet can be applied to the limb 5 cm above the bite site so that a finger can pass under it (loosen if swelling occurs);
- in case of suffocation and inability to breathe, inject adrenaline intramuscularly.
If there are many bites on a limited surface of the body and they merge with each other, then itching and swelling are also possible; in small children, the body temperature may rise and loose stools may appear. But this is only a general toxic reaction to a substance ingested in large quantities, and not an allergy. Although symptomatic treatment may require drinking water, antipyretics for age.
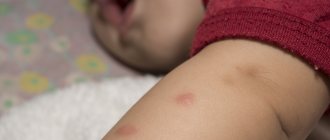
Children under 1–1.5 years old have thin skin and blood vessels, the immune system is in the process of learning, so a regular bite can cause redness up to 5 cm, and lumps can last up to 2 weeks.
And one more point that is important to consider when reacting to mosquito bites. If the redness is more than 5 cm, this size persists for several days, but previously the reaction was normal (this also applies to adults), but now it has become intensified - think about the presence of parasites or a deterioration in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, hormonal disorders.
Fleas in bed
In addition to bedbugs and mosquitoes, there are other parasites: for example, fleas. Flea vinegar is similar to mosquito vinegar. It differs from a mosquito puncture in its smaller size and quantity. Flea bites are usually concentrated in one area. They are very itchy, swollen, and red. In addition, scratches can become inflamed and pathogenic microorganisms can enter the wound.
What are there
There are more than 2,500 species of fleas that specialize in different animal hosts. Usually they rarely change owners, but in the absence of food they can choose another victim. Several species are dangerous to humans in our latitudes.
- The human flea (pulex allerans) has been virtually eradicated, but can occasionally be found. She mainly lives in beds, carpets, upholstered furniture and leaves the nest to drink blood.
- The cat flea (ctenocephalides felis) lives on cats and in their habitats. It is transmitted to dogs and people, as they are much less attached to the owner.
- The dog flea (ctenocephalides canis) behaves very similarly to the cat flea, but is more attached to its owner. In exceptional cases it can run over to a person, but usually cannot survive there.
- Other types of fleas that can bite people are hedgehog fleas, pigeon fleas, rat fleas or chicken fleas.
All species go through four stages of development. Well nourished with blood, adult females lay up to 50 eggs per day. Flea eggs do not have an adhesive effect and can fall out of fur and clothing at any time. This is one of the reasons why fighting them is time-consuming and annoying.
After 3-10 days, larvae emerge from the eggs. They primarily feed on blood in the droppings of adults, as well as dead skin, hair and other organic debris. The larvae are not yet able to suck blood. After a few days in the larval stage, they pupate, and after 7-14 days the adult parasites emerge. The flea lives after hatching on average 4-12 weeks.
What does it look like
The flea's body is brown. She has six strong legs for long jumping and a sucking, burning trunk for eating. Thanks to their flattened sides, they can move over hair, fur, and other surfaces. Depending on the species, an adult flea beetle ranges in size from 1.5 to 4 mm. By the way, fleas cannot fly, but they can jump very far. Their specially built legs allow them to jump distances of up to one meter.
How to fight
Effective flea control is not a one-time action, but a combination of various measures over a long period. The fight must begin by determining the cause of infection. Do your pets have fleas, or did they accidentally jump into the house? The reason could be an old sofa from a flea market, or a mattress from the attic.
If animals have bloodsuckers, then in addition to treatment, it is necessary to disinfect the bed, preferably the apartment. If fleas are found in the bed, then you need to wash the linen in hot water and thoroughly vacuum the mattresses. All of these measures can help with minor infestations. If there is a large area of infestation and a significant number of parasites, it is better to call a special organization.
How to anoint a mosquito bite and how else to help with mosquito bites in a child?
- Wash the bite area with soap and water.
- Cool the bite area for at least 10 minutes to constrict blood vessels to reduce swelling.
- If lumps appear, use absorbent agents that improve blood circulation (heat, such as an evening bath or compress, homeopathic gel with arnica, gel with troxerutin).
- If there is itching:
- if the reaction is very severe, give antihistamines (eg, desloratadine, cetirizine) by mouth;
- From available means you can use ice, a wet paste of salt or soda (do not rub), magnesia from an ampoule, Visin eye drops (externally, on a small area).
- Use topical antihistamines:
- diphenhydramine (age limits are not specified, extensive use is not recommended, as it has a systemic sedative effect, cannot be combined with alcohol and used in the sun);
- gel with the active ingredient dimethindene maleate (for children from one month old; not recommended for large areas of the body).
- Anesthetic agents with menthol, procaine, benzocaine, lidocaine. Approved for use only on small areas of skin.
