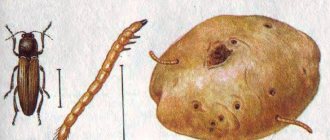
- What does a click beetle look like?
- Where does the click beetle live?
- Reproduction of click beetles and maturation of larvae
- How to deal with click beetles and wireworms
- Chemicals
- Agricultural technology against wireworms Use of traps
- Laying out the bait
The nutcracker was nicknamed an acrobat for his ability to jump and flip. The click beetle is an unsightly looking insect, small and harmless. More often found in gardens, fields and vegetable gardens. The threat is posed by the offspring - voracious wireworm larvae. Staying in the larval stage for 4-5 years, they cause significant damage to vegetable and cereal crops.
What does a click beetle look like?
The size of an adult beetle is 1-2 cm. It has an oval-elongated, slightly flattened body, 2/3 of which is occupied by the head with antennae consisting of 11 segments. Females have short mustaches, but the body is wider and longer.
The color of the cover is with black, brown or purple shades. There are beetles with a yellow color or a metallic tint. This is influenced by habitat and soil components. The elytra are covered with a pattern of spots or stripes.
A process is visible on the insect’s chest, which is inserted into a special recess. This process helps the beetle jump with a clicking sound. If you turn a nutcracker onto its back, it will jump up and roll over.
Prevention
- Autumn digging of the soil reduces the number of pests. The layer of earth is turned over and not broken into clods. In heavily infected areas, it is better to carry out this procedure later, on the eve of frost. Some larvae and adult beetles end up near the surface of the earth and die from low temperatures . In spring and early summer, when eggs are being laid, deep loosening . Detected beetles and their larvae are immediately removed from the ground and destroyed.
- Areas overgrown with weeds, especially wheatgrass and thistle, . The pest loves to feed on the roots of these herbs.
- The wireworm avoids places where legumes used to grow. This fact is taken into account when planning crop rotation. Beans and peas can be planted in rows around the perimeter of the site. Planting calendula and marigolds . The secretions of these plants discourage the wireworm's appetite.
- It is important to monitor the acidity of the soil. At elevated pH levels, lime the soil or add ash (2 liters per 1 m²). This worsens the living conditions of insects.
By carrying out prevention and systematic treatment of the soil with preparations, you can get rid of wireworms on the site in a few years.
More details: you will learn how to deal with wireworms from the video.
Where does the click beetle live?
Scientists have studied 12 thousand species of click beetles. Of these, more than 300 species live on the territory of Russia. Common beetles include dusky, steppe and striped click beetles.
Favorite places of settlement are forest, forest-steppe and steppe zones. Beetles prefer heavy clay and loamy soils with high humidity; they like to settle in dense thickets of wheatgrass.
With the beginning of spring and the first green shoots, pests crawl to the surface. In summer they hide under plant debris and clods of earth.
Other click beetles are parreisa, with a body length of 3.5 cm. These beetles are listed in the Red Book of Russia.
Conditions of appearance
Pests appear in garden plots for various reasons. Firstly, it can easily penetrate from neighboring areas and lay eggs. Often the owners themselves are to blame for the appearance of a click beetle on their property. As a rule, few people adhere to agrotechnical rules in garden plots, planting crops in one place every year. This is especially true for potato plantings, since the weight volume of such plantings is always greater compared to other crops. Potatoes have to be planted every year and there is simply nowhere to move the plantings of this crop, considering how much land the gardener has. Even in villages where people have more land, no one seriously thinks about this problem: they planted potatoes in one place and continue to do so from year to year.
Reproduction of click beetles and maturation of larvae
In May-June, females lay eggs under earthen lumps and in cracks. Clutches are found in the roots and stems of plants, among burdocks, or in rotting wood. The clutch contains 5-15 white, small, 0.5 mm eggs, and in 2 months - 150 eggs.
The eggs lie for 1 month, absorbing water and increasing in size. After 20-30 days, the larval worms emerge. “Newborns” are white in color and resemble stiff wire cut into pieces. Therefore, the larvae of the click beetle are called wireworms.
The larvae of the first year of life do not do much harm to garden plants and feed on other food. At this time, their body length is 0.2 cm. By the end of the year they grow to 7 mm and become mobile, light brown in color.
Growing up wireworms gnaw through potato tubers and root crops and gnaw through roots. Some species snack on earthworms, larvae and pupae of other insects.
3-year-old larvae are already 3 cm long, with dense body covering. The hotter and drier the weather, the more voracious the larvae become, with faster maturation times. For the winter, wireworms hide in the soil in warm and moderately humid places. After the 4th winter, in the spring, adult beetles emerge to the surface.
What does an insect eat?
Adults do not eat anything or feed on the juices of green parts of plants. They don't cause much harm. The real destroyers of agricultural crops are the larvae. The thin, strong structure of the body allows them to easily pierce the skin of root crops and roots.
There are about 750 species of cracker beetles in our area. The diet of each of them is slightly different.
- Wireworms of turfgrass and black click beetle prefer potato tubers and vegetable crops.
- The larvae of shiny, striped beetles eat cereals and sunflowers.
