Types of ticks
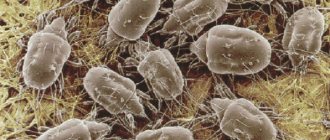
Scientists count more than fifty thousand species and types of ticks.
The most common and dangerous of them:
- Tick-borne Encephalitis. This type of tick is the most dangerous for the southern part of Russia; it is in this part of the country that they develop and reproduce more actively. A carrier of an infection such as tick-borne encephalitis.
- Scabies mite. A type of tick that lives not only on humans, but also on pets (dogs, cats) or any other livestock. Causes a disease called scabies itch. Here you can read in detail about how to cure scabies.
- Ear mite. Ear mites do not pose a great danger to humans and their health. He chooses cats, dogs and cattle as his victims.
- Bed mite. This type of mite has a great thirst for dust, so it chooses habitats with a lot of dust and fluff. Its distinguishing feature is that it does not bite people. Irritation and itching on the skin appears from the excrement excreted by this mite.
- Subcutaneous mite. One of the most common ticks. Life expectancy is two to three months. Due to reproduction, this species can live for more than 9 years without revealing itself in any way. Habitat: under human skin.
The tick's nutrients come from dying skin cells. The manifestation occurs only after weakening of the immune system or other failures of the body. Then irritation and inflammation appear.
There are also:
- Water mites
- Barn mites
- Spider mites
Diagnostics
The whole point of diagnostic measures is to study the effect of the tick on the body.
Diagnosis of a disease involves not only detecting infection, but also determining the number of microorganisms. In most cases, to confirm the diagnosis, a laboratory research method such as studying scrapings from damaged tissue is used. If more accurate data is needed, you will need to use a special extractor that can be used to extract the contents of the hair follicles. You can determine the presence of a tick in other ways. There is a special procedure to obtain accurate data. To do this, cyanoacrylate is applied to the patient's skin. After applying the glue, the treated area of skin is covered with special glass. After the composition has dried, the glass is removed from the surface of the skin. As a result of this procedure, specialists obtain not only a sample of the stratum corneum, but also most of the contents of the follicle.
In microscopic examinations, the sample is examined within five minutes after it is removed. To determine the number of microorganisms, an area of skin measuring one square centimeter is examined. The standard indicator for confirming the diagnosis is the presence of more than five ticks in the above area. If fewer microorganisms are detected, serious drug treatment will not be required.
Blood-sucking ticks
Blood-sucking ticks are one of the most dangerous arachnid species. Their bite can be fatal, because these insects can be carriers of encephalitis, borreliosis and other infections.
Blood-sucking ticks belong to different subgroups:
- Taiga tick. More common in Central Europe, Far East, Eurasia, but also found in other places.
- Dog tick. Lives in mixed forests. The dog tick differs from many of its counterparts in its long development - up to 7 years.
- Pasture mite. Habitats: meadows, pastures, open areas. Lives almost all over the planet. It varies in design with an enamel coating and a rounded end of the body.
- Hualomny mite. A more powerful (large) tick compared to the species presented above. Habitat and residence: Southern part of Europe.
Subcutaneous mites
Another name for the subcutaneous mite is demodex . This name comes from its habitat - the sebaceous gland.
Types of subcutaneous mites:
- Ophthalmic;
- Head (follicular);
- Facial.
The human body is an excellent habitat for demodex. Every third person experiences demodicosis (Demodex infection). Most often, the active appearance of demodicosis occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
Causes and symptoms of demodicosis
There are many causes of this disease, but below are the most common:
- Puberty period. Between the ages of 12 and 18, the disease appears due to hormonal changes.
- Also, demodicosis appears due to some metabolic problems in the body.
- Many girls, young women and women use cosmetics that are completely unsuitable for their skin type. This can also lead to the appearance of subcutaneous mites. It is necessary to carefully read the composition (cosmetics must be natural) and check the expiration date. Hormonal additives in cosmetics also cause demodicosis.
- Severe stress worsens health, which makes it possible for demodicosis to actively develop.
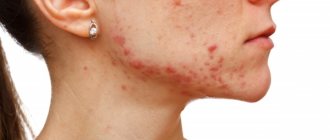
Symptoms of demodicosis on the face:
- Strong tightening of the skin.
