Burrowing wasps are known as clever predators and caring parents. They build nests for the larvae and fill them with food. Each species harvests a specific type of insect - caterpillars, spiders, butterflies. Pelopeis or Scelyphron builds larval shelters out of mud, filling them exclusively with paralyzed spiders. Wasps are widespread in Europe and Asia, but their populations are small. The insect received protected status and is listed in the Red Book of Russia.
Appearance
The burrowing wasp is a slender, thin-bodied insect. There is no external resemblance to ordinary social wasps. Most often, their body color is black. The head is small, lowered down. When examining it, the jaws and straight long antennae are clearly visualized.
The chest is connected to the abdomen by a thin elongated segment. The wasp's abdomen is fusiform or barrel-shaped, but flattened. Its color is bright red or orange. The limbs are long and end in a special comb. This is what distinguishes the burrowing wasp from the paper wasp.
Wasps of this genus have thin transparent wings, but they are used extremely rarely. The size of the female burrowing insect is 25-38 mm. Male burrowers are usually much smaller.
When to see a doctor
After a wasp sting, additional symptoms may develop - each stung person may have a different reaction to the foreign toxin. You need to listen to the well-being of the stung person, and in some situations immediately consult a doctor:
- If the stung person’s health deteriorates sharply.
- Swelling in the area where the toxin enters does not decrease over time, but rather increases.
- Convulsions appeared.
- The general body temperature has increased.
- If a person is bitten by several ground beetles at once.
- The sting hit the soft tissues of the neck and face. For example: lips, tongue or cheeks. A bite to the eye can be especially dangerous.
- Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction appeared.
- There are signs of anaphylaxis.
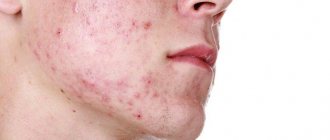
Why is a bite dangerous for humans?
The sting itself and the poison are not dangerous to humans - even the body of a child can independently neutralize toxins from a couple of stings. The greatest danger to the body, oddly enough, is the body itself. This refers to an allergic reaction - when the security measures of the immune system do not work entirely correctly and their actions cause harm. You can die from this.
A wasp sting will be dangerous if the poison has been injected into the soft tissues of the face. The softer the sting site, the stronger the swelling from a wasp sting will be, so the face can swell completely even just once.
If poison gets into the eye, there is a possibility of panophthalmitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye apparatus. If a wasp stings on the neck, tongue or lips, the enormous swelling can block air flow, which can be fatal.
The bite is extremely dangerous for pregnant women. The fact is that in this position a woman is prohibited from using many strong medications, and allergies can harm the child.
What do they eat?
Adult burrowing Hymenoptera feed on plant sap, sugary juices, or secretions of other insects (sweet honeydew from aphids).
Some representatives of this genus drink clean water. And certain burrowing insects squeeze the collected nectar from the crops (the extended part of the esophagus) of honey bees.
The nutritional diet of the larvae consists of various insects (butterfly larvae, spiders, moths, flies). Each species of burrowing hymenoptera selects certain insects as victims. They are skilled hunters.
Wasps are capable of delivering deadly blows with precision. When the victim is stung, it becomes paralyzed and remains paralyzed for a long time.
Distribution of common pelopeia
Pelopia vulgaris is a common species of hymenopteran insects. The range includes Central Asia, Mongolia and adjacent territories. It lives in the Caucasus, North Africa, central and southern Europe. In Russia, common pelopia spreads in Southern Siberia, inhabits the south and selectively the center of the European part, and penetrates north to Kazan. The northern border of the range runs through the Nizhny Novgorod region, where this species is found only in the vicinity of the village of Staraya Pustyn, Arzamas region.
Features of reproduction
Burrowing wasps are solitary insects. They are not dependent on other members of the family, and they are able to take care of their offspring without outside help.
The female burrowing hymenoptera digs a burrow, fills it with supplies, and then lays an egg there. After this, she carefully closes the hole with a plug of earth mixture.
All burrowing insects show care towards their offspring . Adults build a house for the future generation, and also prepare a nutritional base for the larvae. Behavior differs markedly between species.
Females of some burrowing wasp species check nests every day. If by that time the larvae have already eaten all the reserves, then they willingly replenish them with a fresh portion. It is not difficult for one female to simultaneously monitor 2-3 nests with offspring and supply them with food.
Lifestyle
Burrowing wasps are solitary, they live separately, females and males contact only during mating. They are characterized by complex behavior: building nests, caring for offspring. Some wasps build nests in houses and outbuildings, choosing secluded niches, cracks, and ventilation holes. The best option is well-heated attic spaces. Attics under an iron roof are especially relevant for pelopeia. The roof becomes hot under the summer sun, providing high temperatures for the development of larvae.
The construction of cells in a house does not pose a danger to its residents. Females of Sceliphrondestillatorium do not stay to defend their nest. The young wasps that appear the following year are not aggressive. They will leave their house and fly away in search of a comfortable habitat. In the southern regions, the pelopei wasp builds nests in natural shelters (caves, rocks), but in the temperate zone the natural climate is not suitable for offspring. Insects are found near villages or small towns. They seek shelter for nests in heated buildings. In open spaces, buildings made of mud get wet at the slightest moisture, and they collapse after the first rain.
