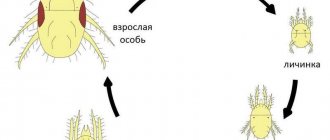
Description of the pest
Ticks are small in size and have an ovoid body shape. Females are larger than males. Body length does not exceed 0.6 mm. Males have large black spots on their sides. Coloring can be:
- light beige;
- yellowish-orange;
- brown;
- green.
Females are usually yellow in color. They overwinter in the top layer of soil. In severe frosts, half of the pests may die. In April-May, females begin active activity. They quickly settle in the raspberry field and lay eggs.
Spider mite.
The eggs have a yellow or fawn tint. The shape is round. They have longitudinal ribs and a stalk at the top. After some time they become colorless.
The lifespan of a female varies between 1-1.5 months. The clutch during this period includes up to 200 eggs. They are formed within 72 hours. The larvae are pink in color and have 3 pairs of legs. When ripe, the color turns red or green. A fourth pair of legs appears.
Photos and symptoms of spider mites on raspberries
Spider mites are arachnid insects with a body length of no more than 0.7 mm. In nature, there are several types of pests, they differ in color. Most often, raspberries are affected by brown mites. But there are insects that are yellowish, green, and even milky in color. It is impossible to see microscopic insects on a plant, but an infestation of a bush can be determined by the following signs:
- a dense web that gradually covers the entire above-ground part;
- brownish or light spots on the underside of the leaves, gradually moving to the upper part;
- curling of young leaves;
- drying of buds.
Important! The appearance of signs of infection on the trunk indicates strong reproduction of the insect.
What harm does a tick cause?
Spider mites on raspberries.
The favorite place of mites is the interveinal depression of the leaf plate. They bite through the epidermis and drink the juice. Parasites prefer fresh raspberry leaves.
The salivary gland secretes an enzyme that destroys the chloroplast. Cankers appear on the outside of the leaves. After a while the leaf curls. Ticks weave webs to breed offspring. The population is increasing very quickly.
The larvae hatch 72 hours after laying. Within 10 days, the transformation into an adult occurs. Ticks can damage ovaries, buds, leaves, and flowers. The stem is the last to be affected.
How to fight with drugs?
The fight against the pest begins at the first signs of its appearance on the bushes, preventing its mass spread. There are several ways to solve the problem.
Chemicals
To reliably destroy pests at all stages of their development, only chemicals are used.
The tick does not belong to the class of insects, so specialized means are needed to combat it:
- Antio is a highly toxic drug that destroys pests at all stages of development after a single spraying.
- Fufanon is a broad-spectrum insectoacaricide. It disrupts the digestive system of pests and causes their death within 24 hours. The protective effect of the drug lasts 2 weeks.
- Akrex is a drug that combines fungicidal and acaricidal properties. The plants are sprayed with a solution of 0.8% concentration 2 times with an interval of 10 days. The product is highly toxic to humans, so protective agents are used during processing.
- Actellik is a non-systemic drug with enteric contact action. Once in the pest's body, the product disrupts the functioning of enzymes that carry out neuromuscular impulse transmission. Accumulating in the tissues of the victim, the drug blocks the functioning of all organs of the pest. The effect of the product begins 2-3 minutes after spraying. The activity of the product lasts 14-15 days.
- Anti-mite – the drug destroys adults and larvae within 2 hours after application. The action lasts 14-15 days. 10 ml of the product is diluted in 10 liters of water and 3 liters are used for 10 medium-sized bushes.
- Dimethoate is a highly toxic product that can be used no later than 40 days before harvesting the first berries. The drug has a systemic effect, accumulates in plant tissues, retains its properties for 25 days.
Carefully! Chemicals must not be used to treat plants during the formation and ripening of berries.
Biological agents
The use of biological products is an excellent alternative for opponents of chemistry. The following agents are most effective in combating spider mites on raspberries:
- Akarin – contains a neurotoxin isolated from the bacteria Streptomyces avermitilis. Paralyzes the nervous system of adult parasites. The drug is applied to the underside of the leaf 3 times with an interval of 10 days. This frequency is necessary to destroy insects hatched from eggs laid by females.
