Gadflies and horseflies are very unpleasant flying insects that love to bother both humans and animals. Are they dangerous? Of course, their bites are very painful, and in some cases can even be fatal. Therefore, knowing how to protect yourself from these large flies is the primary protection for every gardener, fisherman, farmer, hunter, traveler and simply anyone who loves to spend time in nature. At the same time, it is important to be able to distinguish the gadfly and horsefly from each other. Sometimes it is quite difficult, but we will help you cope with this task.
What danger do they pose?
Horseflies and gadflies cause a lot of inconvenience to both humans and animals.
It is very difficult to determine which of them is more dangerous. The danger of horseflies increases due to the fact that they prefer to actively use the blood of the victim. It serves not only as a source of nutrition, but also as an integral part of the reproduction process. At one time, a horsefly is capable of drinking up to 200 ml of blood from the body of its victim. Massive insect attacks on cattle herds can reduce milk yield by a quarter. Farmers suffer considerable losses from this, so they prefer horseflies, not to skimp and to allocate part of the funds specifically for the prevention of their appearance by purchasing. Among the entire subfamily of gadflies, only 2 species, which are common in our country, are dangerous. They do not drink blood, but even without this they pose a serious danger to humans and animals.
Harm to a living organism is caused by implants that an adult female implants under the skin of animals or humans. As a result of the development of larvae inside the host’s body, he experiences deterioration in health, discomfort, weakness and many other unpleasant consequences. In the most severe cases, the larvae can enter a person's eye or head. In this case, only a complex operation will help solve the problem, which will not guarantee the return of full health. It is recommended to use for preventive purposes.
Thus, the difference between a gadfly and a horsefly is colossal. These are completely different insects that differ in reproduction, nutrition and appearance. But these large families are united by similarities - they all cause a lot of inconvenience and trouble to a person and his household.
The ability to distinguish a gadfly from a horsefly should help not only to choose an effective way to deal with them, but also to know what danger they pose in order to properly protect yourself.
Horseflies are a family of dipterous insects distributed throughout the world except for its remote corners. The main task of this living creature is to leave behind offspring. Active reproduction of large flies occurs during warm periods when the female lays eggs. Soon the horsefly larva will be born. What is it and should we be afraid of it?
Features of life
It is not advisable to look for differences between the gadfly, horsefly and spider.
On a note!
The gadfly and the spider are the same insect. The more common name for the biting fly sounds exactly like the gadfly, and the spider is just a regional name for the insect, which was assigned to it in certain areas of the country. Therefore, in order to protect himself, a person must be able to recognize only the gadfly and horsefly, the differences of which must be sought in appearance.
The photo of the gadfly and horsefly clearly shows that the latter are larger flies, which are equipped with two pairs of wings and large bright eyes that occupy most of the body. Gadflies are significantly smaller in size and have less colorful colors. just one pair of wings and more yellow on the body. A photo of the difference between a blind and a gadfly clearly demonstrates the external differences.
Gadfly and horsefly
Also, gadflies and horseflies feed in different ways. Male horseflies lead a herbivorous lifestyle and prefer to feed only on plant juices and nectar. Females do the same thing. Once the female is ready to mate, she becomes very aggressive and switches to a predatory lifestyle.
Interesting!
Horseflies can also feed on animal carcasses. Such food is attractive to them only for a few days after the death of the victim.
Adult gadflies generally feed on it. This explains their short life cycle. Nutrition and accumulation of nutrients occurs at the larval stage. When the gadfly develops wings and the ability to mate, they begin to actively lay eggs and mate.
Life of a horsefly
Where do horseflies live? They live on all continents of the world except Antarctica. They cannot be found on some remote islands separated from the mainlands: Iceland and Greenland. The largest number of horseflies (and, interestingly, also in terms of species diversity) are found in wetlands, at the boundaries of different zones, near pastures and livestock paddocks. Also, the number of insects increases as they approach populated areas.
These blood-sucking flies feel good in light forests, fields, steppes, as well as in deserts and on mountain slopes. Horseflies crowd into bodies of water where the necessary moisture is available. The larvae of most species develop in water. Adults spend most of their lives in flight, being well oriented in the area. They love sunny and hot weather, so they are most active during the daytime on summer days.
