Throughout the planet, there are more than 40,000 species of bedbugs belonging to the hemiptera. Among such densely populated insects there are species that pose a serious danger to humans.
The triatomine bug is a direct carrier of Chagas disease (a parasitic disease).
During a bite, parasitic organisms (trypanosomes) enter the human body, which subsequently develop, killing healthy cells.
South America is most susceptible to this disease, where more than 12,000 people die from this disease every year.
It is impossible to find the triatomine bug in Russia. Established weather conditions are uncomfortable for the insect.
It is possible that a person on a business trip or vacation will be bitten by a kissing bug (the most common bites of which are found on the face, around the lips), the consequences of which do not promise anything good.
Countries of residence
Many people, who know how dangerous the “kiss” of a harmful insect is, are interested in whether it is possible to stumble upon it in the wild in Russia?
Answering the question - where does it live, I would immediately like to note that the comfortable temperature for this type of insect is 20 - 28 degrees. This type of bedbug is most often found in Central and South America. Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Chile, Bolivia, etc. are no exception.
Triatomine bugs also live in Texas, Canada, and countries adjacent to western Europe and the Pacific Ocean. In Russia, the triatomine bug has never been detected, and its bites have not been recorded.
Therefore, when visiting foreign countries, you should be very attentive and careful, and have as much information as possible about the insect.
Where does the triatomine bug live, directly within South America? It can be noted that the nests of tree knits and birds are favorite places for the insect to settle. The dangerous insect is also found in opossum burrows and armadillo burrows.
The peculiarities of the life of the triatomine bug force it to settle near humans and go out hunting at night.
The insect navigates well in the dark, especially at low ambient temperatures. Sensitive receptors clearly detect carbon dioxide, ammonia, and the smell of hair released during human breathing. Winged individuals strive for the light lit in the windows. Of all insect species, 5% live in human homes.
Triatomine bug: habitat and characteristic features
There are more than 130 species of such insects. All of them belong to the family of predators. However, only some of these pests carry Chagas disease. Pests live in hidden areas: they prefer the burrows of tree rats, as well as armadillos. They are less common on trees. The triatomine bug (another name is the killer) often lives near bats, birds, sloths, and opossums.
Such insects pose a danger to people. They attack when a person is sleeping. However, this is only possible if the insect can easily reach the victim. When pests find themselves close to people, they prefer to settle in the walls of adobe buildings or inside unfurnished dwellings, under mattresses or stones, inside dog kennels. The killer bug prefers to attack outside the city or in rural areas.
The pest is larger in size
Most insects are of the carnivoran family.
It is distinguished by the dark color of its outer integument, the presence of an elongated body, 3 pairs of paws and bulging eyes. It is impossible to see him in the evening. A characteristic feature upon contact with a pest is the appearance of bite marks on the face: mainly in the area of the mouth, eyes, and nose.
The kissing bug reacts to carbon dioxide, which is emitted by warm-blooded creatures. Kissing bugs prefer to be in inaccessible places.
Countries where the kissing bug lives
Such insects are not found on Russian territory. The triatomine bug is found in North (more in the middle) and South America. It can move by means of wings, in this way it spreads across neighboring territories. The insect is most often found in Mexico, the USA, and rarely in Canada. This pest also lives in other Latin American countries:
- Argentina;
- Panama;
- Paraguay;
- Peru;
- Belize;
- Bolivia;
- Brazil;
- French Guiana;
- Guatemala;
- Guyana;
- Nicaragua;
- Suriname;
- Colombia;
- Costa Rica;
- Ecuador;
- Salvador;
- Honduras;
- Venezuela.
The closer
geographically to the south pole of the planet, the higher the probability of encountering insects of this family.
For this reason, cases of Chagas disease also appear in Russia, the symptoms of which appear in full later, when a person returns home from a trip where he was bitten by a pest.
This is due to the fact that the triatomine bug is a carrier of infection. If you come into contact with him in another country, it may turn out that Chagas disease develops as a result. A person will find out about this later, already at home.