- Acne.
- Active and frequent peeling.
- Pore expansion.
- Redness.
- Blisters.
- Itching.
- Sores.
- Oily skin.
- Irritation.
Symptoms of demodicosis of the eyes:
Eye irritation.- Deterioration of vision.
- Eyelash loss.
- The appearance of tubercles in the eyelash area.
- Purulent discharge from the eyes.
Symptoms of demodicosis of the scalp:
- Hair loss.
- Severe itching.
- Redness.
- Peeling of the scalp.
- Formation of ulcers in the hair follicle.
You might be interested! What rash can appear on a child’s body and how to treat it?
Demodectic mange on the face
Demodicosis is a fairly common disease. Many people are treated and are cured quite quickly (according to the norms of this disease). The first thing you should do when you notice a rash, ulcers, ulcers, or oily sheen is to contact a specialist. He will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
The appearance of demodicosis usually occurs in winter or autumn. At this time of year, the body weakens and demodex becomes more active.
Demodectic mange can cause a number of other diseases:
- Neurosis
- Psychosis
- Depression
This is due to severe itching, which can even cause insomnia due to constant worry, as well as obvious skin imperfections, which is especially important for women. Therefore, treatment of such a disease should be carried out without delay.
Here you will find in more detail the answer to the question about the treatment of demodicosis on the face.
Demodicosis on the scalp
Perhaps the most convenient place for demodex to live is the scalp. The subcutaneous mite feeds on the sebaceous secretion from the hair follicle. It also lays eggs there.
To completely cure demodex on the scalp you should:
- Strengthen the immune system;
- Elimination of favorable conditions for mites (skin irritation).
Treatment, if correct, takes place on a six-month course. Next comes rehabilitation, which takes about two to three months. Hence the conclusion that it takes a lot of time and patience to recover from demodex.
Demodectic mange on eyelids
The rarest area of the rash is the eyes and eyelids. In most cases, a person cannot distinguish barley from demodicosis. Therefore, if similar symptoms appear, you should contact an ophthalmologist and get tested.
Demodicosis of the eyelids most often occurs in people suffering from ametropia and chronic diseases of the intestinal tract. This disease can also be acquired due to weakened immunity. Treatment for this disease is prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Signs, symptoms, stages of disease development
Based on the location of the mite, two forms of demodicosis are distinguished: cutaneous and ocular. The severity of the condition depends on the degree of demodex concentration.
In the development of the skin type, 4 stages can be traced with characteristic clinical signs:
- Prodromal. The secretion of sebum increases, the pores expand, an oily sheen and acne appear, for which people call demodicosis acne.
- Erythematous. The capillaries fill with blood and enlarge, red spots appear with outlined, slightly raised boundaries. The hairy areas of the head thicken, peel, and whitish scales appear, similar to dandruff.
- Papular-pustular. The ducts of the sebaceous glands become clogged. Tubercles, pink to purple nodules, and pustules up to 2 mm with redness along the edges form on the surface.
- Hypertrophic. With advanced demodicosis, functional tissues are replaced by connective tissues, the affected areas grow, thicken and disfigure the person. At this stage, medications will be useless and surgery is required.
All stages of demodicosis are accompanied by night itching, sleep disturbance, increased irritability, and fatigue.
In the ocular form, the following symptoms of demodicosis appear:
- eyelids turn red and swell;
- there is a feeling of dryness, a foreign body;
- tearfulness increases;
- Sticky discharge appears at the base of the eyelashes, causing them to stick together;
- eyelashes become thinner, become brittle, and fall out.
In advanced cases, inflammation covers the eyeball, conjunctivitis and blepharoconjunctivitis develop. Sometimes demodicosis becomes chronic, when periods of remission and exacerbation alternate.
What does skin affected by demodex look like?
Demodicosis affects the nasolabial part of the face, back and chest. Less common is demodicosis in the groin area.
It can be distinguished by some basic characteristics:
- Usually demodicosis is accompanied by severe itching and redness.
- Appears in the form of a rash, acne, purulent wounds.
- Pores expand.
- The skin becomes covered with an oily sheen.
- Severe peeling occurs.
- The skin of the face looks inflamed, lumpy, and damaged.
