The locust is a fairly large insect from the class of Orthoptera. For a long time, it has represented the main threat to cultivated crops.
Descriptions of locusts can be found in such ancient writings as the Bible, the works of the authors of ancient Egypt, the Koran, and so on.
Description of the insect
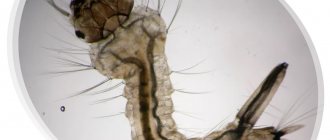
The body of the locust is elongated, the length can reach 20 centimeters. The “knees” of the hind legs are bent, their size is several times larger than the size of the middle and front legs.
There are a pair of hard wing covers, under which are fragile wings with original patterns. When folded, they are quite difficult to notice.
The antennae of locusts are somewhat shorter than, for example, those of crickets, and the head is larger and the eyes are larger. The insect makes a characteristic sound characteristic of males.
The surface of the males' thighs is slightly jagged, and some thickening can be seen on the thighs. During friction, these parts emit a specific sound, which can be of any tone.
Many people believe that the color of a locust depends on its genotype. But actually it is not. The color of an insect has a direct relationship with environmental conditions.
Even individuals belonging to the same offspring, but living in different places, may differ in color.
Another factor influencing coloration is the developmental phase. A younger individual is green in color, and an individual that has entered the gregarious phase acquires the traditional color.
Locusts have the ability to fly; they can travel up to 120 kilometers per day.
Another double
Another green insect that looks like a grasshopper is the praying mantis. Of course, an entomologist can easily distinguish one species from another. However, townspeople are not always able to understand who is in front of them. Moreover: not everyone can see a praying mantis, so cleverly does it “pretend” to be a green twig. Even some insects do not see it among the foliage and land directly on the predatory insect, instantly becoming its prey.
The praying mantis can be recognized by its characteristic stance, reminiscent of one praying. It has a triangular head and very long front legs. During mating, the females bite off the male's head, but even being decapitated, he fulfills his duty to his “wife.”
Locust habitat
Locusts live on almost every continent, with the only exception being Antarctica. Many climate zones are suitable for this insect.
Some species typically live in grassy areas, others prefer to settle in close proximity to water, while others choose semi-deserts as their habitat.
Either a stick or a flower
The stick insect is another grasshopper-like insect. During the day it pretends to be a flower or twig (which is why it got its name), and at night it looks for plant food. Even looking closely at the foliage, you are unlikely to distinguish a stick insect from a twig. In Russia, these insects are green and small, but in New Guinea there are individuals up to 20 cm long. They take on the color of the surrounding foliage. These individuals can often be found at exhibitions of exotic nature.
The grasshopper has “doubles” that are many times larger than itself. The domesticated giant Weta can be found on the Barrier Reef. The insect, similar to a grasshopper, grows up to 9 centimeters, but weighs almost 80 grams. This is a record among insects.
Nutrition
Those individuals that live separately are not known for their gluttony. Over the course of its entire life, one locust can consume up to 300 grams of plants. However, when she gets into a pack, her behavior changes dramatically.
A locust invasion causes enormous harm, since, having met its relatives, the insect becomes omnivorous and begins to absorb everything it sees: reeds, reeds, fruits, grain crops, and so on.
Long flights and lack of food force the locusts to feed on their weaker relatives.
Green, but not a grasshopper
There is an insect that is so similar to a grasshopper that an inexperienced eye will not immediately distinguish one from the other. These are locusts. The life of a locust takes place in two phases. At the moment of “loneliness” the fillies take on a protective color and lead a relatively calm lifestyle. In the second stage they form flocks. This is the main difference between a locust and a grasshopper: an insect similar to a grasshopper is a herbivore.
Flocking together in flocks, the grasshopper's short-whiskered counterparts are capable of destroying hundreds of hectares of crops in a few hours. Such flocks move at an alarming speed, and no means have yet been invented to combat them. What else distinguishes a thunderstorm from a grasshopper? Short mustache, shorter than that of the master of serenades, hind legs, powerful forelimbs. Locusts do not jump, which is why their legs are weaker. Finally, the grasshopper destroys insects, saving people from them, and the locust destroys farmland, causing harm.
Photo of locusts
He sits behind the stove.
Similar to a grasshopper, only black, and our Russian cricket. These insects live in burrows, crevices, cracks, and are found in fields and houses (different species). The cricket has a flat body and a large head. They say that if it chirps in the house, it prophesies sad news. The “song” of the house cricket, intrusive and loud, annoys everyone who loves the comfort of home.
There are a great variety of agricultural pests. Each specializes in a certain type of food: leaves, grass, fruits, vegetables. The locust insect eats all the greenery that comes along the way, and also grabs cereal crops. There is even a popular saying: “They swooped in like locusts.” Indeed, these insects swoop in in huge swarms and destroy everything in their path, leaving nothing to the vanquished.
