Adult representatives of the species live on land, being specialized predators, they absorb an incredible number of flying insects. Dragonfly larvae feed primarily on waterfowl invertebrates or juveniles. The main benefit of these insects for humans is to regulate the number of mosquitoes and crop pests.
general information
Kazara
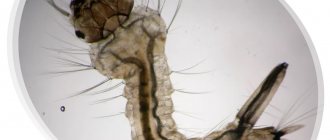
Dragonfly larvae (kazara)
painted in brown-olive tones. Dragonfly eggs are laid in water or in the tissue of aquatic plants. The eggs hatch into larvae of an extremely characteristic shape, interesting in their biological characteristics. These larvae play an important role among other living material of freshwater excursions.
Dragonfly larvae are found everywhere in standing and slowly flowing water. Most often they are found on aquatic plants or on the bottom, where they sit motionless, sometimes moving slowly. There are species that burrow into mud. All larvae can be divided into three groups:
- Larvae of the rocker dragonfly type (Aeschna
) with an elongated body and a flat mask. This includes the largest species that are similar to each other. In the northern regions there are representatives of the genera: Gomphus - grandfather, Onychogomphus, Gordulegaster, etc. - Larvae of the common or true dragonfly (Libellula) type
with a shorter and wider body than the previous ones. The mask is helmet-shaped. They stay mainly at the bottom, often in a layer of silt. The following genera are typical for the northern regions: Libellula - true dragonfly, Cordulla - grandma, Leucorrhinia, Epitheca (Fig. 206), Sympetrum, etc. - Larvae of the lute type (Agrion)
with a very long elongated body, which has leaf-shaped gill plates at the rear end. We have representatives of the genera: Agrion - arrows, Lestes - lyutki, Erythromma (Fig. 207), Calopteryx - beauties, etc.
Variety of dragonflies
Today, more than 6 thousand species of dragonflies are known.
They are distinguished by their color, which can be very different, and their size, which can be from 3 to 12 centimeters. There are several thousand species of lice. But among this huge variety of lice, only three types are dangerous for humans: head, body and pubic. They differ in their habitat.
The entire variety of beetles can be divided into 6 families: predators, weevils, longhorned beetles, leaf beetles, ground beetles and lamellar beetles.
The variety of bedbugs is very large. The most famous of them are house bugs that feed on human blood.
Description
When we are near bodies of water in the summer, we are all accustomed to seeing colorful dragonflies scurrying back and forth. This shy insect, which is almost impossible to catch with your hands, is often prey for fish that hunt in the surface layer of water. A dragonfly's habit of landing on twigs or lily pads that have fallen into the water, or simply a desire to fly too close to the surface, can be fatal. Bleak, chub, trout - all these fish are not averse to eating dragonflies. But few people know that much more often the victim of hungry fish is not the dragonfly itself, but its larva.
The larvae of each dragonfly species have their own unique shape. Frankly speaking, their appearance is not particularly pleasing to our eyes with beauty. Some of the dragonflies have creepy-looking nymphs - this is the scientific name for the larval stage of insect development. Traditionally, dragonfly larvae live and develop in reservoirs or parts of reservoirs with standing water, often silted, overgrown with aquatic vegetation, or swampy. Moreover, they easily survive both in completely fresh water bodies and in brackish ones. Depending on the species, nymphs can live burrowing deep into the muddy bottom, or move in the mud near the surface, or along the bottom itself, crawling along it with enviable leisureliness. Many species also live in thickets of aquatic vegetation, where it is easier for them to hide from external enemies. Depending on the habitat, the color of the nymphs varies - from yellow to almost black.
Development and reproduction
The development of dragonflies, unlike other insects, is characterized by incomplete transformation - there is no pupal stage. Some species living in southern latitudes are capable of producing several generations per year. The mating process takes place right in the air and lasts from a few seconds to 2-3 hours.
After fertilization, the dragonfly lays eggs directly on water, plants and other floating objects. Females of some species are able to dive under water to a depth of 1 meter, remaining dry, thanks to the air bubble that surrounds the body.
Stages of development:
- Eggs are round or elongated. Their color can vary from light yellow to brown, and their number can range from 250 to 500 pieces. Sometimes they are covered with a special mass that resembles jelly, or are collected in strands.