Nutrition
The diet of a horsefly depends on its developmental phase and gender. Insect larvae consume invertebrate animals that live in water bodies or soil. The food of adult specimens, called adults, varies: males feed only on plant products (nectar of flowers, plant juice) or “milk” from aphids, and fertilized females are literally bloodthirsty. For its vital functions, animal blood is required - up to 200 mg per “meal”. While the female is not expecting offspring, she can subsist on plant food.
Females can feed on carrion: the corpses of animals that died 1-3 days ago. Because of this, insects become carriers of infectious diseases.
Reproduction
Caring for procreation and breeding offspring in blood-sucking flies begins in the warm season. The exact period depends on the climate of the area and the specific type of insect. The way horseflies reproduce is identical to the type of reproduction in dipterous insects. Under favorable circumstances, opposite-sex individuals mate, and after some time lay a clutch. Pregnant female horse flies need to feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals.
The development of horseflies takes place in 4 stages:
- Eggs. One female can lay from 400 to 1000 pieces. The eggs have an elongated shape.
- Larvae. They are spindle-shaped and have no limbs.
- Doll. Looks like a butterfly pupa.
- Imago is an adult insect. How long horseflies live depends on the species. But their life cannot be called long: it usually lasts one summer.
The total duration of horseflies from the moment of laying eggs until the death of the imago is up to 4 years.
Meaning in human life
Protection against horseflies
Due to the fact that the abundance of horseflies is observed primarily near pastures, your path, if possible, should not pass through places where livestock is regularly grazed. A measure of personal protection is a thick cotton suit and a hat with a net on the head.
Open areas of the body are treated with “OFF” spray, and in its absence - with any mosquito repellent cream (the effect is weaker).
As a last resort, you can take any cologne (preferably a cheap one), pour a packet of clove powder into it and leave for 7 days. A bottle of this cologne lasts all summer.
traps
flies
Flies (Muscidae - lat.) are flying dipterous insects. In total, more than five thousand species are known. In Russia, only sixty of them are most often found. An adult fly has a dark-colored body 6-7 millimeters long, sometimes with a blue or green metallic sheen. The most developed sense organ is vision. Flies have eyes made up of thousands of tiny lenses, sometimes with three-dimensional vision, and are very sensitive to movement.
A sexually mature individual is capable of laying up to 800 eggs at a time, preferring places with rotting organic waste.
Due to the peculiarities of their diet (flies are very fond of spoiled and decaying foods, animal corpses, feces), flies are carriers of thousands of infectious diseases, including typhoid fever, anthrax, polio, brucellosis, helminthiasis, tularemia, diphtheria, amoebiasis, tuberculosis, and others .
dung fly
FAQ:
- What areas in the apartment need to be treated? The ideal option for the complete destruction of flies is to locate the breeding site of the flies and treat it with strong insecticidal preparations. In a residential building, window sills, window frames, cornices, ceilings, external stands of buildings (if possible), lamps (if there are shades), solar walls and ceilings are subject to treatment. Spraying and spraying insecticide methods are used.
- How to prepare for the arrival of a disinfectant? Remove food, dishes, cutlery, and personal hygiene products. Remove clothes and bedding. Carry out wet cleaning. Provide access to the main processing areas and the possibility of ventilation.
What is the prevention of flies?
It is necessary to strictly comply with the requirements of sanitary legislation. Carry out regular treatment of waste collection sites, thoroughly dispose of any organic waste (including feces), follow the rules for storing and transporting products. The room should be protected using a fine mesh net, wet cleaning and ventilation should be carried out regularly, and the presence of dirty dishes, clothes, etc. should not be allowed. In small rooms, special adhesive tapes give a good effect.
Midges
Common types of horseflies
Approximately 200 species of horseflies are found in the CIS countries. The most common representatives of species and genera are worth considering in more detail.
Rainflies or hemorrhages (Haematopota)
A very common genus of horseflies, including approximately 400 species of insects with a characteristic appearance.
These are ash-gray flies, 6 to 13 mm long, with marbled wing patterns. They hunt silently and attack in both clear and rainy weather. Rainflies live in Eurasia and Africa.
