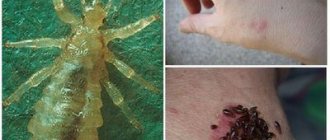
Cruciferous flea beetles are one of the most dangerous pests of cabbage crops and other plants. To cope with them, you need to carry out a set of measures and use all the means available in your arsenal.
The cruciferous flea beetle, or cruciferous flea beetle, usually appears on the leaves of radishes, cabbage, radishes, horseradish, watercress and other members of the Brassica (or Cruciferous) family. You should not expect that this small aggressor attacks exclusively home garden crops - in the wild, the flea beetle feeds on rapeseed, mustard, shepherd's purse and other Cruciferous plants. A massive colony of beetles can destroy an entire crop in a very short time.
What does a cruciferous flea beetle look like (description and photo)
The cruciferous flea beetle is a shiny black bug that damages plants of the cruciferous family. Favorite plants for pests to eat are cabbage seedlings, radishes, radishes, turnips, arugula, etc. Heat-loving beetles prefer to feed on the apical and illuminated leaves, the damage increases in hot, dry sunny weather. Then their gluttony increases significantly.
By June, the aggressiveness of pests decreases. But here comes the second dangerous period - the time of reproduction. Females begin to lay eggs in the surface layer of soil. The eggs take approximately 12 days to develop. The hatched larvae feed on the roots of cruciferous crops and do not cause much harm. The development of larvae lasts 15-20 days. Pupation also occurs in the soil and after about 2 weeks a new generation of beetles is born.
Having emerged on the soil surface in the second half of July, the bugs begin to feed on the leaves of already strong plants. Of course, the harm from them during this period will be much less. They can damage flowers and seed fruits of vegetable crops. However, if no measures are taken to destroy the pests, with the onset of cold weather in the fall, the beetles return to the soil for the winter. And the breeding cycle repeats next spring. Look at the photo to see what the cruciferous flea flea looks like.
Harmful cabbage aphid
An equally dangerous pest for cabbage is the cabbage aphid. It is a very small insect two millimeters long, gray-white. Aphids reproduce pathogenetically, laying small elongated eggs without fertilization, which overwinter on stalks, weeds, and cabbage seeds. In the spring, larvae appear and develop into wingless insects, which again give birth to larvae. After this, females with wings appear, which in mid-summer move to the cabbage from the weeds and begin to reproduce there, each producing 40 larvae.
When aphids multiply en masse, the leaves of cabbage crops are completely covered with aphids, sucking the juice and discoloring the leaves. In this case, the latter curl and the plant stops growing and producing seeds. Control of cabbage pests - aphids - is more effective before July, when the movement of winged individuals occurs.
Cruciferous flea flea - how to fight it using folk methods
Since pest beetles prefer to feed on young leaves of cruciferous crops, the fight against them must begin literally with the appearance of the first shoots. The real danger awaits the seedlings when the first seven-lobed leaves appear on them. Do not wait for fleas to appear, they can instantly jump over a number of growing weeds, start fighting immediately.
Remove all weeds from the bed where radishes, cabbage or turnips grow, loosen the soil between the rows. And then cover the seedlings with a light sponbond, securing it on the sides with stones or boards so that the covering material does not blow away in the wind. The sponbond will protect the seedlings from insects, and water will pass through it well during watering and rain, so the plantings will not suffer from lack of moisture.
If there is no covering material, plantings are dusted using
- tobacco dust,
- wood ash,
- a mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust,
- ash and street dust,
- a mixture of cement powder and street dust.
It is best to pour the prepared powders into a sieve or one layer of gauze, and then sprinkle the plants from them. It is better to treat plantings early in the morning, when the plants remain damp from dew or evening watering. Dusting is not carried out on dry grass. When sprinkling dry foliage, the slightest wind will blow the powder off the leaves, and the treatment will not give any results.
The use of various repellent plants shows good results. Thus, the aroma of marigolds, calendula, garlic, coriander, dill, and wormwood planted next to cabbage, radishes or turnips will repel pests. Moreover, the effect will also be from the dry grass of these plants laid out next to cruciferous crops.
Prevention
Cruciferous flea beetles overwinter:
To prevent the appearance of these pests, you should:
The famous summer resident Oktyabrina Ganichkina advises, after sowing turnips, rutabaga, and other cruciferous crops, to sprinkle dry mustard, ash or ground black pepper on the beds. Then the cruciferous flea beetles will leave this area. If you are planting cabbage seedlings, spray them with a solution of liquid soap and then sprinkle with sifted ash. This way it will better stick to the cabbage leaves and protect them from pests.
You can also use tobacco powder.
The famous gardener and garden designer Olga Voronova advises thinking about mixed plantings. An experienced summer resident says that cruciferous flea beetles do not like the smell of marigolds, calendula, and nasturtium, so you need to plant these flowers near the cabbage seedlings.
This pest also cannot tolerate the aroma of dill, cumin, onions, coriander, garlic, tomato tops and potatoes. Therefore, place some of these plants near the planting of cruciferous crops.