- The larvae can also be called nymphs or naiads. They differ significantly from adult individuals, which is associated with an underwater lifestyle. It is worth paying special attention to the head, which is generally no different from the imago, with the exception of the oral apparatus. The lower lip of the insect is a unique grasping device designed for effective catching of prey - a mask. When capturing food, it opens very quickly, pierces the victim with sharp edges and pulls it to the mouth. Breathing is carried out using gills. During development, the nymph goes through a cycle of several molts, gradually developing and changing.
- Imago is the final stage of life. By the time of the last molt, the insect is already able to breathe air. Under its shell there is an almost formed individual. Before shedding its cover, the larva climbs out of the water onto a plant and sits motionless on it for several days. The old shell bursts, and a fully formed dragonfly emerges.
Dragonflies are the most common predators of the air, capable of absorbing everything indiscriminately. Cannibalism is quite widespread among these insects. Larger individuals easily attack small ones.
Method of obtaining larvae
For prey, geese use a kind of “mormyshnitsa”. The device is a metal tube with a diameter of 15-20 cm and a length of 20-30 cm, one side of it is tightly welded and a mount for a wooden handle (like a shovel) is welded to it. The other side is cut slightly at an angle to the length, and holes with a diameter of about 1 cm are drilled in rows in the walls of the tube.
Dragonfly larvae are dug for fishing 1-3 days in advance. To do this, they look for banks with steep muddy ravine. The jig is stuck into such a bank, at a depth of 0.3-1 m under water, and then, filled with silt, it is raised to the surface. And at the water's edge, they pick out the silt with their hands, pouring water on it. In the silt, you can’t even see the larva, but when doused with water, it begins to flutter and is quickly transferred to a jar of water.
Habitat
All animals settle in places where conditions are favorable for them.
Dragonflies live almost everywhere. But the main factor in their habitat is the humid climate. Therefore, you can find dragonflies near rivers and lakes. A wide variety of them live in tropical and subtropical climates.
The main habitat of lice is the hair of people and animals.
Many people wonder whether lice live in other places? Yes. They can settle, for example, on fabrics, such as body louse. Being parasitic on living beings, lice cannot settle under the skin.
Beetles live everywhere.
There are especially many of them in the tropical regions of the planet. You cannot find them in the Arctic and Antarctica. They live in small numbers on mountain tops. Bed bugs also live everywhere.
Some species can be found even beyond the Arctic Circle.
Fishing with kazara
The most promising time for using goosefish as bait is from the beginning of June to the end of September. When fishing with a float rod, anglers who fish with maggots have a significantly larger catch than anglers who fish with dung worms or maggots.
When placing this bait on a hook, the hook tip is threaded through the body, starting from the head of the larva. You can start planting from the head. As you prefer. It is advisable to place several small larvae on one hook.
The larvae are great for catching ide, fairly large perch, silver bream, chub and many other fish.
Nutrition
All representatives of the animal world can be predators, herbivores and omnivores.
Dragonflies are predatory animals. They feed on a variety of small insects, and their larvae can even eat fish fry. Lice feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals. This only happens when the lice life cycle reaches the adult stage.
Among the variety of beetles, you can find both predators that feed on small insects and herbivores that eat plants. Bedbugs can be predators, parasites, herbivores or omnivores.
Structure
The dragonfly, the structure of which we are considering in this material, has a long and very thin body. It, in turn, is connected to the cephalothorax. On the dragonfly's body we can see three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings
It is also important to note that the wings are transparent; they can have the same size and shape, or different. We will talk about this in more detail when we consider the types
The dragonfly, whose structure can vary by species, can belong to one of two main groups:
- Homoptera.
- Varioptera.
As you might guess, the first group includes individuals that have wings of equal length and shape, while others have the opposite (one pair can be very different from the other). On the dragonfly's head we can clearly distinguish large eyes and antennae. A little more about the senses. The eyes of these insects are complex. They can be divided into two sections:
- the top one, responsible for object recognition;
- the lower one, responsible for color recognition.
You've probably noticed that the transparent wings of dragonflies have veins along their entire length, and at their tips there are spots darker than the color of the wings themselves. This device helps avoid wing fractures by reducing vibration during flights.
Remember how flight occurs in other flying creatures. This is a beautiful and synchronized movement of the wings. Dragonflies have distinguished themselves here too; the movements of their wings can be asynchronous when they are balancing, but synchronous to increase speed
It is also important to know that these nimble creatures can reach flight speeds of up to 50 kilometers per hour.