- Bitoxibacillin is a domestic drug produced since the 80s of the last century. It is especially effective to use the product during the larval stages of pest development. The drug is harmless to humans and animals. The bushes are treated with a solution of 1 mg per 10 liters of water 3 times every 3 days. Spray the inside of the leaf, where the pest mainly breeds.
- Fitoverm is a drug that destroys the digestive system of the pest. Treatment is carried out in cloudy weather with a solution of 10 ml per 8 liters of water. The protective effect of the drug lasts 30 days.
Terms and rules for spraying bushes
Better results can be achieved through comprehensive measures. The use of various methods will ensure the elimination of pests. Before the leaves bloom, spray the plant with a urea solution (6% concentration).
A few recommendations:
- The first time it is necessary to treat the drug before the female begins laying;
- the damaged part is cut off;
- treat the soil surface with chemicals;
- dig up the soil without affecting the roots;
- folk remedies are used at any time;
- treated with insectoacaricides three times. The interval is 10 days.
Fighting cobwebs on raspberries using folk methods
Insect repellents prepared according to folk recipes are not capable of destroying pests. Their effect is mainly repellent, so the bushes are sprayed for preventive purposes.
The following means are used against the pest:
- Onion infusion. 20 g of onions are added to 1 liter of water and left for 7 hours. Then filter and spray the bushes.
- Dandelion infusion. 20 g of roots are infused in 1 liter of warm water for 2 hours.
- Garlic infusion. Take 150 g of garlic pulp per 1 liter of water and leave for 5 days in a dark place. Before use, 5 ml of infusion is diluted in 1 liter of water.
- Infusion of tobacco. Crushed young leaves in the amount of 45 g are poured into 1 liter of water and the bushes are sprayed every other day for a week.
- Mustard solution. 1 package of dry powder is dissolved in 5 liters. water, spray the bush.
- Horseradish decoction. 1 kg of roots is crushed, poured with a bucket of water and boiled. The resulting broth is infused for 2 days, filtered. The resulting product is sprayed on raspberries every 10 days. The decoction is stored in a cool place.
- Vinegar. 1 l. table vinegar is diluted in 5 liters. water and spray.
Prevention of the appearance of the parasite
To prevent the appearance of parasites, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- prevent bushes from thickening and growing;
- fed with mineral fertilizers to strengthen the immune system;
- remove weeds;
- Do not over-moisten or over-dry the soil;
- cut off old plants at the roots;
- treated with Karbofos after harvesting;
- mulch the soil under the raspberries.
Previous
MitesRed mites on indoor plants: how to protect your favorite flowers from the pest
Next
Mites Pear gall mite: means of combating a dangerous pest and simple tips for restoring damaged plants
Varieties
In our country, the most common varieties are:
Common spider mite
Common spider mite (Tetranychus urticae). An insect of light or green color settles on garden crops, including tomatoes, cucumbers, basil, lettuce, currants, raspberries, gooseberries, strawberries, and sweet peppers. Does not disdain indoor roses, tradescantia, geranium, asparagus and any other available flowers.
Red spider mite
Red spider mite (Tetranychus cinnabarinus). The small insect most often ends up in apartments with exotic plants or soil. Found on orchids, indoor and outdoor roses, citrus trees, and palm trees.
In the photo there is a common and red spider mite
Atlantic spider mite
Atlantic spider mite (Tetranychus atlanticus). Unlike its counterparts, the pest prefers conditions of high humidity. As a rule, such a tick feeds on palm trees, citrus and fruit trees, melons, and ornamental conifers. It can be found on cypresses, thujas, and junipers.
Cyclamen spider mite
Cyclamen spider mite (Phytonemus pallidus). The pest prefers to settle in soils. It feeds on bulbous garden plants and flowers - lilies, tulips, petunias, daisies, azaleas, dahlias and others. At home, it often affects violets, cyclamens, chrysanthemums, geraniums, fuchsias, and begonias. The smallest pest. The colony looks like a coating of gray dust.
In the photo there is an Atlantic spider mite and a cyclamen
Feedback from agronomists
Stonikov K.P., 44 years old, Sevastopol If you plant plants that repel ticks in the area near the raspberries, and the remaining crops are located far enough away, provided that preparations are made before the start of the season, there is every chance of avoiding a collision with parasites.
