Those caterpillars that eat apples are moths . And these are the most common and dangerous pests (since there are several types of them).
The most common are apple and oriental. These are butterflies whose larval stage feeds on both the pulp and seeds of the growing apple tree fruit. What causes its early fall and rapid decay. During a pest outbreak, up to ¾ of the entire apple harvest may be lost. In this article we will tell you how to save an apple tree from the codling moth .
Symptoms and characteristics of the insect
Symptoms of damage are increased flight of butterflies 12-17 days after flowering, as well as the presence of 1 to 5 or more microscopic holes on apple ovaries. Also, the appearance of carrion in the form of apples that look full-sized, but when cut open there are gnaws inside them and the seed chamber has been eaten away.
Eastern codling moth on an apple tree
The oriental codling moth is a dangerous quarantine pest of apple trees. Because in the South it develops in five generations and one apple can sometimes be inhabited by 5-7 larvae “worms”. Because of this, it can completely deprive a summer resident of his apple harvest .
Spreading
This butterfly is distributed throughout the European part of the Russian Federation (with the exception of the tundra zone), as well as the Caucasus and Transcaucasia, the Far East and the Baikal steppes, Central Asia, Siberia, Altai, Southern Belarus and Ukraine . It is most harmful in the steppe zone of Ukraine, the Russian Federation and the mountainous Crimea.
The effect of humidity on the pest
The number of this butterfly is most strongly influenced by atmospheric phenomena.
And in particular, the massive death of its caterpillars is observed during long periods of drought and heat (almost 100%), when the moisture in the atmosphere decreases to 30%.
Note! The general death of caterpillars before they penetrate into ripening apples in the northern zone and in the Non-Black Earth Region during dry and hot July is observed much more often than usual.
Caterpillar - what is it?
A caterpillar is a small plump worm . The body is pink or pinkish-reddish in color with grayish dots and has no hairs or pubescence.
The head and cephalothorax are chitinous, reddish-brownish in color, dark and stand out brightly against the apple background. True legs with walking claws are observed.
The hind legs, which are not real, also have claws. The body length of the caterpillars sometimes reaches two centimeters. Below you can see what a codling moth looks like on an apple tree - photos in different life cycles:
Apple codling moth caterpillar.
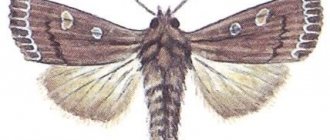
Codling moth butterfly.
Life cycle of a pest
The cycle with complete transformation, characteristic of the genus of butterflies, consists of the flight of adult butterflies, their mating, the butterfly laying eggs in secluded places, the birth of first instar caterpillars, searching, penetration into an apple and the caterpillar feeding on the fruit, leaving the fruit for pupation.
Important! Due to the dynamism and presence of diapauses, the duration of each of the listed stages is variable and varies greatly among gardening zones.
Number of generations
In the north, in apple orchards, there are two generations of the common codling moth, in the south there are three generations, and for the eastern species and in the southern regions of the Russian Federation the number of generations can reach up to five.
First generation
In the northern regions of apple orchards, the first generation appears from the moment small apples grow, that is, from the end of May to the end of June . In the south it can be noted as early as the beginning of May.
Overwintering stage
In the winter period, as a rule, caterpillars of 4-5 instars enter, in impenetrable silky white cocoons. Most often this is the second or third generation of the moth in a given year.
Apple tree varieties not affected by the codling moth
At the moment, there are no varieties of apple trees that are absolutely resistant to codling moths . The only thing that gardeners have accurately noticed is that apples with tasty and very tasty pulp are more often and more intensively damaged by codling moths, but varieties of the “juice” direction are less “favorite” by caterpillars.
Fragrance traps
Codling moth butterflies are very attracted to the smell of fermentation. A trap based on the use of this aroma must be prepared as follows:
- take a basin or jar;
- pour the grounds of kvass into the container (fermented compote or water to which old vegetable oil has been added is also suitable);
- Place the container under the apple tree or hang it on the apple crown.
From this smell, the codling moth butterflies quickly get drunk and drown in the container.
There are a large number of recipes for making heady kvass. For example, it can be prepared from 500 grams of apples (or replace them with 100 grams of dried fruit):
- Pour 2 liters of water over apples and cook for 30 minutes;
- add 0.5 liters of kvass, 0.25 kilograms of yeast and 0.5 liters of whey.