- The small click beetle eats peanuts, beets, carrots, and grain crops.
- The steppe wireworm damages almost all crops.
On a note!
Insects do not disdain weeds. They eat leeks and burdock with great appetite. If proper measures are not taken, pests will completely destroy the entire crop and all the vegetation on the site.
Beetle development cycle
Chemicals
Garden owners are often against chemical poison, but insecticides give 80-90% results:
1). Prestige solution is poured into the hole before planting seed material - potatoes, flowers and other garden crops. Seedlings and grown plants are sprayed. The substance remains in the soil for 1.5 months.
2). Aktara, in diluted form, is used to water the soil before planting.
3). Seeds, tubers and seedlings are treated with Tabu.
4). Bazudin is used carefully against click beetle larvae - it is a toxic substance harmful to living organisms.
5). Adding potassium chloride to the soil followed by digging. Wireworms will disappear in 2-3 years.
6). Pouring a weak solution of potassium permanganate into the wells.
Features of life
The owners of unique and valuable exhibits try to know by heart the search for an effective means of combating or a method of destroying this unwanted neighbor. But what should the owners of private housing do, in whose houses the beetle can also settle quite freely? First of all, it is worth remembering that skin beetles do not appear in an apartment just like that. Pests traditionally choose dry rooms to colonize. In nature, their main source of nutrition is organic food - the remains of animal bodies, bird nests, pollen, and waste products of rodents. They can form symbiosis with various types of insects - from ants to wasps and hornets. The main food of the larvae is substances of protein origin, including silk and wool fabrics, leather products, and feathers. If meat or its processed products are freely available, one can expect that the larvae will choose them as their main source of food.
Agricultural technology against wireworms
Agrotechnical rules in the garden:
- Do not plant annually the same crops that grew here before;
- Treat the soil thoroughly and in a timely manner, and use the moldboard method when plowing;
- In May-June, when females lay eggs, loosen the rows;
- Do not thicken the plantings and remove weeds in a timely manner;
- Dig up the area before the onset of autumn cold weather;
- Plant legumes more often;
- Reduce soil acidity.
- Before planting potatoes, sow oats or barley, then harvest;
- Fertilize the soil with ammonia-nitrogen fertilizers.
Smell repellent:
- add onion peels, mustard powder or a pinch of hot pepper to the holes when planting potatoes, or moisten the tubers with onion decoction;
- mix ash, pine resin and humus, add the mixture to the holes;
- throw 3-4 beans into the holes;
- Click beetles and wireworm larvae do not like the smell of marigolds.
Using traps
If you dig holes in the spring, put last year's grass there, moisten it and cover it, pests will gather there. The bait is burned, and the hole is filled with a new portion of bait. In autumn they are filled with manure.
In another method, 0.5 liter glass jars or plastic containers are dug into the ground, where bait is placed: chopped carrots or potatoes. Check after 2 days.
Laying out the bait
Stick a stick into half a potato and bury it 10 cm so that the cut “looks” down. Check the same after 2 days, collecting larvae. Bury the tuber again, wetting the cut.
2 weeks before planting potatoes, sow oats, barley, corn in the nests, after preliminary swelling of the seeds. Three nests per 1 sq. m. When shoots appear, dig up and destroy the larvae.
Conclusion
If you do not act, then the wireworms will spoil part of the crop or eat it, and this is the labor that is spent on cultivating the plot, sowing and other work. Don't give up and refuse to fight. Reducing the number of larvae is already a success.
Preventive recommendations
A number of useful recommendations from specialists and experienced gardeners will help prevent the appearance of many pests on the site, including wireworms.
What to do:
- Timely removal of weeds will help in the fight against many pests.
- It is advisable to follow the rules of crop rotation so as not to plant the same crop in one place.
- In autumn and spring, it is better to dig deep into the soil on the site.
- It is better to plant leguminous plants interspersed in potato beds.
- An integrated approach to the fight against wireworms will help achieve a positive result.
Inaction on a personal plot or summer cottage in terms of pest control can lead to complete loss of the crop. If someone has a negative attitude towards toxic substances, then at least with the help of simple traps, it is still worth fighting pests. In addition, good results can be obtained if you use a number of agrotechnical measures. Mandatory planting of crops on the site that are not included in the wireworm’s diet also bears fruit. So, a little bit of each method and we can already say that pests are unlikely to feel comfortable on the site.
The wireworm is a click beetle. Description, control measures.
Viral diseases of tulips
Variegation
It is the most dangerous and widespread viral disease of tulips. The history of this disease goes back centuries and has been known since the appearance of tulips in Europe. True, at first flower growers considered the variegated flowers to be new varieties that were in great demand, and tried to propagate them.
One of the culprits behind the death of a large number of the most beautiful varieties of tulips bred in the 17th-19th centuries was, undoubtedly, the variegation virus.
The virus is transferred from a diseased plant to a healthy one mainly by insects (aphids, thrips) and nematodes. A person can also serve as a carrier of viruses if flowers are cut with one tool. If a diseased plant enters, the virus can be spread throughout the plantation.