Horsefly of the species Haematopota pseudolusitanica related to hemorrhages.
Bullfly (Tabanus bovinus)
This is a large fly, 1-2.4 cm long. The body of the insects is brown, the chest, dotted with yellow hairs, is crossed by dark stripes. A yellowish-brown border runs along the edges of the abdomen. The middle part of the abdomen is decorated with a stripe of ashy or yellow triangular spots.
Bullflies live throughout Europe, northern Asia and northwest Africa.
Bullfly (Tabanus bovinus).
Bullfly: male
Bullfly: female
Great gray horsefly (Tabanus autumnalis)
Large dark gray flies, growing from 1.6 to 2.3 cm. They are distinguished from other horseflies by their black abdomen, decorated with patterns of light triangular spots in the center and a diamond-shaped border on the sides.
Heat-loving insects can be found in the central and southern regions of Eurasia, as well as in North Africa.
Horsefly of the species Tabanus autumnalis.
Forest lacewing (Chrysops caecutiens)
A fly, measuring from 7.5 to 10 mm with amazingly beautiful eyes, shimmering in emerald-golden color. And the lacewing is brightly colored, its abdomen is yellow with black spots. Between the thoracic region and the abdomen of the insect there is a well-defined V-shaped inverted pattern.
The range of forest lacewings covers European countries, the Caucasus, northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Forest lacewing horsefly.
Forest lacewing (Chrysops caecutiens)
A fly, measuring from 7.5 to 10 mm with amazingly beautiful eyes, shimmering in emerald-golden color. And the lacewing is brightly colored, its abdomen is yellow with black spots. Between the thoracic region and the abdomen of the insect there is a well-defined V-shaped inverted pattern.
The range of forest lacewings covers European countries, the Caucasus, northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Forest lacewing horsefly.
Common lacewing (Chrysops relictus)
A bright fly with golden-green eyes, a glossy black chest and brownish pubescence. The abdomen of insects is spotted, black and yellow. The wings are mosaic marble with brown splashes. Due to their chaotic coloration, these horseflies received a second name - common pieds. The growth of insects is 9-14 mm.
Residents of Europe and the Western Siberian region become victims of the common lacewing.
Horsefly of the species common moth (common lacewing, lat. Chrysops relictus).
Detailed description: common pied.
Body structure
Horseflies have a wide, flattened abdomen, consisting of 7 segments formed by semirings: the upper ones are called tergites, the lower ones are called sternites. The segments are connected by an elastic membrane that stretches to accommodate the blood that is drunk. At one time, the female is capable of taking about 200 mg of blood, which is comparable to a meal of 70 mosquitoes or 4 thousand midges.
The gender of the horsefly can be determined by the shape of the abdomen: in males its end is pointed, in females it is rounded.
Behind the thoracic region there is a large triangular shield. Wide wings are attached to the middle part of the chest, which are completely transparent, sometimes with smoky spots or a fine mesh. The venation of the wings is quite uniform. When folding their wings, some individuals leave them widely spaced, others arrange them in a small house.
At the base of the wings there are halteres - rudimentary processes of the undeveloped second pair of wings. Paired halteres are thin stalks with a club-shaped ending and serve as a gyroscope or, more simply, a navigator.
Three pairs of horsefly limbs of medium length, densely covered with hairs. Spurs resembling prickly thorns grow on the lower legs of the middle pair of legs. Due to 2 tenacious claws and 3 suction cups at the end of each leg, insects stay on vertical surfaces.
The difference between horsefly larvae and gadfly larvae, why people confuse these insects
The only harm caused by these insects is the painful bites of females. Horseflies lay eggs on plants, so the question of how to remove a horsefly larva is incorrect. We are most likely talking about gadfly larvae.
Many gardeners, while gardening in the summer, repeatedly experience bites from various blood-sucking insects, among which the most intrusive are horseflies and gadflies: the differences between insects are subtle, and an uninitiated person is unlikely to be able to distinguish them from each other in real conditions.
