Lice are human parasites that cause a lot of pain. Lice infestation is called pediculosis. According to statistics, children under the age of 14 are in second place in the number of cases of head lice among all age categories. It is believed that every fifth or even fourth child has contracted lice at least once in their life. Many children become infected with head lice several times. Because of this, lice is considered a childhood disease. This, of course, is not true, and lice can appear in people of any age. In order to prevent complications caused by lice, you need to understand why lice appear in children, why this happens and how to deal with it.
Basic Information About Lice
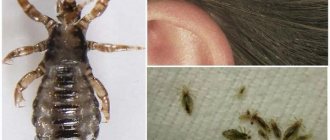
Lice, as mentioned above, are a human parasite. They live only on humans and feed on human blood. They do not live on any other individuals. Therefore, one of the main myths is refuted: you cannot get lice from dogs, cats, parrots and other animals. Lice are transmitted only from person to person.
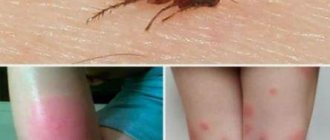
The louse is a blood-sucking parasite. To live, she needs to receive blood several times a day - every 4 - 6 hours. The insect pierces the skin and sucks out the required amount of blood. The bite itself is painless, but the parasite injects saliva during the bite with components that prevent the blood from clotting. This substance causes a person to feel intense itching, and some people may not respond to lice bites.
There are three types of lice:
- head lice – live on the scalp and are most common;
- pubic (plates) - live on the genitals covered with hairs;
- clothing - they do not live on humans, but only feed; for reproduction and life they prefer clothing, bedding and other textile items close to humans.
Lice in children are most often head lice. The life cycle of an insect is a little more than a month. Lice eggs are nits. They stick to the base of the hair, look like white balls and resemble dandruff. But dandruff is easily shaken off the scalp, and it is very difficult to detach nits from the hair. One female can lay up to 400 nits in her life, so the head of a person with lice can literally be swarming with parasites within a couple of weeks after infection.
Sources of lice in children
The most important risk factor for lice in children is being in a group of children. Kindergarten, school, development center, clubs, health camp, hospital, swimming pool - any place where there are many children in a small area at the same time becomes potentially dangerous. Children love to communicate, play together, and hug, fight, roll around, and touch their heads. At the same time, it is very easy for lice to move from one head to another. The louse cannot jump or fly, but moves quite quickly. Can cover approximately 50 cm on any surface in a minute. You can simply shake off the parasite onto another person. Therefore, picking up lice while playing in close contact is easier than ever.
Another factor that increases the risk of lice and nits is that children like to exchange things. These can be hats, combs, hair clips, and other hair accessories. Girls are primarily at risk in this risk group.
A modern reason for the easy transmission of lice in children is the use of gadgets. Children do not take their eyes off the screens of smartphones and tablets, touching their heads for a long time. During which time the lice have time to crawl from one child to another.
Even if the child is still small and does not go to children's institutions, he can pick up lice, for example, on the playground. Lice can stay in the sandbox for up to 4 days, without gaining access to blood, but maintaining viability. So, if a baby likes to roll in the sand, he runs the risk of picking up parasites there.
Lice also appear when visiting a hairdresser with a low level of hygiene. If instruments are not sterilized after each client, insects or nits may remain on them. They can also remain on the headrest or back of the chair, from where they move onto the head.
Even a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool can become a place where a child gets lice. They are not afraid of water and live in it for some time.
So, the main ways in which lice appear in children are:
- close contact during games and communication;
- exchange of personal belongings;
- visiting a hairdresser;
- in sandboxes and playgrounds;
- in swimming pools, baths.
Lately, the number of head lice outbreaks has been decreasing. This is associated with an increase in hygiene levels. But at the same time, in large populated areas, where families live with different ideas about hygiene and the need to treat head lice, lice remain a problem. In a group, one child with parasites is enough for him to constantly infect his classmates.
Prevention
Preventive measures for pediculosis are very simple:
- • Wash your child's hair at least once a week
- • Comb your hair thoroughly with a fine-tooth comb.
- • Explain to your son or daughter not to have too close contact with other children, especially if there is an outbreak of head lice in the group or class.