If dangerous bugs do settle in the plantings, then it is necessary to take control measures. If the degree of damage to plants is small, it is better to use traditional methods; if the scale of the harmful activity is global, then chemical methods may be required.
How to get rid of cruciferous flea beetle on cabbage and radishes
There are other folk ways to combat fleas. After all, chemicals cannot always be used. For example, radish is an early ripening crop; the use of chemicals is not advisable for it. Therefore, take into account the products that are used to spray the plants.
- Birch tar . For 1 liter of water add 1 tsp. tar, shake well in water. Since birch tar does not dissolve well and settles on the walls of the watering can, experienced gardeners advise first stirring the tar with liquid soap, and then slowly adding water and only then spraying the plants.
- Ash infusion . Pour boiling water over the wood ash in a ratio of 1:3, leave to steep for two days, then strain and add liquid or soaked laundry soap, then spray the plantings.
- Garlic solution . Pass 1 cup of garlic and the same number of tomatoes through a meat grinder. Dilute the mixture with 10 liters of water, strain, add 1 tbsp. l. liquid soap and start spraying.
- Solution with dandelions . Grind 500 g of dandelion leaves and roots in a meat grinder, dilute the mixture in 10 liters of water, strain. Add 1 tbsp. l. soap The solution is ready for use.
How to fight cruciferous flea beetle with vinegar
Pests do not like strong odors; the use of table vinegar is based on this property; it has a detrimental effect on bugs. If you take vinegar essence, then dilute it at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. essences per 10 liters of water. When using 9% table vinegar, it is enough to dilute 1 tsp. for 1 liter of water. Remember that you need to spray on dry foliage.
Ammonia to combat cruciferous flea beetle
To prepare the working solution, 1 tsp. ammonia is diluted in 1 liter of water, stirred and sprayed on the plants. The treatment is carried out on dry leaves. When treating with ammonia, in addition to repelling pests, you also fertilize. Ammonia is like a nitrogen plant.
A similar action - processing and fertilizing at the same time - is used when using a weak solution of chicken manure. The leaves, absorbing nitrogen fertilizing, will develop faster, gain strength, and become stronger. The coarsened leaves will no longer be suitable for the bugs and they will not eat them willingly.
Arugula: growing in a greenhouse
- This method of growing arugula is carried out in a pot with soil in which the salad will grow in the future, and in order for the soil to be as suitable as possible, it should be disinfected by calcining it in the oven or pouring boiling water.
- It is worth noting that it is quite possible to prepare a soil mixture with your own hands: to do this, take humus, sand and turf in a ratio of 2:1:2.
- Soil purchased from a specialty store (choose one that is suitable for vegetable seedlings) will also work.
- Arugula seeds should be immersed in advance for 2-3 hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Then we fill the container for future seedlings (depth - at least 10 cm) with a sterilized, thoroughly moistened soil mixture, spread arugula seeds on its flat surface (the recommended distance between them is 1.5-2 cm), fill it with sand (a layer of about 1 cm) and place our an improvised flowerpot in a lighted place, without covering it with anything.
- The first shoots can be seen after 3-5 days.
In the greenhouse
Caring for arugula seedlings in a greenhouse involves:
- Timely and sufficient watering.
- Loosening the soil.
When a pair of distinguishable leaves appears, they should be separated in twos and planted in peat pots or transplanted into a larger container, maintaining an interval of 10-15 cm from each other and 25-30 cm between rows. A similar “trick” during planting will allow you to grow arugula with leaves that are aromatic and piquant in taste.
Chemicals to combat cruciferous flea beetle
The use of chemical insecticides is sometimes not justified, since some crops have a short growing season. Chemicals can be used no earlier than 20 days before harvesting vegetables. If you notice more than 5-7 insects on one plant, then you can’t do without chemicals. And if you decide to use them, choose the most harmless ones.
The most effective and frequently used means:
- Actellik is a drug from the Swiss company Syngenta. The product protects plants well from many pests, including the Colorado potato beetle. Easy to use, just dilute the concentrated emulsion with water and the product is ready for use. Economical: one ampoule of the product (2 ml) is diluted in 2 liters of water; if the pest population is larger, the contents of the ampoule are diluted in 1 liter of water. The death of insects occurs after 10 minutes for 5-6 hours.
- Aktara is a contact-intestinal insecticide that begins to act on pests half an hour after spraying the plants, maintaining effectiveness for 3-5 weeks. Before use, 3 g of the product is diluted in 10 liters of warm water. The product does not accumulate in plants and fruits and is not addictive to insects. However, it is quite effective on other insects, so it is not used during flowering so as not to cause the death of bees.
- Intavir is a universal, inexpensive, effective drug - a tablet used to destroy a large number of pests. It is quite simple to use; you need to dissolve 1 tablet in a small amount of warm water, and then increase the volume of liquid to 1 liter and spray the plants with the resulting solution. During processing, the plant itself is not damaged, but the death of insects occurs as a result of paralysis, due to which the insect stops moving, feeding and dies.
