Precise quantitative characteristics of the life processes of bedbugs. Exactly how long in days, hours, minutes does it take for bed bugs to lay eggs and mature them. How often clutches are laid, at what age, and how many larvae one female parasite gives birth to. How long does the individual live after the bite, how long does it take for the blisters to appear, as well as the time during which the itching stops and the redness goes away.
The bed bug is deservedly considered one of the most unpleasant neighbors for humans. The presence of a parasite in an apartment or house can make the life of the inhabitants of the home extremely uncomfortable and unattractive. Therefore, a person’s desire to get rid of bedbugs—this harmful and dangerous insect—seems quite logical and easily explainable.
To choose the most effective methods of exterminating a bedbug, you need to know its lifestyle and other characteristic behavioral features. Of key importance in such a situation is obtaining an answer to the question of how long the parasite lives, how often it bites a person, how many days it takes for it to become hungry again, etc. The article discusses the most important and relevant points related to the temporary vital signs of bed bugs.
Main breeding sites
Bed bugs multiply in the apartment, choosing secluded places. Quite popular in the apartment are:
- space under baseboards;
- cracks in furniture that is located close to a person’s sleeping area;
- the space between the wallpaper and the wall, the wallpaper joints themselves;
- clothes in the closet and furniture upholstery;
- internal socket boxes;
- Appliances.
Where to look for bedbugs
These places are ideal for breeding in large numbers without harm to the offspring. In most cases, the entire house can become a springboard for active reproduction if favorable conditions are present. But still, both bed and sofa bugs prefer to be located closer to the source of food, that is, to a person.
Consequences of bedbug bites
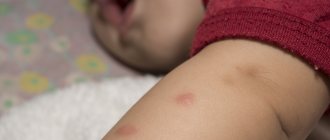
One of the most unpleasant consequences of a bedbug living in an apartment or house is insect bites on the human body. Usually their traces are found on open areas of the skin - in the neck, arms, legs or face. Somewhat less often, parasites get under clothing, in which case other parts of the body are not protected from bites.
How long does it take for a bug bite to appear?
While feeding, the bed bug injects an anesthetic into the skin puncture site, making the bite unnoticeable to the victim. However, the consequences of the parasite’s activity appear the next morning.
First, we are talking about a small red spot, which is located directly at the site of the bite. In most cases, in such a situation, itching occurs, since the effect of the anesthetic has already worn off, but the mechanical effect on the skin has not gone away. As a result, red spots appear at the site of the bite, which are much more visually noticeable.
An allergic reaction to a bug bite often which is expressed in a more serious form - severe itching, rapid reddening of the bite site, hardening of the skin at the puncture site, etc. A frequent symptom of this situation is an increase in temperature, which causes additional and very serious inconvenience. All of the above phenomena are observed within the first day after the bite.
How long does it take for bedbug bites to last?
In most cases - when there is no allergic reaction to the bite - the consequences of the bedbug's activity pass quickly enough. Moreover, today there are many pharmaceutical products on the market that can relieve itching and redness from the skin in a short time.
In addition, so-called “folk” remedies can be quite effective. For example, a weak solution of ammonia, parsley infusion or potato juice. Finding or preparing them is not difficult, and the action of the product on the site of a bug bite is quick and effective.
How long does it take for a blister to appear after a bug bite?
As already noted, a bedbug bite mark is usually detected almost immediately - that is, in the morning. The appearance of a blister is determined by two main factors. The first is the presence of an allergic reaction to parasite bites. The second is the person’s behavior: if he actively scratches the wound at the site of the bite, a blister will probably appear and very quickly. If the victim of a bed bug restrains his own impulses and endures the itching, there is a high probability that the blister will not appear at all.
You need to understand that not scratching the bite site is quite difficult. The fact is that the violation of the skin turns out to be very serious, and the effect of the anesthetic substance injected into the insects during feeding wears off very quickly. Therefore, a person often begins to itch in his sleep, with virtually no control over his actions.