Scelyphron is a heat-loving species. Insects are active at high temperatures. The adult years begin in June. Adult wasps feed on nectar and prefer umbrella plants. The larvae are carnivorous, their food is spiders left by the mother. A cluster of single wasps can be observed on the shore of a small body of water - a puddle, stream, lake. Females use their mandibles and front paws to roll up lumps of dirt. This is the building material for the nest. At night, wasps sleep on trees and bushes.
Nest building process
The house for the offspring consists of elongated cells 3 cm long. Each of them is built and then filled with prey. Only then does the wasp begin building the next cell. Construction takes 1-2 days. The female has to make 12-15 flights to bring the required amount of dirt. After all the cells have been constructed, the nest is covered with an additional layer of dirt.
Spiders are placed in a special way; large and hard specimens are placed closer to the exit. The larva will have time to grow and get stronger before it gets to them. The wasp carries its prey through the air. She drags the first spider, backing away. An egg is laid on it. The rest of the pelopei are pushed into the hole. Over the course of a year, several generations can change. Summer offspring will grow in 30-40 days.
Information. The common pelopei does not show aggression towards humans. The insect is useful by catching spiders and other pests.
Kinds
Burrowing wasps have many species, but the most famous among them are:
- Larra anathema;
- ammophila;
- bee wolf (philant).
Each of the listed species has its own interesting features. Entomologists continue to study the genus of burrowing Hymenoptera and periodically make new discoveries.
Larra anathema wasp
The black-colored Larra Anathema wasp is loved by many gardeners. This is due to the fact that it helps to destroy mole crickets (cabbage moths), which are dangerous insect pests.
When this hymenoptera finds a gnawing individual, it drives it to the surface. There, the wasp makes 3 targeted strikes using precise coordinates and causes complete paralysis. After this manipulation, the wasp lays an egg under the forelimb of the stung cabbage fly.
Paralysis goes away within 5 minutes. Kapusyanka goes back underground. There, the larva of the burrowing larra anathema emerges from the egg and develops over 4 weeks.
During this period she has 5 molts. All this time, an unusual insect lives due to external parasitism on the body of the mole cricket. The cabbageweed loses its life shortly before the moment of pupation of the burrowing Hymenoptera.
Wasp ammophila
Sandy ammophila is an insect whose body is black and whose abdomen is thin and bright red. Hymenoptera has long limbs. Ammophila is a relatively large Hymenoptera. Her body length is 4 cm.
To feed their offspring, the sandy ammophila uses the caterpillars of the cutworms. Having found a potential victim, they drive it to the surface, immobilize it, and then drag it into a dug hole. Moreover, earthworms are much heavier than ammophila itself.
The ammophila lays its egg on an immobilized caterpillar. After this manipulation, she closes the hole and thoroughly disguises the approach to it.
Philanthus bee wolf
The burrowing phylanthus is a large, and also quite strong, hymenoptera. Its size varies from 12 to 15 mm. The head of the philanthus is too large compared to the body and is endowed with powerful jaws. The chest of the philanthus is black, the abdomen is bright yellow. 1-3 white stripes are visualized on the back.
The insect is called the bee wolf because it attacks honey bees while they collect pollen. Philanthus grabs her with his paws, stings her in the neck and quickly takes her life.
Moving intensively with its paws, it squeezes out the nectar from the expanded part of the bee’s esophagus, which it has already collected, and absorbs it with its tongue. Having completely emptied the bee, he takes it to his burrow for the purpose of feeding the offspring.
Philanthus causes serious damage to beekeepers, since it most often lives next to the hives, and the bees are afraid of it and stop flying out for honey and do not leave their home. The queen bee stops laying eggs, and the entire colony loses strength over time.
Habitats of common pelopea
Common pelopei lives in the temperate zone and is found only in rural areas. It can be found in open places next to wet puddles with clay soil, and less often it appears on flowers. For nests it chooses well-heated attics of brick buildings. Prefers attics with iron roofs that are well lit.
Pelopei is a lover of heat
Does not settle in unheated buildings (sheds, warehouses). In nature, it nests only in southern territories. This species has not been recorded in urban areas.
Benefits and harms
Burrowing wasps are mostly beneficial insects. They destroy mole crickets and other burrowing pests, which they use to feed the larvae.
And the bee wolf causes harm . Beekeepers with large apiaries are forced to constantly fight the invasion of such insects, which are the main pests of their honey bees.
What to do if the pharmacy is far away
Mint juice will help relieve swelling from a wasp or bee sting
Most often, wasps are found where there are a lot of tasty ripe fruits and berries, that is, in those places where they are grown, sold, and processed. A first aid kit with the necessary medications is not always at hand, and the nearest medical facility may not be close. Then the main assistants will be the folk remedies available.
In order to relieve swelling and reduce pain, you can do the following:
- lubricate the bite site with mint juice;
- apply an aloe leaf, previously washed, crushed, with the top layer cut off, to the affected area;
- make a compress from a decoction of tansy flowers;
- lubricate the stung area with tea tree essential oil;
- wipe the sore spot with the urine of a child or healthy adult.