- Bankol is a biological, low-toxic drug that quickly decomposes in the soil, but with its help you can get rid of pests in one treatment. The main active ingredient of Bankol is bensultap, a neurotoxin of annelid sea worms. This product does not accumulate in treated plants, soil or water. Before use, the product is first diluted in a small amount of water, then the volume of the solution is adjusted to 5 liters and the plants are sprayed. The drug acts on bugs through contact and through the intestines, the pests stop moving and feeding, and as a result die within 1-3 days.
Chemical treatment is carried out in dry, windless weather on dry foliage. If it rains within 1-2 hours after treatment, the treatment must be repeated. Also, do not water the plants immediately after treatment.
When using chemicals, always carefully read the instructions for use of the drug, dilute the drugs and work using protective equipment.
Identifying the pest
Cruciferous flea beetles are not like regular fleas. These insects were named so because they are able to jump a sufficient distance thanks to their hind legs. Insects are bugs with a body length of 1.8-3 mm.
Here are the types of cruciferous flea beetles that exist:
- blue;
- wavy;
- black;
- notched and others.
Each species of these insects is named so because of its color. They are called cruciferous because these bugs love to feast on plants from the cruciferous family.
These insects are also called flea beetles, as they prefer to overwinter, including in the soil. Pupation also occurs in the ground.
Earth fleas begin their harmful activities with the arrival of spring warmth. Then they crawl out of their hiding places and begin to feed on weeds from the cruciferous family. When gardeners plant seedlings, nimble insects move here. They gnaw numerous through holes in young leaves, and destroy the surface layer on older leaves.
Here are the crops that can be attacked by this pest:
- leaf mustard;
- various types of cabbage;
- swede;
- horseradish;
- turnip;
- salad;
- beet;
- alyssum;
- matthiola.
- turnip;
- radish;
- lefty
Flea beetles not only spoil the appearance of flowers and vegetables, but can also significantly reduce crop yields. Therefore, it is necessary to fight them, but we should start by preventing the appearance of the pest.
How to poison cruciferous flea beetle on strawberries
Some gardeners complain that the cruciferous flea beetle appears on strawberry bushes. Strawberries do not belong to the cruciferous family and the appearance of bugs on strawberry leaves only indicates that cruciferous plants grow nearby - radishes, turnips, cabbage. etc.
A fairly common reason for the appearance of pests on strawberries is the proximity to planted green manure - rapeseed and mustard. Since bugs are highly mobile and easily move from one plant to another, it is not surprising that pests are found here too.
But the voracious insect does not disdain strawberry leaves, eating both old and young leaves. In order to somehow preserve the harvest, if you find fleas on strawberry leaves, you need to urgently get rid of them. Since strawberries quickly begin to bloom and then bear fruit, chemicals obviously will not help. Therefore, it is better to use folk remedies: dusting with wood ash, tobacco dust, spraying with solutions of vinegar, ammonia, infusions of strong-smelling plants.
Signs of parasitism
The presence of cruciferous fleas in the garden is determined by the appearance and condition of the plants. First, even before the visible appearance of individuals, the leaves begin to wither despite abundant watering. This is especially noticeable if fleas are found on radishes or cabbage. Such leaf damage is associated with the appearance of parasite larvae and their impact on the root of the plant, which disrupts its normal functioning.
After the larvae hatch, ulcers and gnawing appear on the leaves. Depending on the type and number of fleas, it is even possible to completely destroy the leaf down to just the veins.
How to prevent the appearance of cruciferous flea beetle on plants
It is best to prevent the appearance of the pest in advance. Preventive measures are based on how the pest lives and reproduces.
- Fleas are most active in dry, hot, sunny weather. In cool, damp weather they are less active. Therefore, water plant seedlings and cabbage seedlings more often; pests do not like damp soil.
- To reduce damage from insects next year, dig up the area before winter as late as possible, literally before the frost itself. This will release overwintering bugs to the soil surface. If you dig up early, the bugs will go underground again and quietly overwinter there.
- In addition, it is necessary to observe crop rotation and plant cruciferous crops in a different place every year. When planning the beds, keep in mind that for cabbage, radishes, radishes, arugula, etc., allocate other places where cruciferous crops have not previously grown.
- In early spring, before planting seedlings and sowing early-ripening cruciferous vegetables, the beds must be kept clean, that is, weed them in advance. This will not create conditions for the bugs flying out of the ground to feed.
- Among cabbage, turnips, radishes, watercress, arugula, plant dill, garlic, coriander, caraway seeds, as well as marigolds and calendula. Their pungent smell will repel pests.
Arugula: growing on a windowsill at home
- It’s very easy to grow arugula on a windowsill at any time of the year. The soil for sowing seeds is taken the same, and it is disinfected.
- Holes are made in the sowing container to drain excess water, and it is filled with expanded clay (2-3 cm).
- Pebbles or broken bricks are also suitable, then a moistened soil mixture is poured in (the surface is leveled), after which the seeds are laid out in the top layer of soil, as when sowing seedlings.
- 4 days after planting the seeds, you can see the appearance of small shoots. When they grow up, plant them one or two in separate pots (the distance between the seedlings is approximately 20 cm).
In a pot
- Do not allow flowers to bloom in your “vegetable garden” (the inflorescences must be cut off) - this type of arugula is not suitable for food due to the leaves becoming stiff.