All of the above applies mainly to the reaction to a bedbug bite of an adult. If the parasite has bitten a child, the situation can be much more unpleasant. The fact is that a child’s body, which is not yet fully formed, does not have the full-fledged protective systems present in adults.
The consequence of this is a much more severe reaction to a bug bite. It is expressed in the rapid reddening of the bite site and the appearance of blisters. With numerous bites, the temperature often rises, a runny nose and other similar painful phenomena appear. In addition, it is much more difficult for a child to fight the itching and restrain the desire to scratch the bite site.
How long does a bug bite itch?
Typically, the consequences of a bedbug bite in the form of itching in an adult appear within 2-3 days. For a child, this time may increase slightly. It is quite possible to alleviate the sensations with the help of various ointments and folk remedies, some of which were listed above.
The indicated time frames apply to situations where there is no allergic reaction to a bug bite. If it is present, the situation noticeably worsens, and the time during which itching is observed increases by several days. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, especially if we are talking about a child. Delay in such a situation can lead to unpleasant complications, while at the same time, taking medications prescribed by a specialist can eliminate all negative consequences for the body within 3-4 days.
It is necessary to note one more significant point. The presence of bedbugs in an apartment or house most likely means regular night bites. In this case, their effects are cumulative, which can lead to more unpleasant results in the form of numerous redness, constant itching, fever and even nausea. Naturally, in this case it is necessary to consult a doctor, and also call specialists to carry out insecticidal treatment of the room to destroy bedbugs.
How long does it take for redness from bedbug bites to go away?
The time it takes for the effects of bites to subside depends on several factors. The first of these is the person’s age. As already written above, in the vast majority of cases, an adult body copes with the consequences of the parasite’s actions much faster and more painlessly than a child’s body.
The second important factor is the number of bites. If we are talking about 2-3 cases per night, the blister disappears in 2-3 days, and within 4-5 days, as a rule, no traces remain in the form of irritation and redness. If the bites become regular and numerous, the consequences are observed over a noticeably longer period of time.
The third factor that can reduce the time during which the consequences of bites are observed is the use of special drugs or folk remedies. With proper selection and application, such methods can remove blisters and redness within the first two to three days.
Reproduction rate and area affected by bedbugs
Reproduction of bedbugs occurs according to a certain pattern, which determines the speed of spread of the insect within a specific time frame. To understand how quickly bedbugs reproduce, it is worth considering the process of laying eggs of one female:
- During her entire life, the female mates only 2 times. The seed is deposited in the abdomen and is used for fertilization at the right time.
- A female can lay from 5 to 8 eggs per day. In a week you can get up to 56 eggs.
- This rate of egg laying will allow the female to produce 400 eggs over a full life cycle - this is the beginning of the appearance of a new colony of the parasite.
The process of laying eggs of one female bug
Each new “soldier” is ready for further reproduction after 30 days.
Life cycle of bedbugs
The lifespan of an adult insect is 12-14 months. The maturation period takes about 30-35 days, but if conditions for development are unfavorable, the larva goes into suspended animation.
During this period, life processes slow down, but as soon as conditions change for the better, the larva comes to life and goes through the entire life cycle starting from the interrupted stage.
The development process of a parasitic insect occurs in 3 stages. First, the fertilized female lays eggs. The egg then develops into a larva (nymph). After a short period of time, the larva becomes an imago (mature individual).
There is no intermediate transformation into a pupa, so entomologists classify bedbugs as insects with an incomplete cycle of transformation.
The bedbug's diet consists exclusively of blood. It is necessary for it at all stages of maturation and for further viability.
Reproduction through violence
The method of reproduction of these insects can be called violent. The mating male uses a painful and quite traumatic method of insemination: he attacks the female, pierces her abdomen with the genital organ and injects sperm into the resulting hole.
The injected seminal fluid is enough for the female to reproduce offspring for the entire life cycle. She spends it gradually, as needed. In starvation conditions, the digested part of the seed can even become additional nutrition for the female.
Thus, a female mate only once in her entire life. Males are capable of sexual intercourse up to 200 times a day.
Males are promiscuous in sexual relations and can attack another male or a nymph incapable of fertilization.