Nutrition and maturation
It is believed that this insect got its name because of its excessive intrusiveness. Females do not see any purpose in their existence other than to drink blood; it is for this reason that they often hang around people and animals, without thinking about danger. Males are calmer, their life cycle is shorter, so they do not need blood, while females can drink 0.2 g of blood at a time, which is a huge dose for such a small insect. Livestock suffer the most from these bloodsuckers: cows begin to give less milk, get sick and literally go crazy from their annoying neighbors.
Horseflies need blood not only as food, but also as a substance that allows them to reproduce. One female is capable of hatching more than 2 thousand eggs laid in the ground per season. Often the laying sites are plant leaves or moss.
The larvae mature for 2 weeks in the shell, then hatch and remain in an underdeveloped state for another six months and feed on the remains of plant food. Only in spring does the process of final ripening begin, which lasts more than a month.
Due to the fact that animal carcasses are also a favorite delicacy, they are carriers of dangerous diseases, including polio, ulcers, etc.
Appearance
The horsefly does not even reach 3 cm in length. Its body is more elongated, unlike an ordinary fly. They have a large head, with disproportionately large eyes, allowing them to observe and attack moving subjects.
The wings are transparent or gray, single, like those of a fly. The body can be monochromatic: brown, gray, almost black, or beige with dark splashes.
Features of the gadfly
Nutrition and maturation
Very often there is confusion between horseflies and gadflies. The difference between them is nutrition. The latter practically do not feed and pester people and animals simply by their nature, imposing themselves like flies.
After hatching, females look for a mate, lay larvae and die immediately. Their life cycle lasts very short; they reserve strength for this time while still in the egg.
Adults are more intrusive than horseflies, since their goal is to lay eggs in the folds of the animal's body.
Mating of the male and female occurs a few days after hatching. They can live another month to have time to lay offspring. One individual is capable of laying about 700 eggs on the body of one animal.
The most common places for laying are:
- groin area,
- stomach,
- hips.
Due to the fact that the animal’s body temperature exceeds the ambient temperature, after 3-5 days the bloodsucker larva hatches from the egg and moves under the host’s skin to the spine. There she bites a hole in the skin for breathing. After maturation, it falls out of the hole, remains for some time in the animal’s place of residence (stall, barn) and flies away.
The appearance of the gadfly is practically no different from the appearance of an ordinary fly. It does not exceed 1.5 cm in length. It has small transparent wings, large eyes and a black or brown body.
It does not attack humans directly; even the human gadfly uses bloodsuckers in contact with humans to implant eggs under a person’s skin. Eggs are often carried by mosquitoes.
Conclusion
Horseflies and gadflies differ not only in size, but also in their feeding habits and lifestyle.
The horsefly matures over a period of more than 9 months, but the gadfly hatches in a matter of days and goes to the mating sites. Despite the fact that the latter do not drink blood, they bring more unpleasant sensations when they get under the skin of an animal or person.
The horsefly, being a blood-sucking insect, causes inconvenience to both animals and people in the warm season. Many people are familiar with its obsessive buzzing and painful bites. In hot weather, far from cities, horseflies stage real attacks, interfering with comfortable outdoor recreation or work in the garden. They also annoy livestock. What kind of insect is this and why does it attack?
Nutrition
Adult gadflies cannot feed due to their physiological characteristics. They live off the reserves they accumulated as larvae.
The larvae can obtain nutrients while in the body of their host. The main nutrient for them is blood fluid. The gadfly larva can migrate in the body of its host, choosing the best places for comfortable living and feeding. Often this place is the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of insects
Commonly encountered species of the described insect include:
- Bullfly - considered the largest species of the described family, reaching a length of about 20 mm. The bullfly is a two-winged insect belonging to the horsefly family. This type of horsefly lives in Europe, colored brown, with dark stripes and yellowish hairs located along the body. Horsefly photo
- Lacewings or moths - about 250 species of horseflies are equated to the described genus. The most common horsefly is the common lacewing, reaching a length of 14 mm and having a rather bright color of its body. The chest of this insect has a blackish color, while the abdomen is complemented by original yellow spots. The wings of the lacewing have a mosaic color, the top of which is completed by brown spots located on them. The huge compound eyes have an emerald-golden color, Lacewing photo
- An ordinary raincoat - with a modest color and wings with a complex smoky pattern. The described type of insect can produce, so to speak, a real horsefly bite, even in gloomy and cloudy weather.