- • Girls' long hair can be tied into a ponytail or braided.
In most cases, early detection of lice and a responsible attitude to treatment allows you to quickly deal with the problem.
Why do lice appear in children?
Lice can appear on a child's head regardless of his personal hygiene. Lice are not only found on homeless people and people with low social responsibility. On the contrary, it is easier for insects to get to the blood on a child’s clean scalp, without a layer of grease and dirt. And it is easier to pierce the delicate skin of a child than that of an adult.
There are two inexplicable myths about the causes of lice in children and the treatment of head lice, which some parents adhere to:
- Lice appear from stress. A louse is a very specific insect, it exists in reality, it cannot just appear on a child’s head. Lice can only be contracted from an infected person.
- Lice infestation is a natural stage of children growing up; it happens to everyone; there is no need to treat lice in children. Because of this misconception, there are epidemics of pediculosis. If you don’t fight parasites in a team, then one child will continue to infect the rest. Lice in children do not disappear on their own; they need to be dealt with.
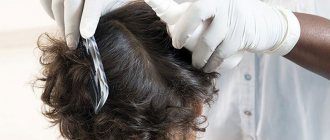
In children's institutions, the appearance of lice in children is inevitable, alas. Prevention of head lice means regular examination of the heads by parents and employees of child care institutions for the timely detection of infected children. Many parents resist such an examination, considering lice to be something shameful. They are sure that this simply cannot happen to their child. However, it is not a disease of any particular social group. Anyone can have lice, regardless of status and wealth.
Helpful information! Outbreaks of the disease most often occur at the beginning of the school year, when children gather in schools and kindergartens. During this time, it is important to examine children's head and hair daily. Parents of girls with long hair need to do this especially carefully. Nowadays braids are very popular among children. You should not leave them braided for a long time. Every evening it is advisable to comb your hair, looking at the back of the head and behind the ears. This is where nits most often appear. Adults can move around the entire head.
If a child is diagnosed with lice in kindergarten or school, do not panic. It's just a disease for which there are remedies. There is nothing shameful or indecent about this. The main thing is to take timely measures to get rid of parasites and prevent the child from suffering from itching and other problems.
Symptoms
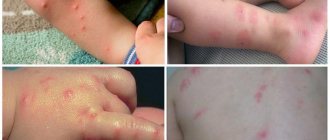
The most common symptom of head lice is an itchy scalp. It occurs in 14-36% of cases as a reaction to insect saliva, which they inject into the bite site to thin the blood. The degree of itching depends on the time of infection and the number of parasites.
When first infected, it may take 4 to 6 weeks for the head to begin to itch. During this period, head lice can be easily transmitted to other people. In case of repeated infections, itching appears after about 24-48 hours
When examining the head, you can see live insects and their eggs (nits), which are firmly attached to the hair shaft closer to the scalp. Nits are most often found in the occipital fossa and behind the ears, and are easier to spot than fairly fast-moving lice.
How dangerous are lice for children?
Head lice has several main symptoms. First of all it is itching. The bite sites are very itchy. The child scratches the scalp, scratches and abrasions appear on it, and crusts form. An infection can get there. In rare cases, infectious agents can enter the bloodstream and cause truly serious illness. It is also worth noting that in modern conditions many children suffer from allergies. When lice bite, saliva gets onto the skin and into the blood. It may contain allergens that cause severe reactions in children. The area next to the bite becomes very swollen, red, irritated, and itchy.
Theoretically, lice can act as carriers of diseases, but in practice such cases are not recorded in our country. People with weakened immune systems should be careful. Since some pathogens can enter the bloodstream through scratched bite sites.
Scratching the bite sites leads to the appearance of crusts and skin problems. In some cases, it can develop into dermatitis and eczema. All these diseases are reversible, but will require additional, long-term treatment.
Please note! If head lice in children is not treated and large numbers of lice are allowed to appear, adult lice leave many traces of their presence in the hair. They secrete excrement and saliva. In the process of growing up, insects go through three nymphal stages, after each of which they shed their outer shell. After hatching from the eggs, they leave exposed nits on the hairs. All these particles remain in the head, stick together, and turn into tangles. They give off an unpleasant odor and cause inconvenience. You can get rid of them only by cutting or shaving your hair.