A violent act can lead to its death, so nature has endowed the larva with the ability to secrete a repellent enzyme that causes a feeling of anxiety in the male.
Sexual intercourse with a male leads to mixing of seminal fluid in the body of the injured party.
As a result, during the next mating, the most viable sperm enter the female’s spermatheca.
Factors preventing reproduction
The life and reproduction of bedbugs directly depends on environmental factors. The female will not lay eggs if the following unfavorable factors arise:
- The air temperature in the room dropped below 14 °C.
- No food source available.
- The humidity increased sharply.
In such conditions, not only will the insect not reproduce, it will not even survive. Immigration to another room will occur, or the parasite will go into suspended animation and wake up when everything returns to normal.
What prevents reproduction
Females and males reproduce quickly only in a comfortable environment. When unfavorable conditions arise, insects slow down the rate of population increase.
Temperature
The optimal temperature for the development and life of an insect is +25…+30°C. Until the ambient temperature drops to +10°C, bedbugs will continue to reproduce, but at a slower rate.
This process stops completely when suspended animation occurs, i.e. when the ambient temperature drops to +5°C and below. Frost from -10°C is fatal for bed bugs.
Humidity
Bed bugs feel most comfortable in warm and dry rooms. Parasites cannot tolerate high humidity; the optimal indicators for them are 40-60%. Low humidity is easily tolerated by adult insects; they replenish the lack of fluid by increasing the amount of blood they consume.
The eggs run the risk of dying, because if there is a lack of environmental humidity, they quickly dry out and the embryo dies. If the humidity is too high (70% or higher), the eggs are susceptible to fungal infections.
Lack of food
A bedbug can live without blood for 3-4 days, a larva - 2-3 days. But even a month of hunger strike does not lead to the death of the bed parasite. If the insect does not receive food within 14-16 days, it will fall into a “inhibited” state - suspended animation. In this state, all processes in the body slow down, and nutrient consumption is reduced to a minimum.
Important! With the lack of food, the ability to reproduce offspring stops.
Anabiosis
Anabiosis is the next stage of “slowing down” the life activity of the bug. This state occurs at a temperature of 0…+5°C. Too high a temperature does not lead to suspended animation, it kills the insect. The larva dies at +45°C, the adult bug lasts up to +70°C.
In this state, the parasite stops moving, feeding and reproducing.
Rapid reproduction effect
To determine how bedbugs reproduce at such a rate, it is worth considering the effect of rapid reproduction. The linen bug can increase the amount of feeding up to 2 times a week. This means that all stages of development occur faster. At this stage, it is definitely not possible to get rid of parasites. New clutches of eggs may appear every day.
Appearance of eggs and larvae
The egg develops in the female body for no more than 3-4 days, after which she lays it. The egg capsule resembles a translucent grain of rice, no more than 1 mm in length, making them difficult to detect.
At this stage of development, the bug is practically invulnerable: the shell of the egg is resistant to shock, temperature changes and does not allow pesticides to enter. Therefore, even after treatment, parasites may reappear in the house.
The larva that hatches from the egg is called a nymph. She looks like a mature individual, but is smaller in size. The color of the insect at this stage is almost transparent; you can even see the sucked blood in the abdominal cavity.
Larvae require a lot of nutrition to grow. At one time they consume less blood than adult arthropods, but feed more often.
The bites are painful and immediately cause itching and burning, because... their saliva does not contain anesthetic. When a sexually mature bug bites, it injects a substance similar in effect to an anesthetic.
Whitish from birth, the larvae begin to change color due to molting. The chitinous shell does not stretch as the bug grows, so the insect sheds it every 5-6 days.
With each molt, the shell becomes darker in color. After the fifth molt, the nymph is ready to reproduce.
How regular nutrition saves the female from death after mating
After forced mating, the female is “traumatized.” In the future, she no longer needs to mate, but she needs to regain her strength in order to begin laying eggs. Regular feeding can save an insect from death.
Human blood supports the functions of the body and prepares it for fertilization by the male's seed. The female should eat once a week.