Symptoms of a horsefly bite
An insect bite is very painful and sometimes has serious consequences. After all, poisonous saliva penetrates into the wound. This liquid contains anticoagulants and toxic substances:
- Toxins entering the human body lead to tissue swelling, pain, itching, burning, redness and quite often allergic reactions.
- Anticoagulants prevent the blood in the wound from clotting, which causes prolonged bleeding and promotes long healing.
In addition to skin symptoms, the following signs of a horsefly bite may be present:
- weakness,
- nausea,
- breathing disorder,
- dizziness.
The horsefly is not an insect that can quietly approach its intended victim. The approach of an aggressive large fly is impossible not to notice. However, sometimes horseflies do not hunt alone. And when one individual distracts the object, the second attacks.
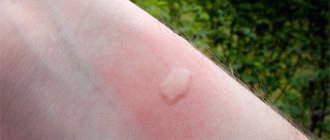
But even if it was not possible to notice the one who committed the attack, this bite cannot be confused with any other. A large tumor appears at the site of the lesion, usually white with a wide red border around the edge.
Consequences: allergies, bumps and infections
Usually, serious consequences do not occur after a horsefly attack, and symptoms disappear after 2–4 days. But there are also exceptions. In addition to allergies caused by fly saliva, the following may appear:
- painful nodes and bumps, as a result of infection with a bite,
- suppuration of soft tissues due to the penetration of a secondary infection when scratching the wound,
- enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes due to infection of the lymph and blood.
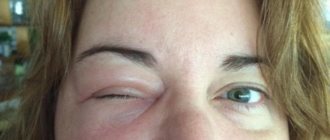
All this threatens that the bite site may become very swollen, as well as the appearance of non-healing wounds, phlegmons and abscesses. Sometimes necrosis of the affected areas occurs.
When attacked by this blood-sucking insect, the localization of the bite site is important. The closer the large blood vessels and nerve endings are to it, the more delicate the skin, the more dangerous the consequences. However, a direct threat to human life can arise only as a last resort, for example, when:
- multiple insect bites,
- presence of allergies,
- the addition of a secondary infection.
Infections carried by horse flies
Horseflies, like many blood-sucking parasitic insects, are capable of transmitting pathogens of infectious diseases dangerous to human health and life, in particular:
- anthrax,
- tularemia,
- foot and mouth disease
- bubonic plague, etc.
Area
Midges inhabit all continents except Antarctica. In other parts of the land, they are ubiquitous, except for isolated isolated islands and deserts devoid of rivers.
The horsefly is a blood-sucking insect that causes significant damage in agriculture. Moreover, horseflies are also very dangerous for humans, especially for children and pregnant women. Horseflies attack humans, are very aggressive insects and can infect humans with infectious diseases, since horseflies love to eat the corpses of animals that may have died due to infection.
Why is horsefly called horsefly? Because for some reason this insect wants to bite in the eye, however, a person, like an animal, manages to close the eye before the bite, as a result, the eye remains undamaged, but the person walks for a long time with swollen eyelids, and cannot see with the damaged eye because of for swelling of the eyelids. That is, he goes blind. That is why this insect got its name - horsefly.
Tabanidae Horseflies are found in various climatic and landscape zones, everywhere. In total, there are over 3,500 species in the horsefly family around the globe.
How to protect yourself from the gadfly in the country
To make the area unattractive to insects, it is necessary to mow the weeds in a timely manner not only around the house and in the yard, but also behind the fence. Open, ventilated spaces are not to the liking of the parasite.
The gadfly reacts sensitively to odors associated with human or animal activity (feces, sweat). Therefore, it is better to arrange latrines and heaps of manure away from housing, and spray them with special preparations that eliminate odors.
You can protect yourself from the gadfly with ordinary sticky tapes - flycatchers, hanging them around the house, in gazebos. Special bags with bait for the destruction of horse flies and spiders are sold, which are laid out in places where insects are likely to accumulate.
If there are a large number of gadflies, horseflies, mosquitoes and ticks on the site, it makes sense to contact special treatment services. The territory is pollinated with special preparations that repel insects. Usually, one such procedure is enough for a season. But these methods cannot be called environmentally friendly, since strong toxic substances are used.