Links[edit]
- ↑
Cirrus Digital: Wasp Potter and the Mudpot Nest - [von Frisch, 1974].
- McKenna, D.D.; Zangerl, A.R.; Berenbaum, M. R. (2001). "Native predator of the hymenoptera Agonopterix alstroemeriana (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae) in east-central Illinois." Great Lakes entomologist
.
Michigan Entomological Society. 34
: 71–75 - via CAB Direct. - PK Piekarski, JM Carpenter, AR Lemmon, E Moriarty-Lemmon, BJ Sharanowski (2018) Phylogenomic evidence challenges current ideas about the social evolution of wasps (Vespidae). Molecular biology and evolution. DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msy124
- James M. Carpenter (1986). "Synonymous general checklist of Eumeninae (Hymenoptera: Vespidae)" (PDF). Psyche
.
93
(1-2): 61–90. DOI: 10.1155/1986/12489. - Carpenter, J. M. and B. R. Garset-Barrett. 2003. Key to the Neotropical genera Eumeninae (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Boletín del Museo Nacional de Historia Natural del Paraguay 14: 52–73.
- Giordani Jay, 1989. Terzo contributo alla conoscenza degli eumenidi afrotropicali (Hymenoptera). Societa Veneziana di Scienze Naturali Lavori 14 (1) 1989: 19–68.
- Giordani Sojka, A. 1992. Di alcuni eumenidi nuovi o poco noti (Hymenoptera Vespoidea). Societá Veneziana di Scienze Naturali Lavori 17, 1992: 41–68.
- Giordani Sojka, A. 1993. Di alcuni nuovi eumenidi della regione orientale (Hym. Vespoidea). Bollettino del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Venezia 42, 30 June 1991 (1993): 151–163.
- Gusenleitner. 1992. Zwei neue Eumeniden-Gattungen und -Arten aus Madagaskar (Vespoidea, Hymenoptera). Linzer Biologische Beiträge 24 (1) 1992: 91–96.
- CSIRO Entomology Division. 1991. Insects of Australia: a textbook for students and research. 2nd edition. Melbourne University Press and Cornell University Press. 1137 pp.
- Saussure, Henri de. 1852. Monographie des guêpes solitaires ou de la tribu des Euméniens. Geneva, J. Cherboulier, Paris, V. Masson.
Folk remedy for wasp stings
To eliminate painful consequences, traditional medicine offers several proven methods:
- Grind fresh parsley leaves in a mortar until the juice appears, then apply a compress to the affected area. Every 2-3 hours, the bandage along with the remedy is changed to a fresh one until the signs of damage are eliminated;
- The leaves of plantain and yarrow, from which a compress is made after thorough washing, have the same effect;
- The pulp of aloe leaves is applied to the bite site. This plant has a strong anti-inflammatory effect;
- For treatment, onions are used: apply a freshly cut onion or a cotton pad soaked in onion juice to the affected area;
- Tea tree oil, used to treat wounds on the victim, has strong antiseptic properties;
- For a compress, they also use gruel with juice from fresh herbs or an infusion of dried ones: mint, dandelion, thyme, wormwood, tansy leaves, golden mustache;
- Fresh urine is a strong antiseptic; many healers advise lubricating the affected area with the urine of a healthy person or child;
- Earwax has similar properties - it is also used as a medicine;
- A validol tablet soaked in water is applied to the wound site;
- A paste of baking soda and water is placed on the affected area. Baking soda also neutralizes inflammation;
- Sugar has the property of drawing out poison. A piece of sugar is lightly moistened with water and applied to the wound for about 0.5 hours;
- For severe redness and swelling, a tomato compress is useful, pieces of which are fixed at the site of the bite for 30-40 minutes. , after which they are replaced with fresh ones.
Wasp bites or stings
The insect uses its sting in case of danger to its own life or during hunting to paralyze the victim. After piercing the chitin or skin, the wasp quickly lets in a toxic substance.
However, if it is possible to do without poison, the insect uses its powerful jaws. They have no teeth, but are strong enough to bite through the chitinous covering of beetles. Wasps try to save poison and use their weapons in emergencies. In a fight with a person, insects always use a sting for protection, which is why the statement arose that the wasp stings. The word “bites” refers to precisely this process.
Interesting Facts
- Yellow and black stripes on the insect's abdomen warn animals and people that it is dangerous.
- Paper wasps are so named because they build their nests from a material very similar to paper.
- Adults consume only liquid food; larvae can feed on solid food.
- A wasp family includes several hundred worker wasps and one queen.
- Austrian individuals do not build nests, but live as parasites in the nests of red wasps.
- There are insects of this type that live alone - solitary wasps.
- The largest wasp is Sphecius. She lives in North America and hunts cicadas.
- They sting only for the purpose of self-defense.
- Insects are most aggressive in the heat and when there is a lot of food around.
Wasps are the name given to all stinging stalk-bellied insects that do not belong to ants and bees. They pose a threat to humans, since an insect bite can cause severe allergies.