On a warm May day you can see a large wasp buzzing as it goes about its business. This is a common hornet - a representative of the family of social wasps. Despite its impressive size, it is not aggressive. Vespa crabro or hornet wasp prefers to feed on fruit juice and other sweet foods. Insects live in large families with a constant hierarchy. The head of the colony is the queen - the only female capable of laying fertilized eggs. The purpose of working females and males is to serve the queen and the growing larvae.
Hornets description
Hornets belong to the genus Vespa (wasps). Hornets - are the largest and most aggressive representatives of the wasp family, the length of the largest species reaches up to 5.5 cm. There are only about 20 species of hornets in the world. Most live in tropical Asia, but the insects are also found in Europe, Africa and North America, where the European hornet was introduced by humans. The venom of some hornets, such as the Asian giant hornet, is extremely dangerous and the sting can be fatal. The hornet is not aggressive and is unlikely to bite unless you attack it or its nest.
Harm or benefit of hornets
Hornets are often considered pests, especially when they nest near people, because... they will aggressively defend their nest if they feel it is in danger.
Hornets are quite dangerous insects, for example the Asian giant hornet is considered the most dangerous arthropod on the planet. When in danger, the insect releases a special “smell” that attracts other hornets. Hornets can attack humans due to the characteristics of perfume.
Hornets cause particular harm to beekeepers, destroying all the bees in the apiary.
One hornet can destroy up to 10 bees. When one hornet finds a bee colony, it leaves a special scent that attracts other hornets. (There is an opinion that hornets destroy only sick bees, although this fact has not been proven.)) There are cases when bees defeat a lone hornet in a battle, surrounding it.
Hornets whose nests have been destroyed or poisoned are considered especially dangerous. In some countries, it is prohibited to destroy hornets; they are believed to be beneficial for the ecosystem.
What hornets look like, their size and structural features
Queen
Hornets have two pairs of wings and six legs. The insect has large and strong jaws. Females are much larger than males. Female hornets have 12 antennal segments. In males 13. Hornet venom contains a large amount of acetylcholine (5%)
Hornet sizes
Hornets vary in size depending on the species.
- Adult European hornets (common hornet) are approximately 2.5-4.5 cm long.
- Eastern Hornet. Dimensions 2.5-3 cm.
- Dybovsky's Hornet - no more than 3.5 cm
- Asian giant hornet - 5.5 cm. Wingspan up to 8 cm.
Health care
In the event of a hornet attack, as first aid to eliminate swelling and irritation, you can use creams whose active ingredients are lidocaine, hydrocartisone, for example, Levomekol, Hydrocortisone ointment, ADvantan, Akriderm.
Fenisti, Suprastin, Tavegil are excellent agents with antihistamine action - taking such drugs makes it possible to reduce allergic manifestations. If blood pressure drops, the patient should take Cordiamine.
If you take into account the home first aid kit, you can alleviate the victim’s condition with the help of:
- Soda. Wet your finger in water, then dip it in baking soda, then rub the affected area so as to completely cover the affected area.
- Juice of lemon, dandelion, plantain. Apply this liquid to the bitten area to relieve itching and swelling.
- A slice of apple, onion. They can be applied to the bite area to alleviate the general condition.
How to distinguish a hornet from other insects
Hornets are often confused with other insects, such as wasps and bees.
The difference between hornets and other wasps
Wasp
The nest of hornets is larger in size than that of wasps. Wasp nests can often be found close to or underground, or inside a loose structure, such as between the inside and outside walls of a house or even inside an old sofa.
If the nest is significantly larger and what you believe contains thousands of members, you are most likely seeing a wasp nest.
Unlike wasps that are yellow and black, the hornet has more colors in its color and has orange and brown shades.
Hornets' heads are larger in proportion to their body size compared to other wasps, and the head structure is slightly different.
European hornets have a reddish-brown head, thorax, first abdominal segment and legs.
Be aware of the difference in size between a hornet and a wasp. One of the main differences between a hornet and a wasp, which is easy to recognize both up close and at a distance, is size. The European hornet grows up to 4 cm in length, and the maximum size of the wasp is 2.5 cm.
Note the large width of the head behind the eyes, this region is wider in overall body size in hornets than in other members of the wasp family.
Differences from bees
Bee
The hornet, like the wasp, has a thin waist between the thorax and abdomen, this distinguishes them from the bee family, which has a thick waist between the thorax and abdomen.
Pay attention to the wings (whether the wings are folded along the length of the body), because members of the wasp family fold their wings along the length of their bodies when resting, but bees do not. There are no serrations on the hornet's sting.
A bee sting has serrations; when bitten, the sting is torn out of the bee's abdomen and the bee dies. And hornets, like other members of the wasp family, have a sting without barbs, which allows them to sting repeatedly without losing the sting. The hornet's sting is longer than that of a common wasp or bee sting.
Nutrition
Hornets can be called omnivorous insects; they are dexterous hunters, but at the same time lovers of plant food. What do hornets eat? Adults have a wide gastronomic diet:
- nectar;
- juice of ripe soft fruits (peach, pear, apple);
- berries - raspberries, blackberries, strawberries;
- aphid secretions;
- honey.