Place the mixture in a warm place and keep it there for several hours.
- take a 3 liter jar;
- put 250 grams of rye bread crusts into it;
- add 20 grams of yeast and 5 pieces of refined sugar;
- Fill the jar completely with warm water;
- cover the container with gauze;
- leave for a day in a warm place;
- After 24 hours, carefully drain the infused liquid;
- Add the same amount of sugar and bread crusts to the sediment again, add one liter of water.
The resulting fermented grounds serve as an excellent bait for butterflies. It needs to be poured into separate containers, filling one third of each. Then hang the jars on the apple tree crowns. This should be done in the evening, and when morning comes, remove the jars. During the day, jars of solution should be stored in a cool place.
Codling moth butterflies are also very greedy for ordinary human food. You can place containers left over from ice cream and mayonnaise in apple tree crowns. It is worth adding to these containers:
Sugar, honey or jam will also work. The sweet smell will definitely attract insects.
The codling moth is one of the most dangerous types of pests for apple trees. It is extremely difficult to fight them. However, wisely prepared traps can help keep the crop safe and sound.
Source: https://otomate.ru/spasaem-urozhaj-yablok-ot-plodozhorki.html
Codling moth on an apple tree: methods of control
Methods of struggle are:
- Agrotechnical;
- Chemical;
- Mechanical;
- Biological.
Attention! Only their simultaneous use will help defeat the codling moth.
Apple trees that are pruned correctly and on time, fed, watered and with properly maintained soil can resist the invasion of these pests. Trees weakened by frost, hail, or overfed with “organic nitrogen” are much easier and more susceptible to pest damage.
In addition, it is necessary to maintain bio-balance in the garden and expand the bio-diversity of species, then natural predators and enemies of codling moths will be able to destroy up to half of the pest, thereby protecting the garden from insect invasion and the use of synthetic poisons on apple trees.
Trichogramma is a natural enemy of the codling moth.
How to fight the codling moth on apple trees? Create conditions under which the development cycle itself will be either impossible or severely disrupted. And the tree and its fruits will become the least suitable for the moth caterpillars to spread and eat.
Watch the video of Oktyabrina Ganichkina’s advice on how to save the apple tree harvest from the codling moth butterfly:
How dangerous is a garden pest?
Of all garden pests, the codling moth has a “good appetite” - one caterpillar damages 2 fruits. At the same time, the insect does not hesitate to infect even crops such as walnuts. Often, extensive colonies of caterpillars populate plantings of pears, apricots and peaches, plums and quinces.
The greatest degree of crop damage is observed on trees that form several fruits from the axil or fruit bud. If they come into contact with each other, then one caterpillar can damage the entire hand. If there are more than half of these brushes, the costs of maintaining and caring for the garden will not be repaid by the resulting harvest.
Expert opinion
Mityuk Stefania Bogdanovna
For garden farms, significant damage is caused if the codling moth damages 10% of the ovaries or 3% of the ripening fruits.
If apple moth butterflies are spotted in the garden in the spring, it is important not to ignore this signal and take measures to prevent the growth of the pest population. We will tell you further about how this can be done.
What helps a butterfly survive?
Its abundance, reproduction by several generations per year and secluded wintering places contribute to this.
Wintering places can be like this:
- In “old” apple orchards, most of the wintering cocoons are located in cracks in the bark, at a distance of up to 60 cm from the ground plane, and others are in the soil near the apple trees themselves, as well as in humus storage areas, supports, chatals, stakes, all kinds of buildings and others shelters located directly in the garden;
- In young gardens, caterpillars overwinter mainly in the ground at the “root collar” at a depth of up to 8 cm, not counting the fact that codling moth caterpillars overwinter in packaging substrates, in box containers, in places for storing apples and they end up there spoiled by them or apples.
Harm
The goal of the moth caterpillar is to penetrate the seed part of the apple and eat it. After that, she leaves the apple and goes looking for another. Over the course of one season, the caterpillar can damage three large or 5 small-sized fruits. As a result, the damaged fruit falls off and loses its presentation.
Gardeners observe damage from the caterpillar under conditions of a mild winter and in the absence of protective actions. In such cases, gardeners record crop losses of up to 90%.