How to identify a kissing bug
Pests stand out from the rest (bed parasites, stink bugs, etc.) by their longer legs, narrow heads, flat body of small width, and color. External signs:
- body color can vary: from dark brown to black;
- on the back you can see orange or red stripes with dots on the sides;
- an adult reaches 3.5 cm in length, but smaller triatomine bugs are more common - 2 cm;
- there are wings, rarely orange spots can be seen on them;
- the head is characterized by a cone-shaped shape, it is black, like the paws, and has a significant length;
- The eyes of the pests are quite large and black, which makes them difficult to see against the background of the head;
- there are no spines on the paws; they are smooth but long.
Triatomine bugs of different species differ in color. The color is determined by the type of pest. Some are black, others are dark brown.
Different types of kissing bugs differ in color
What insects are kissing bugs most often confused with?
Several relatives of other families have been noted that have similar features to the triatomine killer:
- bed parasites: they are characterized by a brown color, have a flat body, 3 pairs of legs, they also attack humans and drink blood, but the color of the shell is slightly lighter and the body shape is more round, and such insects do not cause harm other than discomfort;
- American maple beetles (name in Latin - Ácer negúndo): the body shape and color are quite reminiscent of a triatomine insect, however, there are no pronounced orange-red stripes on the back; such colors can be seen on the chitinous covers, but they are evenly distributed on different parts of the back in the form spots;
- wheel beetles: characterized by a black or dark gray color, the body shape is the same as that of the killer bug, but the head is wide, on which you can see, upon closer examination, a protrusion on which the spines are located, and the legs of the first pair are somewhat shorter with hook-shaped large growths;
- The diamondback bug only looks similar to its dangerous brother, general characteristics: body shape, long legs, but this is where the similarity ends, because the diamondback bug has a lighter (gray) body, there is a diamond-shaped pattern on the back, in addition, this insect has a short neck and a wider head;
- Stink bugs are another type of bug, but the body shape is slightly different, which is largely due to the fact that triatomine bugs are longer, in addition, on the back of stink bugs there is no characteristic pattern for a killer insect;
- edgeworm: the size corresponds to a triatomine insect, but the body shape is slightly different - the pest is wide, there is no semblance of a waist, and the hind legs are significantly thickened and resemble tree leaves; edgeworms are similar to their dangerous counterparts due to their black and orange color, but bright spots are located in other places - on the paws and antennae.
What does it look like
Belonging to the Coleoptera family, the triatomine kissing bug is large or medium in size. The insect has an oblong elongated body (up to 30 mm), a conical head, and wings, with the help of which it can freely move to the desired distance.
Compared to a bed bug, its legs and elongated jaws are longer.
Based on the physiological characteristics, bite marks from kissing bugs are larger in size than those of ordinary bed bugs. It is worth noting that despite the impressive size of the mouthparts, it consumes much less blood than a regular bed bug.
Triatomine bugs lay eggs during warm periods. After the nymphs emerge from them, the insect undergoes 4 periods of molting before an adult is formed. Throughout their lives, parasites feed exclusively on blood.
Possessing an excellent sense of smell, bedbugs easily find their prey (animals or humans). The feeding apparatus is designed in such a way that the kissing bug cannot bite through too dense areas of the victim’s skin.
Therefore, during the hunt, insects try to find the most delicate areas of the skin; their bites are often found around the lips and eyes.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Chagas disease (Chagas) in humans and animals: who is the causative agent, what are the symptoms and how to treat
Bedbug bite in a child and an adult: what it looks like and how you can get rid of it
At what temperature do bed bugs and their eggs die?
In what habitat do parasites and worms live?
What do bed bugs fear most: temperature, smells, what chemicals?
Actinomycetes: morphology, structural features, habitat
Why is it dangerous?
It is not for nothing that triatomine bugs have a reputation as one of the most dangerous insects on the planet. They are carriers of Chagas disease (trypanosomasia). When a bug bites a person or animal, it becomes infected or transmits the infection to the victim.
Trypomastigotes, after infecting the victim, actively multiply in the digestive system of the parasite, after which they transform into trypanasomes. Microorganisms of flagellated species are capable of living inside the parasite for up to 2 years; their remains are excreted from the body of the blood-sucking insect in feces.
The kissing bug can cause the following harm to humans:
- damage to the nervous system;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with the cardiovascular system.
In some cases, the symptoms are mixed, making it quite difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Entering the blood, toxic substances initially affect the digestive system, after which they spread throughout the body.
Video
Killer bugs. Triatomine bedbugs, the most dangerous bedbugs in the world!!!