Varieties
Using movable fasteners to fix the rafter legs to the Mauerlat is the only way to prevent roof deformation during the shrinkage of wooden houses. As a rule, sliders have a fairly typical design, consisting of a static guide base and an angle with a loop that moves along it. The following types of movable fastenings are distinguished:
- Open type. Sliding fastenings for open type rafters are a collapsible structure consisting of a guide, firmly fixed to the rafter leg, and an angle, which is attached to the mauerlat of the rafter frame. Different models differ in only 2 factors: the number of mounting holes, which can be from 1 to 5, as well as the power reserve. The minimum travel reserve of the sliding support is only 60 mm, and the minimum is 160 mm. The larger this parameter, the better the fastening protects against deformation, providing maximum mobility to the rafters.
- Closed type. The sliding support of the rafters is closed, unlike the open one, and cannot be assembled or disassembled. This is a one-piece, monolithic structure that is sold and installed immediately assembled. In this case, the corner attached to the Mauerlat has a loop through which, during the manufacturing process of the fastening, a guide strip is threaded and fixed to the rafters.
Characteristics of movable mounts
Another version of the sliding support design
Why increase the length of the rafters
As a rule, the rafters in their lower part rest on the top of the walls. In houses made of bricks and blocks, the above-mentioned Mauerlat is used for convenience. There is no need for it in wooden buildings. The rafters are fastened directly to the walls.
Let's say that the rafters will not be extended, and the roof will be laid, only slightly extending beyond the plane of the vertical structures of the house or outbuilding. In this case, moisture will drain from the roof directly onto the walls, which will lead to the following negative consequences:
- the wall material will get wet, allowing moisture to pass into the premises, which will certainly lead to the formation of fungus and mold, the activity of which is not beneficial for humans;
- Overmoistening contributes to the rapid destruction of wall material.
- Repeated cycles of freezing and thawing have a similar effect on the frame of a house.
All of the above led to the need to extend the edge of the roof beyond the walls by 45-60 cm in accordance with the existing GOST. Thanks to this, these negative aspects will be eliminated.
Gigantic, leisurely
The largest locusts on the planet live in the humid tropics. The size of females reaches 18 cm, weight - more than 10 g , males are usually slightly smaller. The diet of these insects consists not of cereal crops, traditional for the family, but of herbaceous shrubs and tree branches. The habitat of the insects is northern South America.
The color of males is brighter than that of females; the upper part of their bodies is bright pink, with a general green-brown color of the bodies . But the attractive appearance is deceptive - in a field, a swarm of such giants can eat several thousand tons of crops.
Interesting! This locust is leisurely, it jumps little and practically does not fly, slowly crawling from branch to branch.
Giant locust photo below:
A few words about migratory “Asians”
Separately, it is necessary to say about the Asian migratory locust. This type of insect is capable of daily absorbing an amount of food equal to the volume of feed for two sheep . It is incredibly difficult to fight the “Asian” - before raiding the fields, it forms complex nests in hard-to-reach thickets in swampy areas. You can defeat Asian guests only in the following ways:
- chemistry;
- burning;
- digging.
Locusts are sometimes called the jaws of the wind, and this completely reflects their essence. In regions where locust outbreaks are a frequent event, this phenomenon is described as a black cloud rapidly approaching, leaving only bare ground after disappearing. Therefore, learning to effectively combat this natural scourge is so important.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Interesting Facts
Among the features of the structure and life of locusts, many interesting facts can be identified:
- Due to the fact that the insect has well-developed hind legs, it can move a distance twenty times its body size in one jump.
- When eating, locusts eat everything that is colored green. As soon as food that has greenish tints runs out in a closed room, the locust begins to eat its relatives if they are green in color.
- Insects can fly over vast spaces without landing - up to four hundred kilometers. The longest flight of a swarm of locusts is from the African continent to the islands of the Caribbean Sea. A herd of locusts walking on foot covers an area of twenty kilometers during daylight hours.
- 7,000 tons of citrus fruits were swallowed in 5 days by a community of locusts that attacked an orange plantation in Morocco. Amazing gluttony - one ton per minute.
- Locust is an insect that inhabits all continents of the globe, with the exception of Antarctica. This is due to harsh climatic conditions and a complete lack of food. But an interesting fact is that they are not available in North America. The last known locust outbreak on the continent was in 1875.
- The most unusual way to fight locusts was recorded in the 15th century in France. The judge who was considering the case of damage to the vineyards by insects made a decision to allocate them a plot of land, which the pests were strictly forbidden to leave.