Treatment Chemicals
Spraying of apple trees against harmful insects is carried out with synthetic chemicals based on organophosphorus compounds . But both neonicotinoids and pyrethroids can be used. Below we will look at how to treat an apple tree against codling moths and when, so as not to damage the crop.
Fitoverm
The effect of aversectin (Fitoverm) is complex : penetrating into the caterpillar by absorption into the outer shells during spraying, or after eating apples treated with poison, the poison affects the nervous system of the caterpillar, causing its death.
Attention! The effect of a substance based on “aversectin-S” lasts up to 20 days and cannot be used when pouring apples!
Can we use herbicide?
This is a typical “scam” of modern traders. This substance has nothing to do with HZR, but it can ruin the life of apple trees, because the herbicide is a poison for plants and certainly does not harm the caterpillars.
Advice! Carry out chemical protection of apple trees only with proven preparations from special stores!
Pesticides
Here are the most effective pesticides available on the market that will be effective against worms in apples:
- Pyrethroids: Kinmiks, Karate-Zeon, Lambda-cypermethrin, Sumi-alpha;
- Organophosphorus: Pirimiphos-methyl, Actellik;
- Neonicotinoids (acting systemically): “Tanrek”;
- "Confidor";
- "Talstar";
- "Ram";
- "Fastak".
All of the drugs listed above are from the neonicotinoid family. And all artificial pyrethroids are lipophilic substances that are excellently retained by the cells of apple leaves and fruits and partially penetrate them, guaranteeing an absolute insecticidal effect on caterpillars. But they are applicable only a month before ripening.
Mixed insecticides
How to spray apple trees against codling moths if the garden was previously treated haphazardly and the emphasis was on one particular poison for a number of years? In this case, it is necessary to spray the apple trees with mixtures of poisons. The following tank mixtures are most suitable for this:
- Imidacloprid + Lambda-cyhalothrin;
- Thiamethoxam + Chlorantraniliprole.
Organophosphate insecticides
These compounds (the most famous Dichlorvos, Fozalon, Karbofos, Fufanon ) turned out to be persistent and toxic to nature organochlorine compounds.
These compounds have a low consumption of substance per unit area and a high speed of action on the codling moth, which has made these substances leaders in the fight against caterpillars.
Apple codling moth: how to spray trees against the pest
Spraying an apple tree against codling moth: photo
It is advisable to spray an apple tree against codling moths using the shower method. Special devices and industrial sprayers will help with this. The shower is very tightly capable of covering the entire volume of the green cover of the apple tree, completely all the shoots and even the rudiments of the apples. The consumption of the drug is significantly less.
Wind gusts do not spread the drug solution to neighboring plants, and the risk of poison getting into the neighboring crop is reduced significantly.
Spraying timing
The timing of when to spray apple trees against codling moths varies greatly for each region of the Russian Federation and for each spring. Therefore, it makes no sense to indicate them, since they are determined locally by the time the flight of adult butterflies begins in the spring and its intensity.
in spring
Organophosphorus preparations showed the greatest effectiveness during spring treatment . They destroy the caterpillars during their birth and the pest does not have time to “reach” the small apples. The most effective ones will be:
- "Calypso";
- "Admiral";
- "Sirocco";
- "Zolon";
- "Lannat-20L";
- "Pirinex";
- "Chlorpyrifos".
After flowering
During the mass flight of butterflies, the poisons “Insegar”, “Dimilin”, “Herold” . These drugs belong to the group of insect growth and development regulators. Females lay eggs on a poisoned surface, so the caterpillars will inevitably die.
Combinations of synthetic poisons are also suitable, for example, Thiamethoxam + Chlorantraniliprole .
During the period of fruit ripening
The use of belts, pheromone traps, biological products and decoctions of herbs poisonous to caterpillars is permitted at the time of ripening of summer and autumn apples.
Carefully! The use of synthetic poisons during this period is prohibited!
Dates in autumn
As soon as the leaves have fallen, you can spray and clean the apple orchard in the fall. They spray the crowns with poison, and scrape the trunks and branches of old bark. You should not do this before these deadlines.
Spraying the garden after the leaves fall.
The first period when to treat apple trees against codling moths is early spring. Before the apple trees themselves begin to bloom.
The treatment period consists of two parts - before flowering and after. It ends when the apples begin to “gain color.”
How often should I spray?
In places where the codling moth forms 2 “waves,” winter apples need 4 sprays, and summer apples two.