Demodicosis tends to affect the eye area (eyelids). The foamy discharge from the eyes dries out, after which flakes called eyelash dandruff form near the roots of the eyelashes.
Photo
Below is a photo of a tick bite.
Causes of the disease
So, we know that the source of pathology lives inside each of us. But people behave differently. Some try to be treated for demodicosis, others are not even interested in their problem. In its usual form, the harmless Demodexfolliculorum lives inside us and calmly removes toxins. But as soon as the environment familiar to it changes, the tick causes trouble.
In ophthalmology, there are two stages of this disease - primary lesion and secondary. At the first stage, healthy areas of the eyelids are affected; at the second, the disease develops against the background of existing skin problems (papillomas, neoplasms, etc.) and eye diseases.
Several conditions can lead to the development of the disease:
- hot weather;
- long exposure to the sun without eye protection;
- excess or lack of water procedures;
- problems with immunity;
- high acidity of the epidermis;
- poor vision (farsightedness, myopia).
There are many more reasons contributing to the appearance of the disease. As a rule, doctors refer to the general condition of the body: typical acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, disruptions in the endocrine system, neurological problems, postoperative recovery period during eye surgery (for example, after cataracts).
So why is demodicosis dangerous?
Mites can live in human skin in two forms:
- Sleeping tick. This demodex is in a state of sleep. All he does is eat. The rest of the time it remains motionless and does not cause any particular harm to the skin.
- Active form - the tick actively reproduces and can spread to other parts of the body.
Demodex leads to a number of quite serious diseases:
- Neuroses, insomnia, depression in both women and men.
- Rhinophyma is growths in the nose area that make the skin rough and hard, worsens skin color, and increases the size of the nose. Most often found in men.
- Deterioration of vision.
Signs of rapid reproduction
Knowing how to identify a subcutaneous tick in a person, you can begin effective treatment in a timely manner. Studies have shown that the first signs of infection appear on the second day after a healthy person comes into contact with a sick person. The penetration of insects under the human skin leads to a slight pinkness, but it is soon discovered that the face is red and itchy due to the fact that the iron ore mite on the face has begun to multiply rapidly.
Demodicosis is characterized by the presence of a prodromal period preceding the appearance of specific clinical signs. At this time, the patient may experience flushes of painful blush after alcohol, spicy or smoked food, or when excited. The red spots that appear on the skin at this time resemble rose petals or flames, which is why the disease is also called “rosacea.”
Signs of rosacea
The course of the disease has three distinct stages.
- Erythematous. It is characterized by persistent redness of the skin that lasts for a long time. Skin color can vary from soft pink to bright red or bluish. At this stage, vascular bundles and asterisks often appear.
- Papular-pustular. This steel is characterized by the formation of pustules and pimples. The skin in the affected area becomes thicker and pustules appear.
- Hypertrophic. Characteristic of a complicated course or a case where treatment for subcutaneous mites in humans has not been started. The sebaceous glands become greatly enlarged, and peculiar bumps appear on the face and head, most often in the area of the nose, mouth, chin, earlobes or on the eyelids.
Porous facial skin
If the patient's immune system is weakened, insects will spread rapidly. In this case, the skin becomes porous, and a characteristic “snow squeak” appears when palpated; however, the absence of acne can create a feeling of well-being even in young patients. Severe infestation leads to the appearance of mites in the internal organs of the patient, where they are located freely feeding on the entire surface of their body or acquiring the ability to breathe without oxygen (anaerobic).
The diagnosis is made taking into account external signs and laboratory tests.
Demodectic mange should be suspected if the following symptoms appear:
- Characteristic redness of the skin that occurs for no apparent reason.
- The appearance of rosacea on the skin of the face, located in irregularly shaped groups, reminiscent of dermotoxicosis or urticaria.
- Severe itching, relieved by low temperatures and the use of antihistamines.
- If treatment is not started, the patient notices that the skin on the face has become lumpy, and disruption of the integrity of the abscesses leads to further spread of the disease.
- One of the symptoms may be a subcutaneous rash on the forehead.
