Your questions:
- Where does mold come from?
- How many days does it take for mold to germinate?
- At what point does bread become unhealthy?
- If a person eats moldy bread, will there be any consequences for the body?
- Can mold occur on both wheat and rye bread?
- Mold can be black, white, green... Which is the most dangerous?
- Is it true that sliced bread is the first to go moldy?
- What conditions are needed for mold to grow on bread?
- How to properly store bread at home to prevent it from becoming moldy?
- Why does bread in a plastic bag mold faster than bread in paper or under a towel?
Buy quality bread
The reasons why bread gets moldy are quite simple. Mold on bread forms:
- improper storage of bread. If the finished product is stored in a humid and warm room, these are the best conditions for the growth of fungus;
- violation of sanitary standards and temperature conditions. If the bread is baked incorrectly, you get mold.
- poor quality preparation. Move away from the traditional recipe to minimize costs - get mold on the bread. If you used low-quality products or any substitutes, the result is the same. Low-quality bread becomes moldy much more often and faster than bread baked according to the correct recipe.
Where does mold come from?
The air on the street, at home and in the office, in the air of any industrial premises (except for those where special preparation and sterilization of the air is carried out) contains a wide variety of microorganisms, including mold spores. Bread molding is a process that begins when mold spores enter the surface of the product from the air. Once in favorable conditions, the dispute begins to germinate.
Once the mold spores have sprouted, the product is no longer suitable for consumption.
2. How many days does it take for mold to germinate?
The rate at which visible signs of mold appear depends on many factors: bread storage conditions (humidity, temperature, presence and type of packaging), the type of bakery products and the method of their preparation, the sanitary state of production, as well as the type of mold and its physiological characteristics.
Olesya Savkina
Leading Researcher at FGANU NIIHP, Ph.D.
– Our model experiments show that when bakery products are forcibly infected with mold, the shortest period of time before signs of mold appear is:
- 24 hours – for wheat bakery products prepared in an accelerated way, without dough and sourdough;
- 36 hours - for wheat products prepared using long-term technology - for example, using sourdough or sourdough;
- 40 hours – for rye and rye-wheat bread.
Wheat and rye bread do not become moldy within 24 hours after baking.
3. At what point does bread become unhealthy?
To understand at what point bread becomes dangerous, let's try to understand the mechanism of formation of this type of microbial spoilage. If the bread is infected with mold spores, the germination of the invisible mycelium of the fungus inside the bread and the formation of a “fluffy” colored colony on the surface visible to the eye occurs simultaneously. Until visible signs appear, that is, until a small, 1–1.5 mm in diameter, most often first white, slightly fluffy “dot”—a colony—appears on the surface of the bread, the bread is safe.
If mold is not visible, you need to smell the bread.
A small, nascent mold colony is very difficult to notice. Therefore, you also need to focus on taste and smell. If the product has a slight rancid or moldy odor, this indicates that the process of microbial deterioration has already begun. And it is better not to eat such bread.
4. If a person eats moldy bread, will there be any consequences for the body?
A moldy product is dangerous because mold fungi produce substances that can have an acute toxic or carcinogenic effect. Evidence suggests that moldy foods can pose a serious threat to a person's weakened immune system. They can cause diseases such as aspergillosis, bronchial asthma, as well as the development of cross-allergy to a number of products.
Simply removing the visible part of the mold colony from the surface of the bread is not enough.
Under a microscope, you can see that the mold consists of long, thin, intertwined threads (mycelium) that run throughout the product. They can produce substances hazardous to human health.
What to do if you bought a low-quality product and got food poisoning, read HERE
.
Plant nutrition
There is a belief that even spoiled bread should not be thrown away. But not everyone will agree to eat even a fried or baked moldy product. Therefore, housewives are racking their brains over where to put the contaminated food .
Flour products usually contain yeast. They are used to fertilize the soil before planting. The substance contains B vitamins and carbon dioxide. If a lot of moldy bread has accumulated, then the infected crusts are cut off and broken into small slices. Then prepare a solution consisting of several ingredients:
- two armfuls of stinging nettles;
- 2 kg of sugar or old jam, berries from compotes;
- 1 stick of yeast;
- 4−5 kg of bakery products.
Modern standards set for baked baked goods state a three-day shelf life. After three days, in theory, the bread will begin to go stale, and after another day it will turn into a stale cracker. But in reality, it may turn out that the bread simply does not survive to the stage of breadcrumb formation. Within a day, bread can become covered with unpleasant-smelling and shudder-inducing mold.
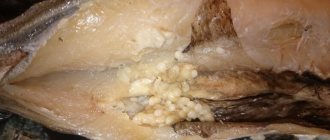
Mold on bread can be different: gray, black, white and even pink. Since childhood, our parents instilled in us a very respectful and careful attitude towards bread. But what to do if mold covers the bread: throw it away, cut it off and serve. How dangerous is mold to the human body? Let's understand these difficult but pressing issues.