How long do bedbugs live without food?
The bug experiences a need for human blood at all life stages. Lack of food makes the insect lethargic and unable to reproduce, but it can adapt to hunger.
Bedbugs that have not been subjected to chemical poisoning are especially tenacious, their energy resources were not spent on detoxifying the body, and they endure hunger more steadfastly.
According to a 2011 study by entomologist Andrea M. Polanco, adults survive between 39 and 106 days without food. More recent studies show that pesticide-resistant bedbugs can go hungry for 11 to 80 days, while an insect without immunity can live for 27 to 143 days.
Optimal conditions for reproduction
House bugs multiply quickly if optimal conditions for this are created. If external factors are normal, then this shortens the period of development of the egg to an adult. Bed bugs reproduce under the following conditions:
- The room temperature is kept constant and is 20-25 °C.
- Air humidity should be 70%.
- There must be many secluded places to create a nest.
- There should be a food source within a small radius of the nest.
Such conditions are often found in homes, so this is an ideal habitat for bedbugs. If you slightly change the conditions in the room, it becomes possible to destroy insects or slow down their development.
Where do bedbugs usually hide?
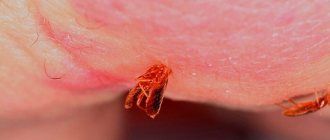
The second difficulty when fighting blood-sucking insects is their secretive lifestyle. Bedbugs choose dark places, cracks and corners, spaces behind paintings and under baseboards, and the undersides of carpets to live and reproduce. It is almost impossible to meet a blood-sucking parasite during the day.
The first task of an exterminator is to locate all bedbug nests. This is a chaotic accumulation of excrement, chitinous membranes, adult insects and larvae. Knowing the characteristics and main places where bedbugs usually hide greatly simplifies the control process and increases the efficiency of room treatment. Large nests are often located near the sofa and bed, in mattresses and under pillows. This is the most comfortable place for bedbugs, which provides them with an abundant amount of food without the cost of moving to a food source.
Blood-sucking bed bugs have a flat and compact body, which allows them to hide in almost any narrow cracks, holes, or hidden spaces. Entomologists and pest controllers name the following favorite habitats of parasitic insects:
- Relaxation area, sleeping place.
The largest concentration of larvae and adults was noted on the underside of the spring block, in the joints of metal and wooden structures of the sofa, on the lower edge of the mattress, in folds, armrests, and on the lower back of the sofa. - Furniture items.
If the population of bedbugs is large enough, their habitat expands to tables, chairs, bedside tables, and soft armchairs. Insects choose places with untreated wood, fabric, various crevices and cracks. - Walls, ceiling and floor.
The favorite refuge of blood-sucking bugs is the space under the baseboard, the edges of peeling wallpaper, peeling paint, cracks and crevices in the flooring.
Among other habitats for bedbugs, it is worth noting the back side of paintings and carpets. Adult individuals choose the perimeter of the product and the place that is attached to the wall as their habitat. You can also find larvae and adults in wall openings intended for sockets and switches, in the upper folds of drapes, curtains and drapes.
Stages of bedbug development
The complete development cycle of the parasite consists of 7 stages. Full development takes only 1 month, so a horde of parasites can completely fill an apartment in 30-40 days. Stage of insect development:
Bedbug development cycle
- The incubation period for larval development ranges from 5 to 20 days.
- After the incubation time has passed, a nymph emerges from the egg. Body length is 1.5 mm.
- After 6 days, the larva enters the third phase of development, increasing to 2 mm. This cycle is repeated every week.
- At the end of the 7th stage, the bug becomes an adult, ready to reproduce. The development time is determined by the feeding rate. The larvae eat only once a week, due to which they move to the next stage of development. The same way bedbugs reproduce, and at what speed they develop, neither do they reproduce as parasites. This is what makes them so difficult to destroy. Life cycle of bedbugs Before you start fighting parasites, you need to carefully study the life cycle of the insect:
- The larva of a house bug develops 5-10 years under normal conditions and 20 years under negative conditions.