If you do not fight parasites, this will negatively affect the child’s psyche. Due to constant itching, the child experiences discomfort, he is forced to scratch, and in front of everyone. He cannot concentrate on his affairs, lessons, responsibilities, games. Can’t fully rest or get enough sleep. Becomes twitchy, constantly feeling tired and stressed. This is accompanied by a feeling of shame that something unpleasant and disgusting is happening.
To prevent this from happening in children, it is important to identify the problem in time and begin the fight.
How to deal with lice in children
There are two main methods of control - mechanical and chemical. Mechanical radical means shaving off the hair. No hair - no lice, because they do not live on bare skin. But this method is only suitable for very young children. Another mechanical method is combing with a comb with closely spaced teeth. For a child with sparse, light-colored hair, brushing the hair for several days in a row may be enough to remove all the adults and nits. But this method is suitable for a small number of parasites in children, when the disease was noticed at the very beginning.
The problem with childhood head lice is that parents find out about it when their head is swarming with insects. That is, it is no longer possible to cope with simple combing. Lice multiply exponentially. In this case, you need to use a special anti-lice shampoo. There are drugs that can be used to treat children. It is important to follow the rules and conditions of use specified in the instructions to ensure the safety of the child and the effectiveness of the product.
For example, you can use the drug Medilis-BIO. It has a pleasant clove aroma, has an acute pediculicidal effect, providing paralysis and then death of larvae and adult lice, has an ovicidal effect on lice eggs (nits), and is approved for the treatment of children over 5 years of age and adults. This is a ready-made lotion that is simply rubbed into the scalp and left for half an hour, after which it is washed off with water. To be on the safe side, after treatment, rinse your hair with a vinegar solution and comb your hair to remove parasites. A vinegar solution is an effective remedy against nits. The fact is that nits are attached to the hairs by a very sticky and durable secretion that cannot be dissolved with regular shampoo. The acidic environment of vinegar dissolves it, the nits come off. So it’s not in vain that this folk remedy has been used in the fight against nits for many years.
Other folk remedies should not be used for children. Firstly, they are ineffective. Secondly, many are dangerous for children. For example, kerosene has been used to remove lice for many years, but it is toxic. In addition, many folk remedies require repeated use. For example, wraps with kerosene, cranberry juice and other substances will have to be done every day for one to two weeks. What child can handle this? It is easier to use a special shampoo or lotion for one-time use.
If the lice have already infested the scalp, leave multiple bites that the child has scratched until there are abrasions and scabs, it is necessary to treat the wounds with antimicrobial and healing ointments.
An effective weapon in the fight against head lice
The main disadvantage of modern pediculicidal agents is that lice develop resistance (resistance) to the toxic substances (insecticides) they contain. “Paranit” is the latest generation lice remedy that helped solve this problem. The drug has a completely different principle of action. It contains dimethicone and mineral oil. These are low-hazard substances that are actively used in the production of hygiene products and cosmetics.
Dimethicone is a silicone oil that, when applied to hair, tightly coats the bodies of lice, plugging the openings through which the insects breathe and maintain water balance in the body. Within a few minutes after treatment, the parasites suffocate. Nits also need oxygen for normal maturation, so “Paranit” is also effective against them. The nit maturation process stops and after a while they die.
Due to the fact that Paranita Sensitive does not contain toxic substances, it can be used to treat children from 1 year of age and pregnant women. Since the drug affects lice physically, they do not become resistant to it.
Complex wrestling
If you find lice in children, be sure to check the hair and heads of all other family members. Pediculosis is a highly contagious disease. One carrier will most likely affect the whole family. Everyone needs to get rid of lice. And even if you haven’t noticed any adults, it’s worth using a medicated shampoo as a preventive measure to kill nits and lice, which may remain invisible.
Lice emerge from the nits within 6–8 days. So within a week after treatment, you need to examine the heads in order to detect new individuals in time. To be on the safe side, you can repeat the treatment after 1 to 2 weeks.