Drawing conclusions
The kissing bug is considered one of the most dangerous insects in the world. It is a fairly large representative of its kind. It is a carrier of Chagas disease pathogens. Tryponasomes living in the human body slowly kill their host.
But this can be avoided if you seek help from a doctor in time. A minute of delay will shorten your life by several years.
Also read the article - Which insects are considered dangerous in Thailand and what you need to know about them
Chagas disease and its symptoms
Despite the fact that the kissing bug can provoke the development of Chagas disease only in 10 cases out of 100, the seriousness of the infection has not been canceled.
There are quite a lot of cases where, after autopsy of the bodies of Latin Americans or permanent residents of Central America who died from a heart attack, damage to internal organs by parasites was discovered.
Before their death, the patients suffered from heart pain, but did not consult a doctor.
There are certain symptoms of a dangerous disease, if you find them in yourself, you need to urgently consult a doctor:
- pain in the heart, shortness of breath;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- excessive fatigue, tiredness;
- loss of orientation (dizziness);
- hyperthermia;
- gastrointestinal system disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- shedding of the skin.
The presence of these symptoms indicates damage to the heart muscle, blood vessels, and lymph nodes. In this case, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Ignoring the disease leads to death.
Recommendations
With the development of the tourism sector, Russians are increasingly visiting other continents, including those inhabited by triatomine bloodsuckers. In order not to spoil your trip and not suffer from its consequences, when going to the countries of South America, you need to arm yourself with knowledge about dangerous insects.
To avoid a deadly encounter
, it is recommended:
- Wear clothing that covers your legs and arms. The head also needs to be protected with any hat.
- Purchase and use special products to repel bedbugs and other insects.
- To avoid attracting bloodsuckers, do not apply perfume to your skin;
- Remain in closed shoes, even if there is a strong temptation to walk barefoot on soft grass.
- Avoid tall thickets and dense bushes, do not touch low-hanging tree branches.
- Fight curiosity to take a closer look at animal homes: burrows, hollows, etc.
- When it gets dark, stay indoors if possible.
- Do not try to take a closer look at the old rickety buildings.
- Close windows at night.
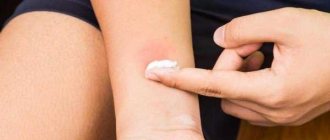
If you are unable to avoid a triatomine bug bite, follow the following procedure:
- immediately after discovering a bite, use soap and running water to wash the wound;
- make a lotion from a mixture of soda and water to relieve swelling;
- soda can be replaced with ice, which must be kept on the wound for at least half an hour;
- monitor your general condition: if you notice dizziness, attacks of nausea and vomiting, rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath, seek medical help immediately.
Important!
Do not scratch the itchy area under any circumstances. If there is no clean water nearby, do not look for the nearest body of water. It is also not recommended to apply freshly picked herbs or leaves to the wound.
Remember: the bite of the triatomine bug is fatal. Therefore, it is better to avoid meeting him than to look for ways of treatment later and not be cured.
Adult insects We also recommend Should you be wary of the water bug? When going to a body of water, especially with stagnant water, you should not be sure that it is completely safe for your health. Be prepared to meet such a person. Methods for removing a tick from a person In Russia, about 40,000 people bitten by ticks go to doctors every year. This usually happens during the months of their especially active life activity - with What you didn’t know about stink bugs The usual habitat of this arthropod is places near rivers and lakes. It is popularly called the stink bug due to the spread of an unpleasant odor. Is it necessary to fight garden ants? Ants scurry around from morning to night, looking for food and generally leading active life activities. Garden ants pose a threat to gardeners
Treatment of bites
Chagas disease has several stages:
- acute lasts about 2 months, can occur without the manifestation of the above symptoms;
- The chronic phase is characterized by the development and proliferation of parasites in the heart muscle and digestive system, resulting in the gradual destruction of vital organs.
Treatment of the disease is possible if it is detected in the acute stage. If the process of disease development enters the chronic stage, cure is impossible. There are only methods for prolonging life that alleviate the patient’s condition.
Consequences
The main damage is done to our immune and nervous systems. The first one is constantly exposed to blows, and then there are attacks from insects.