Habitats
Special attention should be paid to the issue of where gadflies and horseflies live. The vital activity of horse flies is directly related to the availability of fluid. This is why insects prefer to settle near ponds or any artificial water sources. They can also serve as water bowls for animals, especially if the water in them is rarely changed. The higher the temperature and drier it is outside, the more and more often they will need to quench their thirst.
Experienced farmers know very well where gadflies and horse flies come from. After all, insects cannot exist separately from humans and domestic animals. Especially considering the fact that cattle themselves become targets for pest breeding. Horseflies, which prefer to settle near rivers at the larval stage, after reaching sexual maturity, necessarily look for places of mass grazing in order to have a sufficient amount of food.
On a note!
Gadflies cannot exist without mammals, so they also prefer to live in areas where livestock graze. This allows the pest to lay larvae and reproduce. The females are the first to find pastures, after them the males flock to this place.
First aid if bitten by a horsefly
How to react to gadfly bites?
- It is necessary to treat the affected area of the body as quickly as possible, rinsing it with clean water (or with soap). After all, it is worth remembering that these insects are carriers of infection (they do not disdain corpses and feces).
- You can then gently squeeze the liquid out from the bite site. This will help localize the spread of toxic saliva under the skin.
- After removing the dirt, you need to treat the wound:
- hydrogen peroxide solution,
- Chlorhexidine,
- potassium permanganate solution,
- Streptocide,
- propolis tincture,
- Furacilin,
- vodka.
- After treatment, it is better to cover the bite site with a band-aid.
- Regardless of whether the victim is allergic to insect bites, it is worth using some kind of antihistamine that will help reduce swelling and stop itching:
- Tsetrin,
- Claritin,
- Loratadine,
- Suprastin,
- Parlazin et al.
- If severe pain is present, the use of analgesics will be very helpful. Recommended for use as an analgesic and antipyretic:
- Ibuprofen,
- Paracetamol.
- If a horsefly bite does not cause a deterioration in the general condition of the victim, then it is enough to use local remedies for 2-3 days to speed up wound healing:
- Panthenol,
- Fenistil-gel,
- Rescuer.
If suppuration, nodes or lumps appear after a horsefly bite, you should urgently consult an infectious disease doctor. Particular attention should be paid to:
- fever,
- nausea,
- vomit.
All this may indicate an infection of the body, which must be treated under the guidance of a doctor.
Medicines that can be applied to tumors to alleviate the condition after bites, gallery
Bepanten will help heal the wound. Nimesulide and its analogues will relieve fever and eliminate pain.
Treatment with traditional methods
Of course, the necessary medications and protective equipment may not always be at hand, so you need to know what you can use from available means to alleviate the condition of the victim.
- A lotion made from a bandage or any clean cloth soaked in:
- soda solution,
- Corvalbreaker,
- gruel of garlic or onion,
- juice of raw potatoes (you can grate them),
- tomato puree,
- sour cream.
- Regular ice from the refrigerator, previously placed in a plastic bag, will help reduce swelling.
- The juice of an ordinary dandelion will help to disinfect the bite site, which is recommended to treat the affected area. After manipulations, you should wash your hands to prevent milky juice from getting into your eyes.
- A lotion of salt and soda will help clean the wound from insect saliva. To do this, dilute 1 teaspoon of each ingredient in 1 glass of warm boiled water. After the crystals are completely dissolved, a bandage is dipped into the liquid, soaking it completely. Then, the fabric is wrung out and applied to the bite site.
- A paste of fresh plantain leaves can relieve itching and stop bleeding. You can use dry plant materials, previously soaked in warm water. The wet mass is applied to the damaged area and secured with a bandage.
- A compress with a mixture of natural products will help relieve swelling and redness. To do this, you need to take 2 cloves of garlic, ½ medium-sized potato and ¼ onion. All this is ground on a grater or in a meat grinder. The resulting mixture is applied to the bite site, covered with film and secured with a bandage.
Folk remedies that will help with a horsefly bite, photo
Onions are effective as a decongestant
In the composition of the compress, which relieves inflammation and redness, ordinary garlic plays an important role.