Do not forget that lice can appear not only on the head, but also on the personal belongings of an infected person. They tenaciously hold on to the hair with their paws, but can simply fall onto clothes, bed, any surrounding objects, and then from there again move onto children and adults. To destroy parasites, it is advisable to treat the room where infected children or adults were. To do this, you can use different methods. In winter, you can freeze the room by turning off the heating and opening the windows for several hours. Insects die at temperatures below zero, but this is a very radical method. You can use chemical preparations with an acute pediculicidal effect, for example, Medilis-Malathion, Medilis-Permifen, Medilis-Super. They treat surfaces by wiping or spraying. Clothes can be soaked in a pediculicide solution and washed at temperatures above 40 degrees.
It is worth remembering that the comfortable temperature for lice is from 20 to 37 degrees. At levels lower and higher, they stop reproducing and living. They also constantly need food. Without blood, they can live up to 4 days, but more often they die after two days. Nits can fall into a state of suspended animation and spend up to a month in it, after which – when they find themselves in comfortable conditions – they continue their development. So if there are things affected by lice or nits that cannot be washed or treated in any other way, you can simply put them in sealed bags and leave them there for a month. During this time, the pests will die.
How to treat then
Pharmacies offer two types of products. Some paralyze the nervous system of lice. Others disrupt the respiratory system and water metabolism of both the insects themselves and their larvae and nits. Aerosols, sprays, and shampoos from the second group are the safest and easiest to use.
Clothing and bedding of the infected person should be boiled and dried in the sun. It is enough to take pillows, soft toys and other objects where lice may remain on the balcony for several days. Parasites cannot live for a long time without feeding on human blood, so they will die on their own - there is no need to disinfest things if it is possible to simply not use them for some time.
How to avoid lice in children
There is no one surefire way to protect children from lice infestation. But it is important to explain to your child that you cannot use other people’s things:
- put on other people's hats;
- comb your hair with someone else's combs;
- pinning hair with someone else's hairpins;
- attach other people's carnival ears or decorations to your head.
In the pool you cannot use someone else’s towels or wear a cap that is not your own. You should also not give your personal belongings to other children.
The next means of prevention is not to touch heads when playing or communicating. It is necessary to avoid too close contact and maintain sufficient personal space. Of course, this is very difficult, but children over 7 years old will understand such a request
It is important to explain that lice is a disease that needs to be treated. There is nothing funny or shameful about this. If a child suspects he has lice or feels itching and discomfort, he must tell his parents about this. There is no need to shame your child for catching lice. It's not his fault.
Some children do not tell their parents about lice also because they do not consider itching to be a symptom of the disease. The head may not itch much or not at all. Parents may not pay attention to an itchy child, considering the itching to be a manifestation of an allergy or other disease. During head lice epidemics—and indeed at any time—parents should periodically inspect their child's head for lice. If you notice parasites in time, the fight against them will be quick and effective. But it is important to understand that immunity against lice is not developed. You can become infected with them as many times as you like, so don’t let your guard down.
What to do if your child brings lice from school?
This is a very pressing issue concerning both parents and school management. First of all, you need to figure out how to relate to this diagnosis. Some parents, ashamed of a “shameful” problem, keep silent about it, get treatment without telling anyone, and return the child to school. With a high degree of probability, after some time he will return home with lice again. A vicious circle is created. To avoid this, you must report a case of head lice to the school nurse or class teacher.
In turn, the nurse should check all children in the class. Please note that she has no right to publicly disclose the diagnosis, even if it is pediculosis. But at the same time, if one of the children was found to have lice or live nits, she is obliged to notify his parents and the class teacher.
Many mothers, fearing an outbreak of head lice, leave their children at home, demanding that the administration of the educational institution completely disinfect the premises. It is not right. As mentioned above, lice do not live outside the host. According to sanitary standards, there is no need to treat furniture, walls, floors and clothing. Only mats in school gyms are treated
Another very important point that interests parents: does the school have the right to not allow a child with head lice to attend classes without a certificate from a dermatologist? Yes, she has the right to do so. Moreover, after presenting the certificate, the nurse must once again examine the child’s head. These measures may seem quite harsh, but this is the only way to stop the spread of parasites.
If head lice is detected in the class, all parents should participate in prevention. For about a month, you need to regularly examine the head of not only the student, but also all family members.