Those who have experienced the negative consequences of cohabitation with bedbugs, in addition to the obvious reasons, highlight a dangerous decrease in performance and motor activity. Similar reactions occur due to lack of sleep.
Constant anxiety, negative anticipation of bedtime, which obviously will not bring either rest or peace, upset the nervous system. The balance in the body is disrupted.
The inability to get enough sleep reduces the protective mechanisms of the immune system, and as a result, particularly susceptible people can suffer mental trauma.
Children's unstable nervous systems are at risk. Here is a situation that psychologists have repeatedly worked with:
Infestation of a home by insects often causes misunderstanding on the part of others and not only among children. This is an important factor that is missed when discussing the harm bed bugs cause to humans.
Treating a bite at home
In addition to the fact that a person can be bitten by a triatomine bug, there are other ways of infection:
- through poorly washed products;
- from mother to child during childbirth, during breastfeeding;
- during blood transfusion.
Since the chronic stage of the disease can last from several months to ten years, the following drugs are used for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and heart muscle:
- Nufutrimox;
- Benzidazole.
Depending on the symptoms and degree of damage, doctors prescribe symptomatic and pathogenic therapy. If the disease is protracted, medications aimed at combating parasites have no effect, so the main treatment is aimed at restoring vital organs.
Modern medications are also used for treatment, blocking the vital activity and reproduction of parasites in the body.
Effective means to combat
For chemical treatment of garden plots, insecticides of various types are used to influence insects. There are three groups of drugs:
- contact (upon contact with a bug, they penetrate through the skin or shell into the pest’s body and destroy it);
- intestinal (getting into the stomach of the bug along with food, destroying the digestive system and infecting the insect);
- systemic action (contact-intestinal).
The choice of drug depends on the degree of insect damage to the area and the period of plant protection.
| Name of the drug | Type of effect on insects | Speed of action of the drug | Plant protection period |
| Caesar | contact | from 10 minutes | from 2 to 3 weeks |
| Fatrin | contact-intestinal | from 15 to 30 minutes | 2 weeks |
| Boreas (dangerous to bees) | systemic | 24 hours | up to 30 days |
| Chord | contact-intestinal | from 15 to 30 minutes | 7 days |
| Zolon | contact-intestinal | from 1 to 3 days | up to 20 days |
| Tager | systemic | from 3 to 5 hours | from 7 days |
When using pesticides, it is important not to allow the drug to come into contact with mucous membranes, to follow the safety standards specified in the instructions and how to use the solution. Forest bugs always live in conditions that are as comfortable as possible for their existence
If the situation changes, they often find shelter in a person’s home. The stink bug's bite does not pose any danger, especially since it is not capable of biting a person at all. If bedbugs from the street crawl into your house, then don’t panic
Forest bugs always live in conditions that are as comfortable as possible for their existence. If the situation changes, they often find shelter in a person’s home. The stink bug's bite does not pose any danger, especially since it is not capable of biting a person at all. If bedbugs from the street crawl into your house, then don’t panic.
Since they feed on plant foods, once in a home environment, window bugs can settle in indoor plants and gradually destroy them. In this case, it is necessary to clear the apartment of uninvited guests. The easiest way is to throw them out an open window.
There are several methods to combat forest bugs:
- collect manually when the area is slightly contaminated;
- use infusions, which must be made on the basis of mustard and onion peels; they will have to be used to treat the plants several times;
- spray the plantings with karbofos, chlorophos or phosphamide.
Karbofos
Knowing how to get rid of stink bugs, you should choose the safest and most effective methods, and also take into account that there are no highly targeted drugs for their destruction.
The following options are considered the most popular:
- In a residential building, you can use a folk remedy that contains dishwashing liquid and nicotine. It is necessary to crumble a pack of inexpensive cigarettes, add warm water (2 liters) and leave for several hours. After this, add dishwashing liquid to the resulting solution, mix thoroughly and strain.
- A drop of hot paraffin from a burning candle will help quickly neutralize the beetle, and simply heated wax has the same effect.
- In a vegetable garden or orchard, you can use the drug Fufanon Nova, which successfully repels bedbug attacks on cultivated plants and prevents the pest from multiplying. However, such a remedy is not used in an apartment.
- Women's hairspray perfectly seals all the breathing and smelly holes on the shield bug's body.