Sour cream will relieve itching after a horsefly bite. Tomato paste will relieve the condition.
Milky dandelion juice perfectly disinfects the wound and relieves intoxication Plantain juice has hemostatic properties Raw potato gruel relieves itching after a bite A solution of soda and salt will help speed up wound healing
How to treat a gadfly bite
Treatment for a gadfly bite should begin immediately when the first signs appear - burning and itching.
Correctly provided first aid will not allow toxins to penetrate further into the subcutaneous layers, which means skin allergies will be minimal.
We should not forget that horseflies sit on animal feces, and therefore can be carriers of the most dangerous diseases for humans. So, after being bitten by a gadfly, you must:
- rinse the wound thoroughly with plain or soapy water,
- after removing the dirt, it is advisable to drop a few drops of pharmaceutical hydrogen peroxide into the center of the bite or treat the wound around the periphery with brilliant green,
- If there are several bites or the victim is a child, it is necessary to take a painkiller. Panadol and Nurofen have antipyretic and analgesic effects,
- In nature, you can use the help of medicinal herbs. Juice from chamomile stems or plantain leaves has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The juice should be squeezed onto a clean swab and applied to the bite site.
3 effective ways to get rid of flies in an apartment
The bite site must be observed for a day or more. If it is noticeable that the swelling from the gadfly bite is increasing, the itching does not decrease, then it is advisable to take an antihistamine - Suprastin, Tavegil.
Antihistamine tablets are especially necessary for children; they relieve itching well, which prevents further skin infection.
How to treat a water bite in the following days? It is necessary to buy anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointment - Panthenol, Rescuer. Fenistil gel and Lorindent ointment relieve swelling and burning well.
Find out how to catch a rat without a mousetrap (using improvised means).
Find out how to remove lice and nits using vinegar here.
Folk remedies
To create effective remedies, it is necessary to study in detail what gadflies and horseflies are afraid of. Only in this case can you draw up an effective plan for exterminating pests. Simple home recipes are used independently, as well as in combination with the listed chemicals. The second option significantly increases the effectiveness of the selected products and allows you to quickly solve the pest problem.
You can destroy horseflies and gadflies using improvised means. They are always in the house, and if not, then buying them will not be difficult.
- A mix of the most common and inexpensive cologne with chopped dry cloves has worked well. To prepare the mixture, you will need 1 bottle of inexpensive perfume and 50 g of mustard. To grind the spice, you can pass it through a coffee grinder or a very fine grater. Leave the prepared solution for 10 days. After this, treat the infected areas and the person’s clothing.
- A remedy made from mint, soap and lemon ammonia will help get rid of gadflies in nature. Mix the ingredients in equal parts, leave for 12 hours and treat the area.
- The use of liquid soap is also suggested by experts as an effective way to get rid of gadflies for domestic animals. To do this, prepare a concentrated solution by dissolving 200 ml of liquid soap in 5 liters of water. Rinse the animals with the resulting mixture.
Description and photo
In appearance, the horsefly resembles a large fly, up to 3 cm in size, depending on the species. There are more than 200 species in Russia, and more than 350 in the world. It has two developed transparent wings of a smoky color, a large head, a flattened abdomen, a hard proboscis with cutting and piercing stilettos located in it. Horseflies have large, beautiful eyes; they can see their prey from afar.
Females differ in appearance from males: their eyes are wider apart and they have mandibles, which males lack.
Features of nutrition and reproduction
Only fertilized female insects feed on blood; they need blood for the development of eggs; unfertilized ones can feed on nectar. With one bite, a female horsefly can drink up to 0.188 ml of blood. This is enough for her for two days, then she must find the victim again. She needs a portion of blood to lay eggs. 3-4 days after drinking blood, the female lays up to 1000 eggs.
If she manages to bite someone else, she will lay eggs again. Thus, during a season, 1 female with a sufficient amount of blood can lay up to 3500 eggs. They are deposited on moistened plant leaves, mainly near water, and after a few weeks larvae emerge from them, create a cocoon and turn into pupae. After another 3 weeks, an adult insect emerges from the pupa.
The life cycle of a horsefly consists of 4 stages:
- egg,
- larva,
- doll,
- adult insect.