In conditions where three generations of codling moth develop, 5 sprayings are recommended for summer and autumn varieties and 7 for winter ones.
Time of processing:
- Quiet cloudy day and complete calm;
- Pre-dawn or sunset hours.
Because in the heat, the preparations reduce their “toxicity” , and the wind will reduce the quality of processing.
Spraying times in regions
In the south of Ukraine, in the Lower Volga region, Rostov region, Stavropol Territory, spraying should begin 12-15 days after the end of flowering. Repeat spraying approximately 11-18 days after the appearance of the first caterpillars in the first carrion.
In the zone of the North Caucasus, the south of the Lower Volga region, in the Krasnodar Territory, the first spraying is carried out 9-11 days after the end of flowering of apple trees; the second - usually 21 days after the first, and the third - when live caterpillars are found in the carrion; the fourth - 14-19 days after the third.
Additional treatments are possible only in the event of a pest outbreak and only for “winter apples.”
Other tracks
There are other types of pests that also cause harm and need to be controlled. The grayish-brown weevil, called the apple blossom beetle, overwinters in bark cracks or under fallen leaves. When the buds begin to bloom, the pest moves onto the tree. By feeding on the blossoming buds, the flower beetle causes a phenomenon called “crying buds” - holes appear with drops of juice. You can fight the flower beetle with glue belts and straw, where the beetles will crawl.
The pest that lives on apple and pear trees is called the winter moth. Females are different from males; they do not fly. Caterpillars also feed on the buds, covering them with webs. After flowering, the caterpillars descend on a cobweb to the ground and burrow under the leaves. Butterflies appear in the fall, lay eggs for the winter, and should be controlled with glue belts.
The ringed silkworm harms apple, pear and plum trees and is a brownish-yellow nocturnal moth. Silkworms feed at night and hide in the forks of branches during the day. The fight against silkworms should be carried out when pruning the crown, removing branches with eggs. Nests with caterpillars are also removed and removed. The same remedies can be used as against pests that eat leaves. The apple worm is a 2.5-3 mm insect whose wings are transparent. It can both fly and jump. The harm is caused by the larvae of the copperhead - they enter the buds and concentrate on the petioles and peduncles. When sucking the juice, the larvae secrete a sugary substance called “honeydew.”
Fungi settle on the buds that bloom and on the leaves. The tree's yield decreases, the leaves become smaller, and the fruit bud clutch decreases next year. The fight against larvae is carried out with a decoction of tobacco dust, chamomile, and yarrow. Chemicals can also be effective.
Ecological control methods
It is assumed that these methods of combating this insect and its caterpillars on apple trees are the least dangerous for nature. The most effective will be only hunting belts, pheromone traps and bioinsecticides.
Below we will consider the most effective ways to get rid of codling moths on an apple tree using environmental methods.
Pheromone traps
The base in such traps is created as a preparation form of the pheromone “SR-MK” . It is important that pheromones are used synchronously in all apple orchards. And the use of traps only in some garden plots can only cause the accumulation of a large number of male codling moths in these gardens and this will not give any effect.
Fighting codling moth on apple trees using folk remedies
This is the use of decoctions of wormwood, tomato or potato tops, or an infusion of shag , this also includes collecting and burning carrion and cleaning the trunk from old bark in the fall .
Methods without chemicals
How to fight the codling moth without synthetic poisons? Caterpillars can be controlled using biological products. Among the most effective are Lepidocid.
Hunting belts
To destroy the caterpillars of this insect, they make “belts” of canvas , then they only catch, or canvas with poison , then these are killing belts and they are placed a couple of days before the start of the first generation of caterpillars emerging from the fruit, when “worms” of maximum size are noticeable in the carrion — you can wrap the belts around the standard.
The belts should be inspected once every two weeks and all pupae and caterpillars should be cleaned into a container with a solution of liquid soap. And there is no need to look through the killing belts. They are impregnated with FOS every 10-12 days. And then the impregnation is simply repeated.
Glue composition
Hunting belts are smeared with a special adhesive mixture or simply medical Vaseline .
This glue is prepared from 10 parts of oleoresin, 1.5 parts of rosin, 1.5 parts of paraffin and 2 parts of garden pitch. This is all slowly heated over a fire until it becomes a paste. If the mass, when cooling, sets too quickly and sticks weakly, then it is heated again and 1 part of melted fat or butter is added.