Predatory insects, except for the queen, eat their relatives only at the larval stage. Working individuals with enviable diligence shuttle between the nest and the hunting site, bringing spiders, centipedes, and worms to their offspring. Hornets cut up prey with powerful jaws, feeding protein to the growing larvae and queen, which requires strength to lay eggs. Large wasps often attack individual bees and hives. One large individual is capable of tearing apart up to 30 honey plants.
Interesting fact. Hornets do not have a long period of sleep; they are active at any time of the day. To rest, they simply freeze for a few minutes. Numerous hungry larvae, the number of which sometimes reaches up to 500, require a lot of food. A family of predatory insects is capable of destroying up to 0.5 kg of garden pests daily.
Features of the life of hornets
Hornets are social insects, so they can unite when attacking a victim.
The nests have a strict hierarchical system, with queens dominating hornet hives and being the only females capable of reproducing. Queens lay eggs. Most other hornets are asexual workers who perform important social duties such as building the hive, collecting food, feeding the young, and defending the colony.
There are few males and they have only one role - mating with the queen. Males usually die soon after completing their sexual task.
In colder climates, hornet nests are abandoned in winter; young queens and their eggs survive by finding sheltered areas under tree bark or homes.
In the spring, such a queen will lay a new nest, and soon her young will become workers and take over the duties of the new hive, leaving the queen to breed.
She will produce more workers to expand the hive and before she dies, she will produce a breeding generation of new queens and males (drones) to start everything over again.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Hornet
Hornet wasps are quite prolific insects. However, not all females are fertile. Uteruses are capable of reproducing offspring. They are usually large in size. It is the females who become the founders of the hornet family; they begin the construction of the house (nest). Before laying eggs, the queen, with the onset of the first heat, searches for a safe, convenient place to build a house. She lays eggs after building the first few hundred.
Further, her responsibilities include searching for food and caring for future offspring. It takes some time for the eggs to mature. First, larvae emerge from them, then adults. When new members of the community become like adult hornets, they take over all the responsibilities of their parent. The queen continues to lay eggs, and the worker wasps get food, guard the house, complete its construction, and care for the larvae.
After four weeks, new hornets emerge from the larvae. They usually kill the queen due to her inability to reproduce any more. Some individuals simply kick her out of the nest. Representatives of the genus living in the European part do not live long. Their total lifespan is only a few months. Only queens have a long life expectancy. They are able to spend the winter in suspended animation.
Hornets can give a good rebuff to their enemy as a whole flock. To protect themselves, they know how to quickly mobilize forces. In case of danger, this animal releases an alarm pheromone. If such a signal is noticed by his relatives, then the attacker faces real danger.
Hornets nests
Hornets nest
Insects create nests by chewing wood into papery building material.
The color of the nest may vary:
- brown
- yellow
- yellow-white
- beige
Often nests can be seen on roof eaves and under decking, tree hollows, birdhouses, caves, and attics. Outdoors, hornets usually build nests high above the ground, such as in trees, on utility poles, or in dense bushes.
Most often the nest is discovered in the fall when the leaves have fallen, by which time most of the hornets will be dead or dying, leaving only the queen to hibernate and survive the winter.
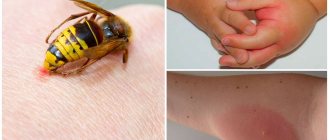
Reaction to a hornet sting
If someone is stung multiple times or has a severe allergy to insect venom, systemic reactions may occur that can affect the entire body. Typical symptoms and reactions to bites:
- Strong pain
- Redness
- Swelling around the bite site
If a person is allergic:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Cold extremities
- Blue discoloration of the neck, eyelids, face, ears
- Attacks of suffocation
- Swelling of soft tissues
- Red spots on the body
- Loss of consciousness
First aid
No benefit of a hornet can cover the harm that such insects can bring to humans. Since some individuals have an individual intolerance to poison, quick and consistent action is required after an attack.
Namely:
- The first thing to do is to remove the poison and sting particles - this must be done by lightly pressing on the affected area.
- Next, wash the wound with soapy water, alcohol or potassium permanganate.
- The patient must take an antihistamine. In case of a bite in the neck, mouth, or severe swelling of the mucous membranes, which makes breathing difficult, the victim needs to be injected with an antidote.
- If your body temperature rises, you need to take an antipyretic drug and drink plenty of water.
- In case of severe pain, the victim can be given a painkiller.
- To reduce the risk of rapid spread of poison throughout the body through the bloodstream, you need to apply ice, something cold or moistened sugar to the already treated wound.
- If you have difficulty breathing, you must open every window in the room, unbutton all items of clothing that are squeezing the victim, and remove your collar and jewelry.
- When the condition improves, the patient should be offered warm tea and a blanket.
- If signs of anaphylactic shock appear while waiting for an ambulance, place the patient on a hard surface, and also carefully monitor that the victim’s tongue is not stuck and there is access to oxygen.
It should be noted that it is forbidden to give aspirin to patients, since it has the ability to thin the blood, thereby facilitating the process of spreading the poison through the blood, which will provoke complications.