The variegation virus changes the color of the flower. In pink, purple and lilac varieties it becomes heterogeneous, streaks and stripes appear on a white or yellow background. Only in some places the original color of the flower is preserved.
It is even more difficult to determine the disease in white and yellow varieties, because shading on flowers and leaves is weak or not noticeable at all. In this case, the disease is detected by indirect signs.
In diseased plants, the tepals are narrowed, especially at the point of attachment to the stem, the flower is smaller, and the stem is shorter. Near the stem, the tepals do not touch each other and a gap appears to form between them.
There are faintly visible light green stripes on the stems and leaves. Sometimes, under the influence of the variegation virus, chlorophyll is not formed and the stems become transparent, as if waxy, and the leaves curl and droop. In some varieties, a change in the bottom pattern is observed.
Control measures. There are currently no special drugs or pesticides to combat the pestine virus.
Preventive measures remain the cornerstone in the fight against a dangerous virus. If a disease is detected, the plant is removed and destroyed. It's better not to use a shovel, because... By cutting the roots, you can transfer the virus to neighboring healthy plants, and by loosening the soil on top, carefully pull out the diseased plant.
It is unacceptable to use one tool when cutting flowers and decapitating. Breaking off flower stalks with your hands also does not always guarantee sterility.
The proximity of tulips to lilies, on which the variegation virus can be present without visible signs of infection, can be especially dangerous. Growing tulips next to lilies is undesirable, and after lilies it is unacceptable.
August disease (Augus disease) or necrotic spot
Caused by tobacco necrosis virus. It was first discovered in 1931 in Holland on tulips of the August variety, hence the name of the disease. The virus is transmitted through fungal spores that parasitize the roots of weeds and some cultivated plants (tobacco, potatoes, legumes, tomatoes, etc.). Infection occurs when fungal spores come into contact with damaged tulip roots.
When a cross section of the bulb is taken, transparent spots are observed, which later also turn brown. Augusta disease affects tulips both in the ground and during forcing. Early varieties are more susceptible to diseases.
Control measures. Removing all diseased plants along with a clod of soil. The soil is disinfected or steamed. For an amateur gardener, the easiest way to disinfect is to “fry” the soil removed from the diseased plant.
You need to know the enemy by sight
It is important to understand that all existing species of insects called skin beetles have their own distinctive characteristics and even food preferences. For example, museum residents prefer to eat stuffed animals
Skin beetles can also get into a person’s home:
- Smirnova is a pest with a brown body up to 3 mm in size, prefers to settle in window frames, as well as in the area of window sills;
- fur coat - the body color is black, has characteristic white dots on the carapace in the amount of five pieces, it is this that most often spoils food, cereals and grains;
- ham - judging by the name, the food preferences of the pest are quite obvious, its distinctive feature is the high reproduction rate and abundance of larvae, this bug can be identified by the gray-yellow stripes in the wing area;
- carpet - in this species only the larvae are dangerous, which are distinguished by their impressive gluttony, adult individuals have sizes from 2 to 4 mm, the main sources of food for pests are organic matter - from human skin scales to cat fur.
Home penetration
Carpet beetles appear in an apartment due to their ability to move through the air. The pest prefers to fly in dry weather, like most of its Coleopteran relatives. Experts warn:
Where to look for the source of danger?
If at least one individual is found in a house or apartment, you should sound the alarm. The leather beetle is quite prolific - the female lays more than 100 eggs during her life; therefore, an unattended pest population can easily destroy a home library, woolen carpets or a collection of favorite clothes made from natural materials. The homes of hunters who make stuffed animals for their collection are also at risk.
Insects choose dry and warm places for their settlement. They can be found in mattresses, kitchen sofas and seat upholstery, above heating radiators (in the cracks of the window sill). You can also find an adult insect in places traditional for household pests: under wallpaper, baseboards, and wall cladding parts. Among the insect's unusual habitats, one can note flower pots - this is where the bug is often successfully taken by surprise.
Help from professionals
It is important to understand that severe infestation of premises by pests requires exclusively professional treatment, preferably using hot fog generators that combine thermal and chemical effects. Specialists are ready to offer their clients enormous experience in treating pests of both small residential spaces and in protecting warehouses, museums, and retail areas
After just one visit from specialists, you can easily get rid of any sources of danger, stop the invasion of adult bugs or their larvae, and also prevent their reappearance. The main thing is not to waste time and immediately contact professionals when a problem is discovered.
Fighting with contact methods
Even the most outspoken defender of wildlife is unlikely to argue that such a scourge as the skin beetle in an apartment needs to be actively fought. The simplest solution in this situation is to use a vacuum cleaner, with which you can easily and quickly collect pests. The optimal solution for collecting insects is a vacuum cleaner with disposable paper bags (they are then burned) or a water filter. The treatment will have to be carried out in the detected habitats of the bugs every day, for a week or more.
Another fairly simple solution is the use of steam generators, which make it possible to destroy the enemy even in hard-to-reach places, including under baseboards and in window sill cracks. Small pieces of furniture and clothing can be exposed to low temperatures by temporarily leaving them in the cold.