- Since the stink bug breathes through the pores on its body, you can try to neutralize the insect before it has time to release its smelly liquid using ordinary water. To do this, you need to fill the container with water, dissolve soap in it and quickly throw the bug into this solution.
The liquid, which is toxic to the beetle, will not allow it to empty its odorous glands and will save your home from an unpleasant odor. After some time, when the insect dies, the solution can be poured into the toilet.
Since the stink bug is not one of the insects dangerous to humans, there are no chemicals whose action is aimed specifically at its destruction. Therefore, the fight against it should only begin if the number of insects begins to increase sharply, which can lead to serious consequences for your garden plot.
What to do if you find a kissing bug at home
Kissing bugs pose a fairly serious threat to human health. Therefore, when they are detected, it is necessary to get rid of harmful insects as soon as possible.
To do this, it is recommended to treat the apartment with special insecticidal agents.
Toxic agents should be placed in deep cracks and small cracks in the floor and walls should be covered with them. If you are on a business trip or vacation in countries where there is a risk of exposure to triatomine bedbugs, check your canopy carefully before going to bed.
For better security, change your cheap hostel to a more expensive hotel.
Classification
Species marked (Tc) are carriers of Trypanosoma cruzi
- the causative agent of sleeping sickness.
Tribe Rhodniini
Rhodnius
- Rhodnius brethesi
Matta, 1919 (Tc) - Rhodnius colombiensis
Moreno Mejía, Galvão & Jurberg, 1999. - Rhodnius dalessandroi
Carcavallo & Barreto, 1976 - Rhodnius domesticus
Neiva & Pinto, 1923 (Tc) - Rhodnius ecuadoriensis
Lent & León, 1958 (Tc) - Rhodnius milesi
Carcavallo, Rocha, Galvão, Jurberg (in: Valente et al., 2001) - Rhodnius nasutus
Stal, 1859 (Tc) - Rhodnius neglectus
Lent, 1954 (Tc) - Rhodnius neivai
Lent, 1953 - Rhodnius pallescens
Barber, 1932 (Tc) (main vector in Panama). - Rhodnius paraensis
Sherlock, Guitton & Miles, 1977 (Tc) - Rhodnius pictipes
Stal, 1872 (Tc) - Rhodnius prolixus
Stal, 1859 (Tc) (vector in Colombia, Venezuela, Guatemala, Honduras and parts of Nicaragua and El Salvador). - Rhodnius robustus
Larrousse, 1927 (Tc) - Rhodnius stali
Lent, Jurberg & Galvão, 1993 (Tc)
Tribe Triatomini
Triatoma
- T. amicitiae
Lent, 1951b - T. arthurneivai
Lent & Martins, 1940 (Tc) - T. bassolsae
Aguilar et al., 1999 (Tc) - T. baratai
Carcavallo & Jurberg, 2000 - T. barberi
Usinger, 1939 (Tc), the main vector in central and southern Mexico. - T. bolivari
Carcavallo, Martínez & Peláez, 1987 - T. bouvieri
Larrousse, 1924 - T. brailovskyi
Martínez, Carcavallo & Peláez, 1984 - T. brasiliensis
Neiva, 1911b (Tc) is the main vector in the Brazilian Caatinga region. - T. breyeri
Del Ponte, 1929 - T. bruneri
(Usinger, 1944) re-erected by Lent & Jurberg, 1981 - T. carcavalloi
Jurberg et al., 1998 - T. carrioni
Larrousse, 1926 (Tc) - T. cavernicola
Else & Cheong, in Else et al.,1977 - T. circummaculata
(Stal, 1859) (Tc) - T. costalimai
Verano & Galvão, 1958 (Tc) - T. deaneorum
Galvão, Souza & Lima, 1967 - T. delpontei
Romaña & Abalos, 1947 (Tc) - T. dimidiata
(Latreille, 1811) (Tc) is an important vector in Mexico, Central America, Colombia and Ecuador. - T. dispar
Lent, 195 (Tc) - T. eratyrusiformis