Makeev O.S., 49 years old, Pskov I am not against acaricides on the plot, but they have a very aggressive effect on raspberries, so it is better to limit yourself to treating the bushes in spring and autumn (with the required frequency). If there have already been precedents for removing mites, it is better to carefully monitor the plants during the warm season. It is much easier to immediately eliminate lesions than to remove an entire colony later.
Malyshev L.I., 38 years old, Bryansk Sometimes you have to destroy ticks several times a season. If you do this with one drug, pests may develop resistance. It is better to use a new type of product each time. This is not always possible, so I recommend at least alternating 2 drugs. Then the struggle will bring better results. If you use one type of product, then even following all the recommendations will not help remove parasites.
Young shoots are more at risk
Recognizing the enemy by sight
Spider mites can affect not only raspberries; more than three hundred species of plants become its “victims”. It is essentially a sucking pest that parasitizes plants. The beetle itself is half a centimeter in size, yellowish in color and shaped like an oval. The parasite has 4 legs, with which they stick to raspberry leaves and damage them. The arachnid creature can also have other colors: brown, pale green, orange. But don't think that you can examine the pest yourself. Biologists study it. Our job is to recognize the parasite in time and exterminate it.
The female lives on average for a year. During this time, she is able to lay more than 200 eggs. During any phase of its development, the parasite lives on the inside of the leaf.
The first sign of a spider mite on a plant is yellow-greenish dots on the leaves and cobwebs. Of course, the green part of the raspberry, damaged by the parasite, begins to turn black and fall off. This, in turn, negatively affects the growth of raspberries and fruits. The peak of spider mite activity occurs on summer days. The number of spiders increases with the beginning of spring and summer. Scientists have noted that before moving to raspberries, spider mites can adapt to weeds
That is why it is very important to get rid of weeds on the site in the spring, thereby reducing the number of parasites getting on raspberries
Immediately after cold weather, spider mites settle on early varieties of raspberries. This could be the Sunshine variety. Later they can be seen in mid-early ones, such as Lazarevskaya or Balsam. However, the parasite also affects late plant varieties, such as Mirage. In other words, spider mites love any raspberry. It adapts well to chemicals and loves warm temperatures. Days are considered ideal. When the temperature ranges from 24 to 32 degrees Celsius.
What to process
Remember that mites are not insects, but arachnids, so treating raspberries against mites is carried out not with insecticides, but with acaricides (or insectoacaricides). Suitable preparations are Fufanon, karbofos, metaphos, colloidal sulfur. Since spider mites affect so many garden crops, you won’t solve the problem by fighting the mite only on raspberries - you need to treat the entire garden. If there are a lot of mites, the plantings are treated several times - after fruiting and in the spring, before buds open. Trim old raspberry shoots in a timely manner.
Signs of parasitism
Symptoms of damage to red and black currants depend on the species of parasites. Plants face attacks from spider mites and bud mites.
Kidney mite
The pest can be identified by the appearance of the buds. They enlarge and become deformed. The round buds then develop into irregularly shaped leaves. The bud mite causes the leaves to lose color and acquire a rough texture.
After some time, the affected currant shoots stop developing. Insects quickly spread throughout the plant. If measures are not taken in time, there is a risk of crop death.
Cobweb
Spider mites are easy to identify. The key symptom is the formation of a thin web, which is localized on the leaves, between the shoots, and on the berries. Pests feed on the juices of currant leaves. As a result, the affected fragments lose their shape and become covered with spots. The processes of decay begin in them.
Description of the Belarusian sweet blackcurrant variety, planting and care rules
Read
Mistakes when caring for a beautiful indoor flower
Actions that lead to increased pest activity:
- the use of organic fertilizers, this contributes to the withering of flowers and leaves;
- too frequent watering: it is recommended to water balsam no more than 2 times a week in winter, and every other day in summer;
- infrequent watering is also harmful: when the soil dries out, the flower weakens;
- the temperature is low or, conversely, high, it is recommended to maintain this indicator at +18...+22°C;
- when the balsam develops, it needs to be fed once every 10 days; this should not be done too often, the flower may die as it cannot tolerate excess nutrients;
- dense installation of pots on the windowsill;
- Water is not removed from the pan, which contributes to waterlogging of the soil and root system;
- The leaves of the flower are not sprayed (this should be done daily).