- The larva hatches into a nymph, which goes through 6 stages of development in 1 month. After this, the individual is ready to mate.
The bug lives quite a long time - 14 months under normal conditions. If you lower the air temperature, then life expectancy can increase by another 1 year due to suspended animation.
Living with blood-sucking parasites is completely unbearable. The insect population is growing exponentially due to rapid reproduction and resistance to negative factors.
Life expectancy and nutritional habits
The characteristic features of the various stages of the life cycle of a bed bug, as well as the nuances of its nutrition, are of serious importance for the topic under consideration. Therefore, it is advisable to move on to answering questions related to this topic.
How long does a bed bug live?
The standard lifespan of an adult bed bug is about a year. Among the parasites there were some who lived for 14 months and even a year and a half. It is quite possible that this is not the limit and, under favorable conditions, the lifespan of the parasite may be even longer.
As noted above, the duration of maturation of bedbug eggs is a week or two, and the time for the formation of an adult insect from a larva is about one to one and a half months. The indicated time intervals can be added to the lifespan of an adult bedbug.
It is necessary to take into account that the parasite, like most other insects that live near humans, does not always live the entire period allotted to it. This statement is even more true if we remember the obvious harm caused by a bed bug. Therefore, it is not surprising that a person strives to make the life of a parasite as short as possible.
How many days do bedbugs live without food?
One of the important features of a bed bug is its survivability. First of all, it manifests itself in the ability to go without food for a long time. This significantly slows down most of the insect's life processes, but does not lead to death. For example, in the absence of food for one and a half to two months, females stop laying eggs, and larvae stop growing and molting. But this does not at all mean the death of the population - as soon as nutrition is established, the parasites return to their normal life schedule, quickly restoring the abilities that they had lost for a while.
It is necessary to note two more significant nuances. Despite clearly defined food preferences in the form of human blood and, less commonly, animals, when starving, bed bugs use everything they can for food. For example, the seminal fluid obtained by the female during fertilization. There are known cases where bedbugs exchanged blood “obtained” by one parasite, which distributes food among several individuals. All this increases the viability of the insect population, making the task of exterminating them more difficult.
How many bites does one bug make per night?
An adult bed bug can make from one to ten bites per night. Usually their number varies from 3 to 5. A characteristic feature of the parasite is its movement in a straight line while feeding, so the bite marks are an elongated and almost straight chain. The standard distance between adjacent bites is 1-2 cm.
Bed bug larvae require less blood. Therefore, they rarely bite more than once. Moreover, it is much more difficult for them to pierce human skin than for an adult parasite, which has developed all the organs necessary for this.
How long does a bug live after being bitten?
direct relationship between the lifespan of a bed bug and its bites. At the same time, when considering this issue, it is necessary to take into account that it is after eating that the parasite is most vulnerable. First of all, this is expressed in three things. The first is a serious increase in body size, often reaching one and a half to two times.
The second point is a change in the color of the bug’s body from translucent and faded to bright red or burgundy, which makes the insect more noticeable, especially against the background of light bedding or human skin. The third nuance is a decrease in motor activity and movement speed. A well-fed bedbug moves noticeably slower than a hungry one.
As a result, the life of a bedbug often ends immediately after a bite, when a person simply crushes it, not having time to retreat to cover, tossing and turning in his sleep. Often, traces of a crushed parasite can be easily found on a sheet or duvet cover.
Why are there more bedbugs?
The unprecedented increase in the number of insects is associated not only with adaptation to new insecticides:
- Centralized heating and improved living conditions have made the living conditions of bedbugs more comfortable.
- Every year the world's population is growing. More people means more parasites can feed and survive. Scientists estimate that the global population of bed bugs is increasing by 100-500% annually.
- The volumes of consumption of goods and the insects transmitted with them have increased.
- The pace of global migration and mobility of the population has accelerated, with which bloodsuckers also move.
- Insects spread quickly in areas with dense multi-storey buildings and even faster in old buildings and small-sized housing. In large cities the problem has reached catastrophic proportions.