For lubrication, you can also prepare a mass of 450 grams of wax, 290 grams of rosin and up to a liter of oil, preferably vegetable oil. First, slowly heat up the first two components, and then add oil so that even after cooling on the spoon, the mass would be sticky, but not dripping.
Integrated Protection
Integrated protection of apple trees from codling moths is the best answer to the question “how to protect an apple tree from codling moths.”
Such protection is a special approach to the “collective use” of all available methods of containing or exterminating the codling moth, covering mechanical, physiological, biological, biogeocenotic, agrotechnical, chemical methods of control and regulation of the number of caterpillars used for the main purpose - this is the lowest cost of funds and the minimum damage to nature to reduce the number of moths on apple trees .
The apples have darkened inside
Wet low-temperature burn. Sharply defined brownish spots appear on the skin, the flesh underneath is slightly damaged. A similar problem is low temperature fruit decay, where dark spots first appear on the flesh and gradually spread until only a thin layer of healthy tissue remains under the skin. Apples that show signs of scorching and decay rot easily. The cause of burns is too low temperature and high humidity in the storage or failure to meet harvest deadlines, and apples collected from heavily pruned young trees are often susceptible to low-temperature decay of fruits.
Solution. Carry out all garden work on time; try to improve the conditions in the storage. Follow the garden pruning schedule and technology.
Reader questions:
Do starlings on an apple tree eat caterpillars?
Although there is information circulating on the Internet that these birds feed on the caterpillars of this harmful insect, this is not so. They are pecked en masse only by different types of tits , and then at the moment of their emergence from the apples and crawling to wintering places.
Flowers protecting the apple tree from worms
Another “panacea” for worms in apples from the Internet, especially spread by supporters of “BIO-farming”, is planting special types of flowers under apple trees that scare and kill the pest.
It’s a pity, but this method cannot give anything other than disappointment and a crop lost from the pest, because biology is not “led” by fashion trends, and the butterfly does not die only from the smells of plants .
Regular treatment of apple trees against codling moths in the summer will provide many tasty apples in the fall and winter!
Apples rot
Bitter fruit rot. Brown spots with clear outlines appear on the fruits, then they stratify into dark and light, slightly pinkish, concentric circles. The pulp becomes bitter and has an unpleasant odor, apples quickly deteriorate, and rot easily spreads from diseased fruits to healthy ones. Storing apples in the cold does not protect against disease, since rot can develop even at temperatures around zero.
Solution. The fungi that cause the disease settle on open wounds after improper or careless pruning and gradually move to the fruits. Trim fruit trees strictly according to technology, disinfect tools when moving from tree to tree, be sure to cover large cuts with varnish or Rannet paste.
Black fruit rot. Concentric circles of gray velvety growths appear on the apple, and the fruit quickly turns black.
Solution. Preventive measures are the same as against bitter rot.
Lack of moisture
In dry times, if the tree is not watered abundantly enough, it redistributes moisture in its body, drawing it from the fruits and giving it to the leaves. As a result, the apples wrinkle, dry out and tear off the stalks without ever ripening.
It’s time to water a tree when the soil taken from under it does not clench in a fist, but easily crumbles
An adult tree will require at least 1 thousand liters of water during the growing season. Just three waterings are enough; the soil should be saturated with water to a depth of about 0.4-0.6 m. You cannot pour water directly on the trunk or very close to the trunk. It is recommended to do this in grooves or holes dug around the circumference of the crown.
The apple tree needs to be watered in special grooves made along the periphery of the crown.
The apples are very small
Potassium deficiency. The fruits are unusually small compared to the norm for their variety and previous harvests, and are poorly stored; at the same time, flowering could be unusually abundant. If, in addition, the orchard suffered from frost in the winter, and in the middle of summer the leaves were wrinkled, curled and died along with the petioles, we can talk about potassium starvation of the plants. Potassium deficiency is often characteristic of light and especially peaty soils.
Solution. The next time you dig up the soil in autumn, apply phosphorus-potassium fertilizers (azophoska, nitroammofoska or special autumn fertilizers). Industrial fertilizers can be replaced with ordinary wood ash. Phosphorus-potassium fertilizing not only replenishes the deficiency of microelements, but also increases the frost resistance of fruit trees. Remember that potassium is an antagonist of calcium and displaces it from the soil, so strictly follow the dosage of fertilizers.