Can mold occur on both wheat and rye bread?
Any baked goods, especially when stored packaged in plastic film, are an ideal place for mold to develop. It affects products made from both wheat and rye flour.
An exception is products with low humidity: dryers, crackers, straws, crispbread, bread sticks. All of them are less susceptible to mold due to low humidity, but if stored improperly in a damp room and if the integrity of the packaging is damaged, mold may develop on these products due to dampness.
If you eat something moldy, you need to look for an antidote.
Enterosorbents, as a rule, are safe and are quickly eliminated from the body along with toxins, without reducing the fluid content. Until recently, wood derivatives were mainly used - activated carbon, lignin-based preparations - polyphepane and cellulose. Their effectiveness reduces “promiscuity” - they remove everything from the body, including vitamins and beneficial microelements.
odorless and tasteless drug Enterosgel The gel is stirred in water or chewed and washed down with water at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 0.5-1 glass of water. Course – 3-10 days.
Polysorb is similar , 1 packet of which contains 1 teaspoon of enterosorbent. This single dose is poured into 100 ml of water and drunk 1 hour before meals. The course is 3-5 days, taken only in the form of an aqueous suspension (so as not to accidentally inhale the drug if you pour it on the tongue).
Carbon-mineral enterosorobent Ecoflor not only collects toxins, but also restores beneficial intestinal microflora, since it contains bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. It is taken 2-3 times a day 10-15 minutes before meals with a small amount of water (30 ml) for 5-14 days. The package contains 5 g of the drug, that is, a single dose.
A very interesting drug, Rekitsen, is based on wheat bran fermented with wine yeast. Entering the intestines, recicene binds toxic substances and at the same time enriches the body with dietary fiber, amino acids, enzymes and pectins. Dosage – 1 tbsp. spoon three times a day, course - at least 4 weeks.
Mold can be black, white, green... Which is the most dangerous?
Bread affected by mold is covered with a fluffy coating of various colors: white, gray, green, yellow, bluish, black. Most often, green, inky (blue-green) and black mold develop on bread.
The most poisonous are yellow mold (Aspergillus flavus) and black rot (Aspergillus fumigatus).
- Yellow mold
produces a powerful mycotoxin, aflatoxin. It can cause damage to the body, in addition, the fungus itself, when entering the body, causes severe damage to the lungs and can even lead to death. - Black rot
produces the alkaloid fumigoclavine, which can cause severe intoxication, has hemolytic and antigenic effects and pronounced allergenic properties, and causes aspergillosis.
“However, in addition to these molds,” notes Olesya Savkina
, “several dozen more types of molds form mycotoxins and substances toxic to humans.
Of course, there are also safe types of mold that people have learned to use for food production, for example, for gourmet cheeses - Dorblu, Brie, Camembert. Such “cultured” mold is considered safe, but allergic reactions to the microbial protein are possible in people with a predisposition.
Any mold is unacceptable in baked goods.
Possible consequences
Long-term consumption of foods colonized by mold fungi leads to changes in the blood formula (the number of red and white blood cells decreases), the appearance of signs of damage to the central nervous system (insomnia or drowsiness, confusion, delirium, hallucinations), and in severe cases, death is possible.
When living in rooms affected by mold, mycotoxin can cause allergic diseases, immunodeficiency conditions, aggravate the course of various acute and chronic pathologies, and with prolonged exposure, accumulating in the tissues of internal organs, stimulates the development of malignant neoplasms.
What conditions are needed for mold to grow on bread?
Bread comes out of the oven sterile, but during transportation and storage, the surface of the bread can become contaminated with fungal spores. As mentioned above, mold spores are ubiquitous in the air. They are activated and germinate as soon as they find conditions favorable to them - a moist environment in which nutrients are present.
Humidity in the kitchen is one of the causes of mold.
9. How to properly store bread at home to prevent it from becoming moldy?
At home, bread is usually stored in the kitchen, where air humidity can fluctuate greatly. It depends on the ventilation system, the area of the kitchen and the outflow of vapors above the stove. That's why:
- Bread is best stored in a dry, dark place, away from sources of dampness and heat. For example, in a bread box, at a temperature of plus 20–25 ° C and air humidity not higher than 70%, away from sources of strong heating or cooling.
- Make sure that the bread is not near surfaces where condensation forms. It is not recommended to place the bread bin on a window or in the stove area, where temperature and humidity fluctuations are greatest.
- If bread is stored in plastic packaging, make sure it is not exposed to the sun. Under direct sunlight, condensation begins to form inside the package, and this is favorable for the development of mold.
For information
When cooking on the stove with insufficient ventilation, the air humidity in the kitchen may exceed 70%. The exact humidity in the room is determined by a special device - a hygrometer.