Del Ponte, 1929 (Tc) - T. flavida
Neiva, 1911c - T. garciabesi
Carcavallo et al., 1967 (Tc) - T. gerstaeckeri
(Stal, 1859) (Tc). - T. gomeznunezi
Martinez, Carcavallo & Jurberg, 1994 - T. guasayana
Wygodzinsky & Abalos, 1949 (Tc) - T. guazu
Lent & Wygodzinsky, 1979 - T. hegneri
Mazzotti, 1940 (Tc) - T. incrassata
Usinger, 1939 - T. indictiva
Neiva, 1912 - T. infestans
(Klug, 1834) (Tc) is the main vector in the Southern Cone. - T. juazeirensis
Costa & Felix, 2007 (Tc) - T. jurbergi
Carcavallo et al., 1998b - T. klugi
Carcavallo et al., 2001 - T. lecticularia
(Stal, 1859) (Tc) - T. lenti
Sherlock & Serafim, 1967 (Tc) - T. leopoldi
(Schoudeten, 1933) - T. limai
Del Ponte, 1929 - T. longipennis
Usinger, 1939 (Tc) - T. maculata
(Erichson, 1848) (Tc) - T. matogrossensis
Leite & Barbosa, 1953 (Tc) - T. mazzottii
Usinger, 1941 (Tc) - T. melanica
Neiva & Lent, 1941 (Tc) - T. melanocephala
Neiva & Pinto, 1923b (Tc) - T. melanosoma
Martínez et al., 1987 (Tc) - T. mexicana
(Herrich-Schaeffer, 1848) - T. migrans
Breddin, 1903 - T. neotomae
Neiva, 1911d (Tc) - T. nigromaculata
(Stal, 1872) (Tc) - T. nitida
Usinger, 1939 (Tc) - T. obscura
(Maldonado & Farr, 1962) - T. oliveirai
(Neiva et al., 1939) - T. pallidipennis
(Stal, 1872) (Tc), an important vector in southern and central Mexico. - T. patagonica
Del Ponte, 1929 (Tc) - T. peninsularis
Usinger, 1940 (Tc) - T. petrochiae
Pinto & Barreto, 1925 (Tc) - T. phyllosoma
(Burmeister, 1835) (Tc) - T. picturata
Usinger, 1939 (Tc). - T. platensis
Neiva, 1913 (Tc) - T. protracta
(Uhler, 1894) (Tc) - T. pseudomaculata
Correa & Espínola, 1964 (Tc) - T. pugasi
Lent, 1953b - T. recurva
(Stal, 1868) (Tc) - T. rubida
(Uhler, 1894) (Tc) - T. rubrofasciata
(De Geer, 1773) (Tc) - T. rubrovaria
(Blanchard, in Blanchard & Bulle, 1843) (Tc) - T. ryckmani
Zeledon & Ponce, 1972 - T. sanguisuga
(Leconte, 1855) (Tc) - T. sinaloensis
Ryckman, 1962 (Tc) - T. sinica
Hsaio, 1965 - T. sordida
(Stal, 1859) (Tc) - T. tibiamaculata
(Pinto, 1926b) (Tc) - T. venosa
(Stal, 1872) (Tc) - T. vitticeps
(Stal, 1859) (Tc) - T. williami
Galvão, Souza & Lima, 1965 (Tc) - T. wygodzinskyi
Lent, 1951c
T. arenaria (?) (Walker, 1873) (?)
What harm does it do?
The appearance of the marbled beetle is one of the most important problems for farmers. The bug poses a threat to more than 100 plant species, including agricultural crops. The insect is indiscriminate when it comes to food; its diet includes:
- fruits: apples, pears, peaches and apricots;
- berry crops: rose hips, sea buckthorn, grapes, currants, cherries, raspberries, etc.;
- subtropical crops: citrus fruits, figs, persimmons and olives;
- nuts: hazelnuts, peanuts, cashews and many others. etc.;
- grains and legumes: peas, beans, beans, soybeans, wheat, corn, barley;
- vegetables: peppers, tomatoes, eggplants, cucumbers;
- ornamental tree crops: plane tree, holly, cercis.
emkost_bak fgbucnmvl alex_jem2017
If you do not start fighting the insect in time, it will not only cause colossal damage to the crop, but can even destroy it.
The larva and adult feed on the same thing, piercing the outer tissues of plants and sucking the juice from them. Because of this, the stems become lumpy, and the tissue that forms under the bark resembles cotton wool. Affected fruits and vegetables lose their true taste and do not have time to ripen, crumble to the ground or begin to rot on it (cucumbers, pumpkin, etc.).