Symptoms of subcutaneous mites in humans
Analyzes
Testing for subcutaneous mites is the key to making a correct diagnosis and effective treatment. Demodex infection can have a different course; asymptomatic carriage is often found, in which there are no external signs. Therefore, you need to know how to recognize a tick with high accuracy.
Testing for subcutaneous mites
By looking at a skin scraping under a microscope, you can find out what a mite looks like under human skin. In order for the analysis to give unambiguous results, you need to follow the following recommendations.
- 2-3 days before the procedure, stop taking medications and using cosmetics.
- You should not wash your face before scraping.
The scraping is applied to a glass slide and examined under a microscope. Ticks look like thin long bodies, and their larvae look like oblong dark grains. In the video you can see how this happens:
Self-analysis is carried out using adhesive tape, which is attached to the forehead at night, and examined under a microscope in the morning.
Treatment
Only a specialist can prescribe complete and competent treatment. The first test for demodicosis may show a negative result. The larvae and subcutaneous mites themselves are quite difficult to identify, so it is better to carry out the analysis several times for an accurate result.
Means necessary for both treatment and prevention:
- Vitamin preparations.
- Antiparasitic drugs.
- Immunomodulatory agents.
Medicines often prescribed by doctors for the treatment of demodicosis:
- Ointments: sulfuric, clindamycin, with metronidazole.
Sulfur ointment also shows effectiveness in the treatment of scabies in children.
- Klion.
- Metrogil.
- Amitrosole.
- Alcohol-based products.
Medicines
To prevent tick reproduction, use the following means:
- "Metronidazole" - antimicrobial gel, course of treatment - up to three months;
- “Tetracycline” ointment, “Tobrex” eye drops, “Tsipromed” - antibacterial agents that help prevent infection, the course of treatment for demodicosis is up to two weeks;
- eye drops “Vitabakt”, “Okomistin” - antiseptics that help prevent the appearance of other infections, the course of treatment is from one to two weeks;
- drops “Opatonol”, “Lecrolin” - antihistamines that help get rid of allergic symptoms, course - one week;
- drops "Indocollir", "Diclo-f" - non-steroidal drugs prescribed when non-infectious diseases are added to the infection;
- drops such as “Artificial tears” - used for dry eyes, the course of treatment is up to two months.
Treatment of blepharitis of the eyelids should be carried out simultaneously with treatment of the face. So, to remove waste products of parasites, washing your face with antibacterial soap should be supplemented with a massage. To prevent re-infection, it is recommended:
- use disposable wipes to remove dirt from the face and eyelids;
- iron pillowcases and towels daily;
- regularly clean glasses, razors and other items in contact with the face from contamination;
- exclude cosmetics and get rid of products that have come into contact with parasites.
For a complete recovery, close contact with other people should be avoided.
Prevention
For prevention, you should follow a few simple rules:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Choose quality cosmetics.
- Set up and balance your diet.
From the above, we can conclude that proper treatment and timely detection of the problem can reduce the number of difficulties arising due to the appearance of demodex. You should not self-medicate, because this often only adds to the hassle.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of blepharitis can be carried out not only with the help of medications. Non-drug therapy can also be carried out. So, it is useful to wipe your eyelids with decoctions of calendula or chamomile, or make lotions from green or black tea. To enhance the effect, you should resort to physiotherapy. It is worth taking medications to strengthen the immune system: vitamins and vitamin-mineral complexes. During treatment, it is recommended to avoid spicy, sour and salty foods. It is necessary to seek the help of specialists such as a dermatologist, nutritionist, gastroenterologist and allergist. To cleanse the skin, you can use soap with added tar and rinse it off thoroughly, avoiding contact with the cornea. Additionally, tansy can be used as an antiparasitic agent, a strong decoction of which should be rubbed into the surface of the head. Another effective remedy is propolis. It is necessary to dissolve 5 grams in 100 ml of water and instill this solution into the eyes. This will help relieve irritation, dryness and itching.
Kalanchoe juice will help get rid of skin ulcers: the product should be applied to the edges of the eyelids with a cotton swab. If the crust does not come off the eyelids and pus forms, it is worth treating the area with brilliant green diluted with vegetable oil. Tinctures of ginseng root, eleutherococcus, and echinacea are also indicated for the treatment of blepharitis. An integrated approach will help get rid of this complex eye disease.