10. Why does bread in a plastic bag grow mold faster than in paper or under a towel?
If you store bread in a plastic bag, and even tightly closed, there is nowhere for the moisture to evaporate. And inside the hermetically sealed polymer packaging, fairly “comfortable” conditions are created for the development of mold. Bread in paper packaging or without packaging molds more slowly, but stale faster.
Product processing
Despite the recommendations of biologists, housewives are finding ways to treat spoiled bread. The mold that has formed on the crust of the product is cut off along with the crumb at a distance of 1 cm from the affected area. You cannot eat contaminated food raw; drying it, rubbing it with vinegar and vegetable oil will not help.
Nothing can be done with a whole loaf, since the fungus has spread over its entire surface. If you bake it in the oven, the mold will still remain inside the crumb. Therefore, bread with damaged areas cut off is divided into thin slices. Then they are fried in a small amount of vegetable or butter. The degree of cooking depends on how badly the product has been damaged. Sometimes you have to fry the slices until they become croutons.
But it’s better to bake the peeled and cut loaf in the oven. The pieces are first rubbed with spices - salt, dried herbs and garlic. During the cooking process, all harmful microorganisms die, as they cannot withstand very high temperatures. The result will be delicious crackers or croutons.
If the bread is completely covered with mold, the product has a pronounced unpleasant odor, gray or green color, then no treatment will help. In this case, you can cut off the infected areas and dry the loaf a little in the oven. It is then crushed and fed to the birds. Their body will digest such food.
Bonus for readers: we answer a subscriber’s question about lavash
“Good afternoon, I bought lavash yesterday, but this morning it became moldy and I had to throw it away. But if mold grows for several days, does that mean that if I had eaten it yesterday, I would have eaten pita bread that was already affected by fungi?”
– If yesterday there was no mold, no visible signs, no changes in smell or taste, then at that time the product was safe for consumption. If there was even a speck of mold on the lavash that you might not have noticed, alas, the lavash is already in the risk category, says Olesya Savkina
. – Our long-term research shows that, on average, visible mold colonies appear on the surface of baked goods within 3–7 days. In conditions favorable for mold, this period can be reduced to 1–2 days. Lavash is one of the most susceptible products to mold. But since it takes at least 24 hours for mold to develop from spores on the surface of pita bread, we can say that the product was safe the day before. Once the mold has sprouted, the product becomes unfit for consumption.
Take the TEST
and find out
what kind of furfural you are
. No joke, it helps you understand how safe what you eat is.
Thank you for reading this text to the end. Follow the news, subscribe
mail.
When quoting this material, active link to the source
required.
Tips for proper food storage
The more often you inspect your refrigerator, the less spoiled food there will be. Try to check the contents of your refrigerator at least once a week. If, for example, you notice a couple of moldy berries in a container with strawberries, then do not rush to get rid of the sweet delicacy completely; remove only the spoiled berries; simply rinse the rest under running water.
Food will be fresher in a refrigerator that is regularly maintained. Even one wash a month will be enough to avoid the spread and even the appearance of mold.
Of course, an important factor is the correct choice of products and careful reading of the expiration date line. The fresher the product you buy, the better and longer it will be stored.
Be extremely careful when purchasing products! Be as careful as possible when choosing a manufacturer you can trust! Take care of your health!
Bread is a staple on the table, without which almost no meal is complete, especially if it is freshly baked. Today, few people resort to baking on their own, preferring ready-made store-bought products. In mass production, not all required technologies may be observed. Therefore, unfortunately, it often happens that already 2 days after production, a moldy coating forms on it. This article will tell you why this happens, what needs to be done about it, and what the danger is.
To eat or not to eat?
The question of whether it is possible to eat noble cheese with white or blue mold has not been relevant for a long time. This category of products has many admirers; there are also those who do not understand their taste. But no one would think that expensive cheese, covered with a velvety moldy coating, is spoiled.
Ordinary moldy cheese is a completely different matter. Plaque on it means that pathogenic fungi are developing on the surface, and possibly inside, and the product has begun to deteriorate. The same is true if plaque is found on sour cream, butter, yogurt - products that should not come into contact with mold in any way.
It is difficult for a non-specialist to say specifically what mold can be eaten. Judging by the same cheeses, you can eat white and blue mold. But this division is too general. For example, some toxic molds belonging to the genus Aspergillus look like relatively harmless white mold, but grapes or tomatoes with such mold should not be eaten. In turn, some types of green mold are quite harmless and are used in the food industry.
Of course, everyone assesses the risks themselves and decides which products to consume. If one person does not even think about whether it is possible to eat moldy bread, another will cut out the spoiled piece and calmly eat the rest. Many housewives do not see anything wrong with guests eating pickles or mushrooms from which mold has been washed off.