- Menthol-containing, distracting-cooling agents:
- toothpaste;
- balm "Star"
- If the redness is more than 10 cm in diameter, itching and swelling are very bothersome, you can apply hormonal ointment. But I want to warn you that no matter how relatively safe modern hormonal ointments are, they are still absorbed and affect general processes.
There are ready-made forms “after bites”; they have a complex composition; in addition to essential oils, they may contain some undesirable components - aldehyde, preservatives, silicones; not all of them indicate at what age to use.
Carefully! Never use hormonal ointment for future use, just in case or if the problem is not pronounced. Even a single use of hormonal ointment can awaken the focus of a dormant chronic infection.
How to relieve inflammation
For some people, mosquito bite marks go away for quite a long time: dark spots that appear after scratching wounds and pimples can remain for more than one month. To get rid of bites, you need to use special medications and folk remedies.
On a note!
You cannot mask traces of mosquito attacks with powder or foundation during the inflammatory process. Such actions contribute to clogging of the wound and its decay.
Allergy to wasp and bee stings
A trip to the country, a picnic in the forest or at the sea can be dangerous, especially for those who like to drink sweet drinks and scatter watermelon rinds and pieces of fruit around them.
When a bee or wasp stings, poison enters the human body, causing severe pain, swelling, and inflammation. With multiple stings of more than 5 bees, with stinging of the face, lips, tongue, with contact with a vessel or with individual sensitivity, the likelihood of extensive, life-threatening reactions (Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm) is higher.
Life-threatening reactions usually appear a few minutes after the bite, and after the first bite in life they may not occur. After the first bite, an allergic mood may form, which will manifest itself only with repeated bites. Therefore, if you or your child have already been bitten by a wasp once and that time everything was just swelling and pain, you should not think that the next time will be the same. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and have a syringe with epinephrine in your first aid kit.
Advertising
List of sources
- Stanek V.Ya. Illustrated encyclopedia of insects. Prague: Artria; 1977. .
- Safina L.F., Fassakhov R.S., Reshetnikova I.D. Skin manifestations of allergic reactions to stings of hymenoptera insects // Practical Medicine. - 2011. - No. 3, - pp. 140-142.
- Dremova V.P. Urban entomology. Harmful arthropods in the urban environment. — Publishing house “IzdatNaukaServis”. Ekaterinburg. - 2005, 278 p.
- Lawlor G. – Jr., Fischer T., Adelman D Ch. Allergy to insect venoms. in the book Clinical immunology and allergology - M.: Praktika, 2000. pp. 346 – 356.
- Zaikov S.V., Mikhey L.V., Kulik L.G., Allergy to non-stinging insects // News of medicine and pharmacy. - 2010. - No. 345. - p. 36-37.
First aid for wasp and bee stings
- Remove the sting, if possible without damaging the vial of poison attached to it - move it to the side with your fingernail or business card and pull it out. It is better not to use tweezers, as this usually damages the vesicle.
- Wash the bite area with clean water, soapy water, or hydrogen peroxide.
- Apply ice to the bite site for 10–15 minutes.
- If your arm or leg is bitten, give it an elevated position, remove rings and bracelets, if any.
- If severe itching bothers you, apply a wet bandage with baking soda, or just a paste of baking soda, or, if you have it with you, any antihistamine ointment.
- Give an antihistamine (drops, tablets) based on age.
- If the pain is severe, give paracetamol or ibuprofen; they are allowed for children and are prescribed in dosages according to age.
- If the bite was made to a vessel, face, tongue, or you observe that the stung person has difficulty breathing, swelling of the face increases, the face turns blue, there is nausea, vomiting, headache, immediately call an ambulance.
Before the ambulance arrives:
- Apply a tourniquet 5 cm above the bite. If it is the head or neck, pinch the bite site with your fingers and hold.
- Apply cold.
- Take an antihistamine by mouth.
- If you have it in your medicine cabinet, give an intramuscular injection of the hormone prednisolone or dexamethasone. If the person is choking and unconscious, give an intramuscular injection of epinephrine. Discuss the dosage according to age and the injection technique with your doctor in advance.
How to avoid bee and wasp stings?
- Do not leave cut fruits and sweets on the table.
- Immediately remove cores and crusts into a sealed trash bag.
- The container for compotes/juices must have a lid.
- Teach children not to drink from the bottle, especially from opaque containers. First you need to pour it into a glass and inspect the contents.
- Do not use perfumes or creams with sweet or floral scents.
- Do not wave your arms to ward off wasps and bees.
- If you have already stunned the wasp, take it as far as possible without touching it with your hands, since the insect may still be alive, they could step on it with bare feet or put a hand on it.
- Use repellents.