- Locusts are on the menu of many peoples of the world. These insects are eaten in thirty-six countries located on the African continent, twenty-nine Asian countries and twenty-three countries on the South American continent. Research has proven that locusts are a nutritious food that can replace meat, they are low in fat and high in vitamins.
There are no similar entries.
Spiny devil, 70 mm
The appearance of this grasshopper is striking, but it is thanks to its unusual needles that it can protect itself. It received such a terrible name precisely because of its unusual and intimidating appearance.
It is completely covered with needles. If predators or birds try to get close to it, it begins to wave its front legs and threaten with sharp spines. You can meet him along the Amazon and listen to the serenades he sings throughout the night.
Spiny devils feed on plant foods, but are not averse to eating other insects. It reaches 70 mm in length and is enough to repel its opponents. Also, to scare off his opponents, he came up with a cunning plan. When he sees that a predator is approaching him, he sharply raises his hind legs, which are brightly colored, and while the predator comes to his senses, he quickly crawls away.
Decorative options
Since the underside of the roof canopy is visible, the desire arises to make this part of the structure more decorative. There are possibilities for this. You can simply round the limb of each filly, or you can make their bottom curly throughout the entire visible area.
Using a jigsaw you can actually make shaped cutouts in the middle part of the boards. Here you need to know when to stop and not overdo it with too many of them, which can weaken the structural strength of the fillies.
For greater decorativeness, it is advisable to cover visible wooden elements with oil paints or colorless varnish to preserve the texture of the wood.
Reproduction
The males begin the love games of locusts. They secrete a special enzyme that can attract females. Jumping onto the female, the male deposits a spermatophore at the base of the female's ovipositor. This process can take up to 14 hours. After fertilization, the female locust lays eggs in the ground or on fallen leaves, enveloping them in a special liquid that freezes and hardens. Thus, the clutch is protected throughout the entire period of egg maturation.
Each locust cocoon contains from 50 to 150 eggs. The female lays from 6 to 12 clutches during her life. There can be up to 2000 cocoons per square meter. The offspring of locusts go through three stages of development: egg, larva, and adult. After winter, larvae emerge from the eggs, similar to adult locust insects only without wings.
Forty days after five molts, a full-fledged locust individual develops from the larva, capable of producing new offspring. The lifespan of the pest ranges from 8 months to 2 years.
In warm regions and subtropics, locusts develop throughout the year. After 14-16 days, a new generation appears, ready to actively move and reproduce.
Differences from nearby species
If you look at a photo of a locust, you can see that the insect looks very similar to a grasshopper, but they belong to a different order. Grasshoppers - to grasshoppers and long-whiskered, and locusts - to locusts and short-whiskered. The difference is also that the pest has shorter and less strong limbs. There are differences in lifestyle:
- grasshoppers are predators, locusts are herbivores;
- long-whiskered - nocturnal insects, short-whiskered - daytime;
- grasshoppers lay eggs on plants or under the bark of trees, while locusts lay eggs in the ground.
What is a filly on the roof
The filly is an element that is present on the roofing frame. The purpose of this element is to lengthen the rafter leg, which rests on the mauerlat of the structure, made of brick or blocks, and is located on the top frame of the structure made of logs or beams.
To put it simply, a filly in a rafter system is a piece of board used as a continuation of the rafter system, resulting in an overhang on the roof. As a rule, this element is suitable for the rafter system in cases where the rafter leg does not have the required size, which prevents the formation of an overhang.
To install fillets on the rafter system, it is recommended to choose boards whose cross-section is much smaller than that of the boards suitable for the rafter system. In addition, thanks to this approach it is possible to significantly facilitate installation work.
The use of this material in the rafter system can significantly facilitate installation work on the construction and further repair of the roof frame. In addition, it is possible to significantly reduce the level of load on load-bearing walls and foundations.
This is due to the following:
- since the length of the rafter leg will be much shorter, it is not necessary to provide for an overhang of 40-100 cm beyond the plane of the walls for further arrangement of the overhang, as a result the structure is quite light, short and not so expensive in cost;
- installation work is carried out on boards that are thinner compared to the building material suitable for arranging the rafter system, as a result the weight of the structure becomes much less;
- if necessary, it is possible to quite easily align the line at the overhang, and if an error is made in the construction, then it will be enough to replace this element;
- If during operation the support of the eaves overhang begins to rot, then it will be enough to replace the damaged element rather than carry out repair work.
In addition, it is worth considering that fillies in the rafter system can be used during the construction process as a decorative element. If necessary, this product used in the rafter system can be given any shape, making it as decorative as possible.
Attention! For a better understanding, it is recommended to look at what the fillies on the roof look like in the photo.